teradata TDVAN5 Exam Questions
Questions for the TDVAN5 were updated on : Feb 20 ,2026
Page 1 out of 5. Viewing questions 1-15 out of 72
Question 1
On a Vantage system, the data load process has recently become much slower than normal and is
now running for two hours in low concurrency. During the time the process is running, the
Administrator measured the following average values from ResUsage:
System CPU busy = 75%
WIO = 25%
Inter-AMP parallelism = 90%
Average BYNET usage = 10%
Which resource is most constrained?
- A. CPU
- B. I/O
- C. BYNET
- D. Parallelism
Answer:
B
Explanation:
WIO (Work in I/O) is at 25%, which indicates that the system is spending a significant amount of time
waiting for I/O operations to complete. This suggests that I/O is the most constrained resource in this
scenario. A high WIO typically points to I/O bottlenecks, causing delays in processes like data loading.
The other resources appear to be less constrained:
CPU: The system is busy with 75% CPU usage, which indicates the CPU has available capacity (not
fully utilized).
BYNET: With 10% BYNET usage, there is no indication of network congestion.
Parallelism: Inter-AMP parallelism is at 90%, which suggests that parallel processing is functioning
well and not the bottleneck.
Thus, the data load slowdown is likely due to I/O constraints, making I/O the most constrained
resource in this case.
Question 2
Which table identifies whether a particular workload is suffering from a shortage of AMP Worker
Tasks?
- A. ResUsageSpma
- B. ResUsageSawt
- C. ResUsageSps
- D. ResUsageSvpr
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The ResUsageSawt table captures detailed statistics related to AMP Worker Tasks (AWTs). It provides
insight into how many AWTs are in use, waiting, or available, which helps identify whether a
particular workload is suffering from a shortage of AWTs.
ResUsageSpma provides information about memory usage and swapping but not specifically about
AWTs.
ResUsageSps focuses on session-level resource usage but does not track AMP Worker Tasks.
ResUsageSvpr provides data on virtual processor (vproc) usage and performance, not specifically on
AWTs.
ResUsageSawt is the correct table to examine for AWT-related issues.
Question 3
An Administrator manages a Vantage system that experiences large loads and updates during the
night, on weekdays. On Saturday night, significant analytical processing occurs using the data from
the prior weeks. The results of this processing are saved to support rapid reporting in the following
week.
The business requires this Vantage system to be available as soon as possible in case of a catastrophic
system failure.
Which backup strategy meets this need?
- A. Daily delta backups
- B. Weekly cumulative backup on Sunday and Wednesday, and delta backups on the remaining days
- C. Weekly full backup, cumulative backups on Tuesday and Friday, and delta backups on the remaining days
- D. Daily full backups
Answer:
C
Explanation:
This strategy strikes a balance between minimizing recovery time and reducing the overall storage
and performance impact during backups.
Weekly full backup ensures that a complete copy of the data is available at the start of the week,
which is critical for quick recovery in the event of a catastrophic system failure.
Cumulative backups on Tuesday and Friday ensure that any changes made since the last full backup
are captured without needing to apply multiple delta backups, reducing the time required for
restoration.
Delta backups on other days provide incremental backups of the system with minimal performance
impact, ensuring the system is consistently backed up without using excessive resources.
Question 4
The data science team reports that they do not have enough memory to run in-database Python
scripts when the scripts operate simultaneously.
Which workload management feature should the Administrator use to resolve this issue?
- A. Throttles to limit the concurrency of Python scripts
- B. Exceptions to place Python scripts consuming too much memory into a penalty box
- C. Virtual partitions to assign separate memory space to each Python script
- D. Planned environments to specify periods when data scientists can run Python scripts
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Using throttles in workload management allows the Administrator to limit the concurrency of Python
scripts running in the system. By controlling the number of Python scripts that can run
simultaneously, you can prevent memory exhaustion and ensure that enough resources are available
for each script to execute without causing failures due to memory constraints.
Question 5
Which data type could support an index definition on a table?
- A. DATASET
- B. JSON
- C. Large Object (LOB)
- D. Geospatial
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Geospatial data types can support index definitions in Teradata. Geospatial indexing is used to
optimize spatial queries, enabling efficient searching and retrieval of data based on spatial
coordinates (e.g., points, lines, polygons).
The other data types do not support indexing directly:
DATASET: This is used to store unstructured or semi-structured data and typically does not support
indexing.
JSON: While JSON data can be used within Teradata, it is typically not indexed in the traditional
sense.
Large Object (LOB): LOBs (like BLOBs or CLOBs) are generally used for storing large amounts of
unstructured data and are not suitable for indexing due to their size and nature.
Question 6
Which spool threshold can an Administrator set to define workload management exception criteria?
