the open group OGEA-101 Exam Questions
Questions for the OGEA-101 were updated on : Feb 18 ,2026
Page 1 out of 7. Viewing questions 1-15 out of 105
Question 1
Complete the sentence. A business scenario describes
- A. shortfalls between the Baseline and Target Architectures
- B. business domain gaps, such as cross-training requirements
- C. general rules and guidelines for the architecture being developed
- D. business and technology environment in which those problems occur
Answer:
D
Question 2
Consider the following ADM phases objectives.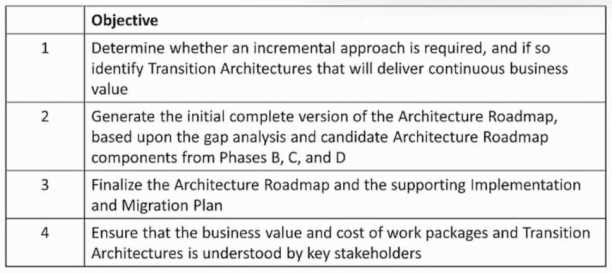
Which phase does each objective match?
- A. 1F-2E-3F-4G
- B. 1E-2F-3E-4F
- C. 1G-2E-3F-4F
- D. 1E-2E-3F-4F
Answer:
C
Question 3
Complete the sentence. When considering agile development, Architecture to Support Project will
identify what products the Enterprise needs, the boundary of the products, and what constraints a
product owner has; this defines the Enterprise's ____________
- A. operations
- B. backlog
- C. lifecycle economics
- D. workflow management
Answer:
D
Question 4
What information does the Architecture Requirements Repository within the Architecture Repository
hold?
- A. A set of guidelines, templates, and patterns to support the development of architecture requirements
- B. The parameters and structures to support governance of architecture requirements
- C. A log of the governance activity related to architecture requirements
- D. The architecture requirements which have been agreed with the Architecture Board
Answer:
D
Question 5
Refer to the exhibit.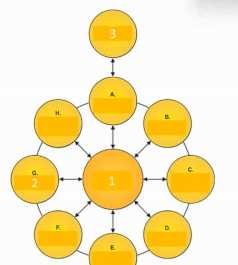
Consider the illustration of an architecture development cycle.
Select the correct phase names corresponding to the labels 1, 2 and 3?
- A. 1 Continuous Improvement - 2 Migration Planning - 3 Architecture Vision
- B. 1 Requirements Management - 2 Implementation Governance - 3 Preliminary
- C. 1 Requirements Management - 2 Change Management - 3 Strategy
- D. 1 Architecture Governance - 2 Implementation Governance - 3 Preliminary
Answer:
C
Question 6
Complete the sentence. The TOGAF standard covers the development of four architecture domains,
Application, Business, Data and ____________
- A. Technology
- B. Transition
- C. Segment
- D. Capability
Answer:
A
Question 7
Complete the sentence. The purpose of Enterprise Architecture is to
- A. take major improvement decisions.
- B. guide effective change.
- C. govern the stakeholders.
- D. control the bigger changes.
Answer:
D
Question 8
Complete the following sentence. In the ADM, documents which are under development and have
not undergone any formal review and approval process are _________
- A. in between phases
- B. known as "Version 0.1"
- C. invalid
- D. called "draft"
Answer:
D
Question 9
What ensures that a project transitioning into implementation also smoothly transitions into
appropriate Architecture Governance?
- A. Implementation Strategy
- B. Implementation Governance Model
- C. Transition Plan
- D. Migration Plan
Answer:
B
Question 10
Refer to the exhibit.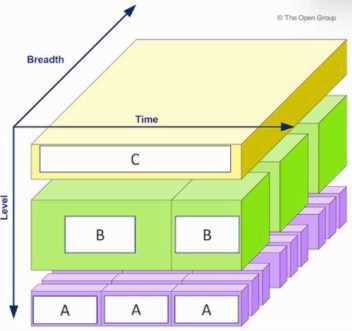
Consider the diagram showing a classification model for Architecture Landscapes.
What are the items labelled A, B and C?
- A. A-Corporate Capability, B-Portfolio Capability, C-Project Capability
- B. A-Strategy Architecture, B-Tactic Architecture, C-Operational Architecture
- C. A-Architecture Vision, B-Business Architecture, C-Architecture Development
- D. A-Capability Architecture, B-Segment Architecture, C-Enterprise Strategic Architecture
Answer:
D
Question 11
Refer to the table below: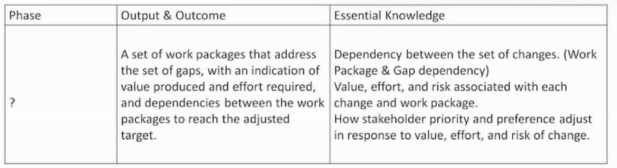
Which ADM Phase(s) does this describe?
