the open group OGB-001 Exam Questions
Questions for the OGB-001 were updated on : Feb 18 ,2026
Page 1 out of 2. Viewing questions 1-15 out of 30
Question 1
Which of the following is an end product of business capability modeling?
- A. A value stream stages catalog.
- B. A business process model.
- C. An organizational map.
- D. A business capability map.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
This answer is based on the definition and purpose of a business capability map as “a technique for
the representation of an organization’s business anchor model, independent of the organization’s
structure, processes, people, or domains” . A business capability map is an end product of business
capability modeling, as it shows the complete set of capabilities that an organization possesses or
requires to achieve its goals and objectives. A business capability map provides a high-level and
stable view of what a business does or can do, regardless of how or where it does it. The other
options are not correct, as they are not end products of business capability modeling.
Question 2
Consider the following Business Capability Example: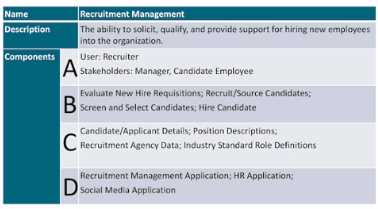
Which of the following ore A and C?
- A. Actors, Actions.
- B. Organization, Data.
- C. Who, What.
- D. Roles, Information
Answer:
D
Explanation:
This answer is based on the definition and components of a business capability as “an ability that a
business possesses to achieve a specific outcome” . A business capability consists of four
components: who, what, where, and how. Who refers to the roles or actors that perform or enable
the capability. What refers to the functions or activities that constitute the capability. Where refers to
the locations or channels where the capability is executed or delivered. How refers to the processes
or methods that govern the capability. In the image provided by the user, A and C are examples of
who and what components, respectively. Therefore, A and C are roles and information, which are
two types of who and what components.
Question 3
Which of the following are two concepts used for structuring a business capability model?
- A. Categorizing, Grouping
- B. Mapping. Sorting
- C. Aligning. Layering
- D. Stratification, Leveling
Answer:
A
Explanation:
This answer is based on the TOGAF Series Guide: Business Capabilities , which states that “A business
capability model is a structured representation of the capabilities of an organization. It is typically
structured using two concepts: categorizing and grouping.” Categorizing is the process of assigning
capabilities to different categories based on their nature, purpose, or function. Grouping is the
process of arranging capabilities into different levels or layers based on their granularity, abstraction,
or dependency. The other options are not correct, as they are not concepts used for structuring a
business capability model.
Question 4
Consider the following business capability model, where cells of a model are given different colors to
represent levels (note the letters G, R, Y, P also denote the colors used = Green, Red, Yellow and
Purple):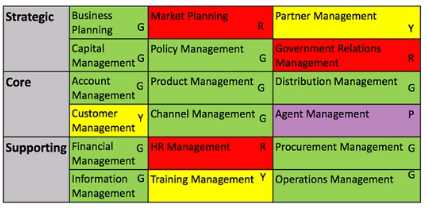
Which of One following best describes the technique?
- A. Capability Mapping
- B. Heat Mining
- C. Perspective Analysis
- D. Gap Analysis
Answer:
B
Explanation:
This answer is based on the definition and purpose of heat mapping as “a technique for visualizing
data where values are depicted by color” 3
. Heat mapping is a technique that can be applied to a
business capability model to represent different levels or aspects of the capabilities using a color
scale. For example, the colors can indicate the maturity, importance, performance, or alignment of
the capabilities. In the image provided by the user, the colors represent different levels of maturity or
readiness for transformation. The other options are not correct, as they are not techniques that use
colors to represent levels or aspects of capabilities.
Question 5
In what TOGAF ADM phase is the Information map translated into data models?
- A. Phase A
- B. Phase E
- C. Preliminary Phase
- D. Phase C
Answer:
D
Explanation:
his answer is based on the TOGAF Standard, Version 9.2 - Phase C: Information Systems
Architectures 2
, which states that “The objective of Phase C is to develop Target Information Systems
(Data and Application) Architecture descriptions that will enable the enterprise to address the
Request for Architecture Work and stakeholder concerns.” In this phase, the Information Map is
translated into data models that describe the structure and relationships of the data entities required
by the enterprise. The data models are part of the Data Architecture, which is one of the two
components of the Information Systems Architecture. The other options are not correct, as they are
not phases where the Information Map is translated into data models.
