Splunk SPLK-2002 Exam Questions
Questions for the SPLK-2002 were updated on : Feb 18 ,2026
Page 1 out of 11. Viewing questions 1-15 out of 160
Question 1
Which instance can not share functionality with the deployer?
- A. Search head cluster member
- B. License master
- C. Master node
- D. Monitoring Console (MC)
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The deployer is a Splunk Enterprise instance that distributes apps and other configurations to the
members of a search head cluster1
.
The deployer cannot share functionality with any other Splunk Enterprise instance, including
the license master, the master node, or the monitoring console2
.
However, the search head cluster members can share functionality with the master node and
the monitoring console, as long as they are not designated as the captain of the cluster3
.
Therefore, the correct answer is B. License master, as it is the only instance that cannot share
functionality with the deployer under any circumstances.
Reference: 1: About the deployer 2: Deployer system requirements 3
: Search head cluster
architecture
Question 2
As of Splunk 9.0, which index records changes to . conf files?
- A. _configtracker
- B. _introspection
- C. _internal
- D. _audit
Answer:
A
Explanation:
This is the index that records changes to .conf files as of Splunk 9.0.
According to the Splunk
documentation1
, the _configtracker index tracks the changes made to the configuration files on the
Splunk platform, such as the files in the etc directory.
The _configtracker index can help monitor and
troubleshoot the configuration changes, and identify the source and time of the changes1
. The other
options are not indexes that record changes to .conf files.
Option B, _introspection, is an index that
records the performance metrics of the Splunk platform, such as CPU, memory, disk, and network
usage2
.
Option C, _internal, is an index that records the internal logs and events of the Splunk
platform, such as splunkd, metrics, and audit logs3
.
Option D, _audit, is an index that records the
audit events of the Splunk platform, such as user authentication, authorization, and activity4
.
Therefore, option A is the correct answer, and options B, C, and D are incorrect.
1: About the _configtracker index 2: About the _introspection index 3: About the _internal index 4
:
About the _audit index
Question 3
A search head cluster member contains the following in its server .conf. What is the Splunk server
name of this member?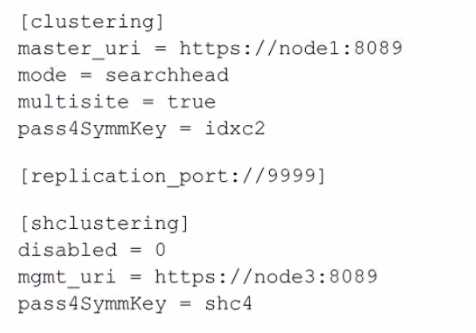
- A. node1
- B. shc4
- C. idxc2
- D. node3
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The Splunk server name of the member can typically be determined by the serverName attribute in
the server.conf file, which is not explicitly shown in the provided snippet. However, based on the
provided configuration snippet, we can infer that this search head cluster member is configured to
communicate with a cluster master (master_uri) located at node1 and a management node
(mgmt_uri) located at node3. The serverName is not the same as the master_uri or mgmt_uri; these
URIs indicate the location of the master and management nodes that this member interacts with.
Since the serverName is not provided in the snippet, one would typically look for a setting under the
[general] stanza in server.conf. However, given the options and the common naming conventions in a
Splunk environment, node3 would be a reasonable guess for the server name of this member, since
it is indicated as the management URI within the [shclustering] stanza, which suggests it might be the
name or address of the server in question.
For accurate identification, you would need to access the full server.conf file or the Splunk Web on
the search head cluster member and look under Settings > Server settings > General settings to find
the actual serverName. Reference for these details would be found in the Splunk documentation
regarding the configuration files, particularly server.conf.
Question 4
Which props.conf setting has the least impact on indexing performance?
- A. SHOULD_LINEMERGE
- B. TRUNCATE
- C. CHARSET
- D. TIME_PREFIX
Answer:
C
Explanation:
According to the Splunk documentation1
, the CHARSET setting in props.conf specifies the character
set encoding of the source data. This setting has the least impact on indexing performance, as it only
affects how Splunk interprets the bytes of the data, not how it processes or transforms the data. The
other options are false because:
The SHOULD_LINEMERGE setting in props.conf determines whether Splunk breaks events based on
timestamps or newlines.
This setting has a significant impact on indexing performance, as it affects
how Splunk parses the data and identifies the boundaries of the events2
.
The TRUNCATE setting in props.conf specifies the maximum number of characters that Splunk
indexes from a single line of a file.
This setting has a moderate impact on indexing performance, as it
affects how much data Splunk reads and writes to the index3
.
The TIME_PREFIX setting in props.conf specifies the prefix that directly precedes the timestamp in
the event data.