- A. Maximum Spool Rows
- B. Spool Skew
- C. Hot AMP Spool
- D. Max Spool Space By AMP
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Spool Skew is a threshold that an Administrator can set in workload management to detect and
manage uneven distribution of spool space usage across AMPs (Access Module Processors). When
spool skew exceeds a certain threshold, it can trigger exception handling or corrective actions,
helping to prevent performance degradation caused by unbalanced resource utilization.
The other options are less commonly used for defining workload management exception criteria:
Maximum Spool Rows: This is not a standard threshold for workload management.
Hot AMP Spool: While this refers to uneven spool space usage on a specific AMP, spool skew is the
more appropriate term and metric used for setting thresholds.
Max Spool Space By AMP: This isn't a standard workload management threshold. Spool space limits
are generally applied system-wide or per user, not by AMP.
Question 7
An Administrator received reports that a high priority business intelligence (BI) report is failing. This
report is a large transaction comprised of multiple SQL statements. Analysis revealed that a TASM
filter is rejecting one of the SQL statements in the transaction, and this is causing the entire report to
fail.
Which workload management adjustment could the Administrator take to prevent this report from
failing?
- A. Add the application ID for the report to the filter Bypass list.
- B. Define a new workload for the high priority report.
- C. Enable prevent mid-transaction throttle delay.
- D. Add exclusion criteria for multistatement requests to the filter.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
By adding the application ID for the high-priority report to the filter Bypass list, the TASM (Teradata
Active System Management) filter will no longer reject any SQL statements from this specific report.
This ensures that the entire report can execute successfully without one of its statements being
blocked, thereby preventing the report from failing.
Question 8
A role, TestingSprint, was created and assigned to members of a testing unit. This role is temporary in
nature and will be dropped after the sprint ends. The manager of the testing unit is also assigned to
the role and wants to drop it once work is complete.
Which option can the Administrator use to fulfill this request?
- A. Grant the DROP ROLE privilege to the TestingSprint role.
- B. Grant the DROP ROLE privilege to a newly created role, and then grant that role to the manager.
- C. Re-grant the TestingSprint role to the manager, specifying the WITH GRANT OPTION.
- D. Re-grant the TestingSprint role to the manager, specifying the WITH ADMIN OPTION.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Granting a role with the WITH ADMIN OPTION allows the recipient (in this case, the manager) to not
only use the role but also manage it. This includes the ability to drop the role when it is no longer
needed, as requested by the manager.
Question 9
An Administrator reports a power user running a query that is consuming significant CPU in a final
step product join and impacting other users due to the high priority of the workload.
Upon contacting the user in the application team, they are advised that the query is a request from
the CEO and needs to be completed. The team decides to remediate the situation by changing the
workload to a lower priority.
Which Viewpoint portlet should be used to make this adjustment?
- A. Workload Designer
- B. Application Queries
- C. Query Monitor
- D. Workload Health
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The Workload Designer portlet in Viewpoint is used to manage and adjust workloads, including
setting priorities for different workloads. To address the situation where a high-priority query is
consuming too many resources, the Workload Designer can be used to adjust the priority of the
workload that the query belongs to, ensuring that the impact on other users is reduced while still
allowing the query to complete.
The other options are less suited for adjusting workload priorities:
Application Queries is used to monitor and manage queries related to specific applications but does
not provide direct options to change workload priorities.
Query Monitor allows the monitoring of active queries and possibly aborting problematic queries
but does not handle workload priority changes.
Workload Health is used for monitoring the health and performance of workloads, but it is not the
tool used to modify priorities.
Question 10
Which statement accurately characterizes privileges?
- A. Granting a privilege at the user level does not affect DBC.AccessRights.
- B. Granting a privilege at the database level automatically causes that privilege to be inserted in DBC.AccessRights for each object contained in the database.
- C. Databases have privileges on all objects created within them without the need for explicit grants.
- D. Users have no privileges on any objects they create unless specific grants are made.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
When a privilege is granted at the database level, it applies to all objects within the database, and
this is reflected in DBC.AccessRights, which tracks access rights for users and roles on specific objects.
Question 11
A web application executes millions of tactical queries on different tables of a large Vantage system,
as shown below:
The most frequent query of the application is using the following SQL with this variable parameter:
The application owner requested to check for optimizations to improve the runtime of the query.
What should the Administrator suggest in this situation?
- A. Create a sparse join index on Receiptline, with CustomerNumber as an input parameter.
- B. Create a NUSI on Receiptline on each of the columns: ProductTypeId, OrderTypeId, VendorId.
- C. ALTER the tables ProductType and OrderType to use a sparse map that includes only a subset of the AMPs.
- D. Instead of directly accessing table Receiptline. a global temporary table should be used, that needs to contain prefiltered rows with CustomerNumber = <parameter>.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
A sparse join index can be used to store a subset of rows from a table based on the condition of the
most frequently queried parameter, in this case, CustomerNumber. By creating a sparse join index on
the Receiptline table with CustomerNumber as an input parameter, the query can access a smaller
subset of the data more efficiently, which can significantly improve performance, especially when
millions of tactical queries are involved.