Question 6
Which of the following best describes a TOGAF Business Scenario?
- A. A technique for constructing business models in a form enabling reasoning, insight, and clarity.
- B. A method for ensuring that the business processes deliver the required outcomes.
- C. A complete description of a business problem in both business and architectural terms.
- D. A specification of the conventions for a particular kind of business architecture view.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
This answer is based on the definition of a TOGAF Business Scenario as “a technique for articulating,
developing, and validating the requirements of the business” 1
. A TOGAF Business Scenario is a
complete description of a business problem in both business and architectural terms, which enables
individual requirements to be viewed in relation to one another in the context of the overall
problem. A TOGAF Business Scenario consists of six elements: business environment, actors, roles,
business process, desired outcome, and quality attributes. The other options are not correct, as they
do not describe a TOGAF Business Scenario.
Question 7
Which Mop during development of a business scenario ensures that each iteration is managed as a
mini-project?
- A. Documenting Step
- B. Reviewing Step
- C. Gathering Step
- D. Planning Step
Answer:
D
Explanation:
This answer is based on the TOGAF Standard, Version 9.2 - Business Scenarios , which states that
“The Planning Step ensures that each iteration is managed as a mini-project. It involves defining the
scope of work for each iteration; identifying the participants; scheduling the activities; allocating
resources; defining deliverables; establishing quality criteria; and setting up communication
channels.” The Planning Step is part of the development process of a business scenario, which
consists of four steps: Planning, Gathering, Documenting, and Reviewing. The other options are not
correct, as they are not steps that ensure that each iteration is managed as a mini-project.
Question 8
In which pan of a business scenario are business capabilities and value streams modelled?
- A. When identifying and documenting desired outcomes
- B. When identifying the business and technology environment
- C. When identifying the human actors
- D. When identifying, documenting and ranking the problem
Answer:
B
Explanation:
This answer is based on the TOGAF Standard, Version 9.2 - Business Scenarios , which states that
“The business and technology environment is a description of the current situation in terms of
business processes (including business capabilities), people (including skills), information (including
data), applications (including software), infrastructure (including hardware), and governance
(including standards).” Business capabilities and value streams are modeled when identifying the
business and technology environment, as they provide a high-level view of what the business does
or can do, and how it delivers value to its stakeholders. The other options are not correct, as they are
not parts of a business scenario where business capabilities and value streams are modeled.
Question 9
Which approach to model, measure, and analyze business value is primarily concerned with
identifying the participants involved in creating and delivering value?
- A. Value networks
- B. Value chains
- C. Value streams
- D. Lean value streams
Answer:
A
Explanation:
This answer is based on the definition and focus of value networks as “a set of roles and interactions
that are necessary to create value for a customer or beneficiary” . Value networks are primarily
concerned with identifying the participants involved in creating and delivering value, as they show
how different actors collaborate and exchange value with each other. Value networks can include
both internal and external actors, such as suppliers, partners, customers, employees, regulators, etc.
The other options are not correct, as they are not approaches to model, measure, and analyze
business value that are primarily concerned with identifying the participants involved in creating and
delivering value.
Question 10
Which of me following is a benefit of Value Stream Mapping?
- A. It helps to identify value. duplication and redundancy across the enterprise.
- B. It helps to assess an organization s effectiveness at creating, capturing, and delivering value for different stakeholders.
- C. It helps to ensure that investments and project initiatives are prioritized and funded at a level matching with their value.
- D. It highlights the value of Individual work packages needed to develop the business architecture.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
This answer is based on the definition and purpose of value stream mapping as “a technique for
modeling, measuring, and analyzing the flow of value from the provider to the consumer through a
value stream” . Value stream mapping helps to assess an organization’s effectiveness at creating,
capturing, and delivering value for different stakeholders, as it shows how value is generated and
delivered by the organization’s processes, activities, resources, and capabilities. It also helps to
identify the sources of waste, inefficiency, and variation in the value delivery process. The other
options are not correct, as they are not benefits of value stream mapping.