This setting has a moderate impact on indexing performance, as it affects how Splunk
extracts the timestamp and assigns it to the event
Question 5
In splunkd. log events written to the _internal index, which field identifies the specific log channel?
- A. component
- B. source
- C. sourcetype
- D. channel
Answer:
D
Explanation:
In the context of splunkd.log events written to the _internal index, the field that identifies the
specific log channel is the "channel" field. This information is confirmed by the Splunk Common
Information Model (CIM) documentation, where "channel" is listed as a field name associated with
Splunk Audit Logs .
Question 6
If .delta replication fails during knowledge bundle replication, what is the fall-back method for
Splunk?
- A. .Restart splunkd.
- B. .delta replication.
- C. .bundle replication.
- D. Restart mongod.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
This is the fall-back method for Splunk if .delta replication fails during knowledge bundle
replication.
Knowledge bundle replication is the process of distributing the knowledge objects, such
as lookups, macros, and field extractions, from the search head cluster to the indexer cluster1
.
Splunk
uses two methods of knowledge bundle replication: .delta replication and .bundle
replication1
.
.Delta replication is the default and preferred method, as it only replicates the changes
or updates to the knowledge objects, which reduces the network traffic and disk space
usage1
.
However, if .delta replication fails for some reason, such as corrupted files or network errors,
Splunk automatically switches to .bundle replication, which replicates the entire knowledge bundle,
regardless of the changes or updates1
.
This ensures that the knowledge objects are always
synchronized between the search head cluster and the indexer cluster, but it also consumes more
network bandwidth and disk space1
. The other options are not valid fall-back methods for
Splunk.
Option A, restarting splunkd, is not a method of knowledge bundle replication, but a way to
restart the Splunk daemon on a node2
. This may or may not fix the .delta replication failure, but it
does not guarantee the synchronization of the knowledge objects.
Option B, .delta replication, is not
a fall-back method, but the primary method of knowledge bundle replication, which is assumed to
have failed in the question1
.
Option D, restarting mongod, is not a method of knowledge bundle
replication, but a way to restart the MongoDB daemon on a node3
.
This is not related to the
knowledge bundle replication, but to the KV store replication, which is a different process3
.
Therefore, option C is the correct answer, and options A, B, and D are incorrect.
1: How knowledge bundle replication works 2: Start and stop Splunk Enterprise 3
: Restart the KV
store
Question 7
Where does the Splunk deployer send apps by default?
- A. etc/slave-apps/<app-name>/default
- B. etc/deploy-apps/<app-name>/default
- C. etc/apps/<appname>/default
- D. etc/shcluster/<app-name>/default
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The Splunk deployer sends apps to the search head cluster members by default to the path
etc/shcluster/<app-name>/default. The deployer is a Splunk component that distributes apps and
configurations to members of a search head cluster.
Splunk's documentation recommends placing the configuration bundle in the
$SPLUNK_HOME/etc/shcluster/apps directory on the deployer, which then gets distributed to the
search head cluster members. However, it should be noted that within each app's directory,
configurations can be under default or local subdirectories, with local taking precedence over default
for configurations. The reference to etc/shcluster/<app-name>/default is not a standard directory
structure and might be a misunderstanding. The correct path where the deployer pushes
configuration bundles is $SPLUNK_HOME/etc/shcluster/apps
Question 8
What is the best method for sizing or scaling a search head cluster?
- A. Estimate the maximum daily ingest volume in gigabytes and divide by the number of CPU cores per search head.
- B. Estimate the total number of searches per day and divide by the number of CPU cores available on the search heads.
- C. Divide the number of indexers by three to achieve the correct number of search heads.
- D. Estimate the maximum concurrent number of searches and divide by the number of CPU cores per search head.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
According to the Splunk blog1
, the best method for sizing or scaling a search head cluster is to
estimate the maximum concurrent number of searches and divide by the number of CPU cores per
search head. This gives you an idea of how many search heads you need to handle the peak search
load without overloading the CPU resources. The other options are false because:
Estimating the maximum daily ingest volume in gigabytes and dividing by the number of CPU cores
per search head is not a good method for sizing or scaling a search head cluster, as it does not
account for the complexity and frequency of the searches.
The ingest volume is more relevant for
sizing or scaling the indexers, not the search heads2
.
Estimating the total number of searches per day and dividing by the number of CPU cores available
on the search heads is not a good method for sizing or scaling a search head cluster, as it does not
account for the concurrency and duration of the searches.
The total number of searches per day is an
average metric that does not reflect the peak search load or the search performance2
.
Dividing the number of indexers by three to achieve the correct number of search heads is not a
good method for sizing or scaling a search head cluster, as it does not account for the search load or
the search head capacity.