- A. Phase E
- B. Phase B, C and D
- C. Phase A
- D. Phase F
Answer:
D
Question 12
Which of the following is the ability to develop, use and sustain the architecture of a particular
enterprise using architecture to govern change?
- A. An EA Capability
- B. An EA repository
- C. An Enterprise Architecture
- D. An EA framework
Answer:
A
Question 13
Consider the illustration.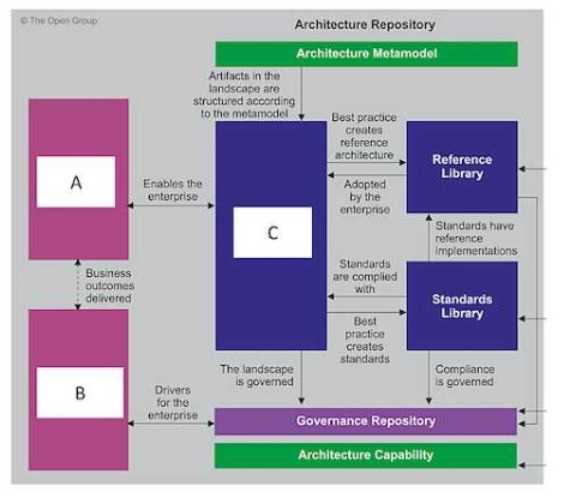
What are the items labelled A B and C?
- A. A-Solution Landscape, B-Architecture Requirements Repository. C-Architecture Landscape
- B. A-Architecture Landscape B-Architecture Requirements Repository C-Solutions Landscape
- C. A-EA Landscape, B-Requirements Repository. C-Artifacts Landscape
- D. A-Architecture Requirements Repository, B-Solutions Repository, C-Architecture Landscape
Answer:
D
Explanation:
This aligns with the TOGAF Architecture Repository model where:
A (Architecture Requirements Repository) contains requirements that drive architecture work.
B (Solutions Repository) stores the building blocks or solutions that support the architecture.
C (Architecture Landscape) represents the architecture assets that depict the current, transition, and
target architecture states across the enterprise
Question 14
Which of the following is a responsibility of an Architecture Board?
- A. Determining the scope of an architecture compliance review
- B. Allocating resources for architecture projects
- C. Conducting assessments of the maturity level of architecture discipline within the organization
- D. Achieving consistency between sub-architectures
Answer:
D
Explanation:
One of the key responsibilities of an Architecture Board within the context of TOGAF is to achieve
consistency between sub-architectures. This board is typically responsible for overseeing the
development and maintenance of the enterprise architecture, ensuring that it aligns with the
organization's overall strategy and objectives. They play a critical role in ensuring that all sub-
architectures (like Business Architecture, Data Architecture, Application Architecture, and Technology
Architecture) work together cohesively and support the overall enterprise architecture vision and
strategy.
Question 15
Which of the following describes the practice by which the enterprise architecture is managed and
controlled at an enterprise-wide level?
- A. Corporate governance
- B. Architecture governance
- C. IT governance
- D. Technology governance
Answer:
B
Explanation:
According to the TOGAF Standard, 10th Edition, architecture governance is “the practice by which
enterprise architectures and other architectures are managed and controlled at an enterprise-wide
level” 1. Architecture governance ensures that the architecture development and implementation
are aligned with the strategic objectives, principles, standards, and requirements of the enterprise,
and that they deliver the expected value and outcomes. Architecture governance also involves
establishing and maintaining the architecture framework, repository, board, contracts, and
compliance reviews 1. The other options are not correct, as they are not the term used by the TOGAF
Standard to describe the practice by which the enterprise architecture is managed and controlled at
an enterprise-wide level. Corporate governance is “the system by which an organization is directed
and controlled” 2, and it covers aspects such as leadership, strategy, performance, accountability,
and ethics. IT governance is “the system by which the current and future use of IT is directed and
controlled” 2, and it covers aspects such as IT strategy, policies, standards, and services. Technology
governance is “the system by which the technology decisions and investments are directed and
controlled” 3, and it covers aspects such as technology selection, acquisition, deployment, and
maintenance. Reference: 1: TOGAF Standard, 10th Edition, Part VI: Architecture Governance, Chapter
44: Introduction. 2: TOGAF Standard, 10th Edition, Part I: Introduction, Chapter 3: Definitions. 3:
TOGAF Series Guide: Using the TOGAF Framework to Define and Govern Service-Oriented
Architectures, Part II: Using the TOGAF Framework to Define and Govern Service-Oriented
Architectures, Chapter 5: Technology Governance.