Question 11
Which of me following is considered a guying principle when creating value streams?
- A. Identify the lop-level value streams from components of capabilities
- B. Create an Initial set of value streams that map one-to-one to existing capabilities.
- C. Avoid going down to operational levels of detail
- D. Start with internal value streams within the organization
Answer:
C
Explanation:
This answer is based on the TOGAF Series Guide: Value Streams 2
, which states that “A guiding
principle when creating value streams is to avoid going down to operational levels of detail. The
purpose of a value stream is to provide a high-level view of how value is created and delivered by an
enterprise.” Going down to operational levels of detail can make the value stream too complex and
difficult to understand and communicate. It can also obscure the strategic focus and direction of the
value stream. The other options are not correct, as they are not guiding principles when creating
value streams.
Question 12
Which of the following is a purpose of mapping capabilities to value stream stages?
- A. To provide a self-contained business that is Independent of the organizational structure.
- B. To Identity which business capabilities are critical to deliver value
- C. To describe the business in terms of services provided and consumed.
- D. To classify, group, and align capacities into categories for a deeper understanding
Answer:
B
Explanation:
This answer is based on the TOGAF Series Guide: Business Capabilities 3
, which states that “Mapping
capabilities to value stream stages allows an organization to identify which capabilities are critical to
deliver value to stakeholders and which capabilities are less important or even unnecessary.”
Mapping capabilities to value stream stages helps to assess the alignment and impact of the business
capabilities on the value delivery process. It also helps to prioritize and optimize the capabilities
based on their contribution to value creation. The other options are not correct, as they are not
purposes of mapping capabilities to value stream stages.
Question 13
Consider the following definition of the elements of a value stream:
What is the element labeled 7?
- A. Outcome
- B. Viewpoint
- C. Value
- D. Concern
Answer:
C
Explanation:
This answer is based on the TOGAF Series Guide: Value Streams 2
, which states that “Value is a
measurable improvement to a stakeholder’s situation that is perceived to be positive by that
stakeholder.” Value is the element labeled 7 in the image, as it represents the benefit or outcome
that is delivered to the stakeholder by the value stream. Value is always defined from the perspective
of the stakeholder, and it can be expressed in quantitative or qualitative terms. The other options are
not correct, as they do not match the element labeled 7 in the image.
Question 14
Which input to Phase A provides context for the architecture work by describing the needs and ways
of working of the enterprise?
- A. Business principles, goals, and drivers
- B. Architecture Vision
- C. Architecture Roadmap
- D. Architecture Principles
Answer:
A
Explanation:
This answer is based on the TOGAF Standard, Version 9.2 - Phase A: Architecture Vision 1
, which
states that “Business principles, business goals, and strategic drivers of the organization are already
defined elsewhere in the enterprise. If so, the activity in Phase A is involved with ensuring that
existing definitions are current, and clarifying any areas of ambiguity. Otherwise, it involves defining
these essential items from scratch.” Business principles, goals, and drivers provide context for the
architecture work by describing the needs and ways of working of the enterprise. They define the
desired outcomes, the guiding values, and the strategic direction of the enterprise. They also help to
align the architecture work with the business strategy and objectives. The other options are not
correct, as they do not provide context for the architecture work in Phase A.
Question 15
What fundamental business architecture concepts should be considered when creating an
Architecture Vision?
- A. Business use-cases, event diagrams, class models
- B. Business capabilities. organization maps, value streams
- C. Business data model, business roles, business processes
- D. Information exchange matrix, class models, node connectivity diagrams
Answer:
B
Explanation:
This answer is based on the TOGAF Series Guide: Business Capabilities , which states that “The
fundamental concepts that should be considered when creating an Architecture Vision are business
capabilities, organization maps, and value streams.” These concepts help to define and communicate
the essence of what a business does or can do, how it is organized and structured, and how it
delivers value to its stakeholders. The other options are not correct, as they are not fundamental
business architecture concepts that should be considered when creating an Architecture Vision.