The other options are less optimal for this situation:
Create a NUSI on Receiptline: While NUSIs can improve query performance, creating NUSIs on
multiple columns (e.g., ProductTypeId, OrderTypeId, VendorId) may not be as effective for improving
this specific query focused on CustomerNumber.
ALTER tables ProductType and OrderType: Using a sparse map for these small tables (55 and 175
rows) wouldn't provide much benefit in terms of performance improvement, as the issue is not with
these tables but with the larger Receiptline table.
Use a global temporary table: While prefiltering data in a temporary table could help in certain
situations, this adds complexity and maintenance overhead. Additionally, it wouldn't necessarily
offer a significant performance boost compared to a sparse join index.
Question 12
The Administrator has received a request to add SELECT rights on the BusinessViews database to end
users, developers, and batch accounts in the accounting unit. The following roles are set up for each
group: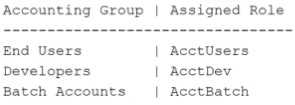
The Administrator created the AcctShared role and will use it in a role nesting strategy to provide the
required access.
Which actions can the Administrator take to fulfill this request?
- A. Grant SELECT on AcctShared to BusinessViews, then grant AcctUsers, AcctDev, and AcctBatch to AcctShared.
- B. Grant SELECT on BusinessViews to AcctShared, then grant AcctUsers, AcctDev, and AcctBatch to AcctShared.
- C. Grant SELECT on BusinessViews to AcctShared, then grant AcctShared to AcctUsers. AcctDev, and AcctBatch.
- D. Grant SELECT on AcctShared to BusinessViews, then grant AcctShared to AcctUsers. AcctDev, and AcctBatch.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The AcctShared role should be granted SELECT access on the BusinessViews database. This ensures
that the role itself has the necessary privileges.
Then, you can nest this role by granting AcctShared to the individual roles of AcctUsers, AcctDev, and
AcctBatch. This role nesting strategy allows the users in these groups to inherit the permissions from
AcctShared without having to directly grant the privileges to each individual role.
This approach maintains a clean and efficient permission structure using role nesting.
Question 13
A capacity planner wants to keep a record of the number of rows that are added and deleted from
certain tables over time and would like to obtain this information without having to change the
application itself.
Which DBQL option should be enabled?
- A. USECOUNT
- B. EXPLAIN
- C. OBJECTS
- D. VERBOSE XMLPLAN
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The OBJECTS option in DBQL (Database Query Logging) records the tables and other objects that are
accessed by queries, including information on how many rows are added, updated, or deleted. This
allows the capacity planner to track changes to specific tables without modifying the application
itself.
The other options are less relevant to tracking row changes:
USECOUNT records how often specific queries are executed, but not the number of rows affected.
EXPLAIN captures the query execution plan, which doesn't provide details on rows added or deleted.
VERBOSE XMLPLAN gives detailed execution plans in XML format, but it is more focused on query
execution and optimization, not tracking row modifications.
Question 14
A system in Viewpoint is regularly reported as being in a critical state due to a lack of available AWT.
No flow control is observed on the system. The Administrator identified that this is due to a recently
completed cloud migration for the system that increased the number of available AWT from 80 to
120.
Which process task is required to set up the system in Viewpoint to address this problem?
- A. Configure the AWT Info data collector with the updated setting of 120 maximum AWT.
- B. Increase by 40 the degraded and critical thresholds for the AWT in the system health setup portlet.
- C. Update the performance data collection portlet job that collects resource usage data with the 120 maximum AWT value.
- D. Adjust the system alert that has been configured for AWT to the recommended critical threshold of 92.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
After the cloud migration increased the number of available AWTs from 80 to 120, the thresholds for
critical and degraded states in Viewpoint are likely still based on the old maximum of 80 AWTs. Since
the system is now falsely reporting critical states due to this change, the thresholds need to be
updated to reflect the new maximum of 120 AWTs. Increasing the degraded and critical thresholds by
40 (to account for the additional AWTs) will prevent unnecessary critical alerts.
Question 15
An Administrator is required to load sensor data from cloud storage. This store contains many
numeric columns.
Which strategy should the Administrator use to optimize the data load?
- A. Use a more generic LOCATION string in the USING clause.
- B. Keep the original VARCHAR data types in JSON or CSV for columns.
- C. Cast column data types to appropriate values in a view of the foreign table.
- D. Collect statistics on all payload attributes.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
When loading sensor data, especially if it involves many numeric columns, casting the data to
appropriate types (like INT, FLOAT, etc.) in a view can significantly improve query performance and
reduce storage overhead. This approach ensures that the numeric data is handled efficiently,
avoiding unnecessary conversions or using inefficient data types such as VARCHAR.