The number of indexers is not directly proportional to the number of
search heads, as different types of data and searches may require different amounts of resources2
.
Question 9
Which command should be run to re-sync a stale KV Store member in a search head cluster?
- A. splunk clean kvstore -local
- B. splunk resync kvstore -remote
- C. splunk resync kvstore -local
- D. splunk clean eventdata -local
Answer:
A
Explanation:
To resync a stale KV Store member in a search head cluster, you need to stop the search head that has
the stale KV Store member, run the command splunk clean kvstore --local, and then restart the
search head.
This triggers the initial synchronization from other KV Store members12
.
The command splunk resync kvstore [-source sourceId] is used to resync the entire KV Store cluster
from one of the members, not a single member.
This command can only be invoked from the node
that is operating as search head cluster captain2
.
The command splunk clean eventdata -local is used to delete all indexed data from a standalone
indexer or a cluster peer node, not to resync the KV Store3
.
Reference:
:
How to resolve error on a search head member in the search head cluster …
:
Resync the KV store - Splunk Documentation
:
Delete indexed data - Splunk Documentation
Question 10
Where in the Job Inspector can details be found to help determine where performance is affected?
- A. Search Job Properties > runDuration
- B. Search Job Properties > runtime
- C. Job Details Dashboard > Total Events Matched
- D. Execution Costs > Components
Answer:
D
Explanation:
This is where in the Job Inspector details can be found to help determine where performance is
affected, as it shows the time and resources spent by each component of the search, such as
commands, subsearches, lookups, and post-processing1
.
The Execution Costs > Components section
can help identify the most expensive or inefficient parts of the search, and suggest ways to optimize
or improve the search performance1
. The other options are not as useful as the Execution Costs >
Components section for finding performance issues.
Option A, Search Job Properties > runDuration,
shows the total time, in seconds, that the search took to run2
. This can indicate the overall
performance of the search, but it does not provide any details on the specific components or factors
that affected the performance.
Option B, Search Job Properties > runtime, shows the time, in
seconds, that the search took to run on the search head2
. This can indicate the performance of the
search head, but it does not account for the time spent on the indexers or the network.
Option C, Job
Details Dashboard > Total Events Matched, shows the number of events that matched the search
criteria3
. This can indicate the size and scope of the search, but it does not provide any information
on the performance or efficiency of the search. Therefore, option D is the correct answer, and
options A, B, and C are incorrect.
1: Execution Costs > Components 2: Search Job Properties 3
: Job Details Dashboard
Question 11
When preparing to ingest a new data source, which of the following is optional in the data source
assessment?
- A. Data format
- B. Data location
- C. Data volume
- D. Data retention
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Data retention is optional in the data source assessment because it is not directly related to the
ingestion process. Data retention is determined by the index configuration and the storage capacity
of the Splunk platform. Data format, data location, and data volume are all essential information for
planning how to collect, parse, and index the data source.
Reference:
Drive more value through data source and use case optimization - Splunk
, page 9
Data source planning for Splunk Enterprise Security
Question 12
Which of the following is true for indexer cluster knowledge bundles?
- A. Only app-name/local is pushed.
- B. app-name/default and app-name/local are merged before pushing.
- C. Only app-name/default is pushed.
- D. app-name/default and app-name/local are pushed without change.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
According to the Splunk documentation1
, indexer cluster knowledge bundles are the configuration
files that the cluster master distributes to the peer nodes as part of the cluster configuration bundle.
The knowledge bundles contain the knowledge objects, such as event types, tags, lookups, and so
on, that are relevant for indexing and searching the data. The cluster master creates the knowledge
bundles by merging the app-name/default and app-name/local directories from the apps that reside
on the master node.
The cluster master then pushes the knowledge bundles to the peer nodes,
where they reside under the $SPLUNK_HOME/var/run directory2
. The other options are false
because:
Only app-name/local is pushed. This is false because the cluster master pushes both the app-
name/default and app-name/local directories, after merging them, to the peer nodes.
The app-
name/local directory contains the local customizations of the app configuration, while the app-
name/default directory contains the default app configuration3
.
Only app-name/default is pushed. This is false because the cluster master pushes both the app-
name/default and app-name/local directories, after merging them, to the peer nodes.
The app-
name/default directory contains the default app configuration, while the app-name/local directory
contains the local customizations of the app configuration3
.
app-name/default and app-name/local are pushed without change. This is false because the cluster
master merges the app-name/default and app-name/local directories before pushing them to the
peer nodes.
This ensures that the peer nodes have the latest and consistent configuration of the
apps3
.
Question 13
When implementing KV Store Collections in a search head cluster, which of the following
considerations is true?
- A. The KV Store Primary coordinates with the search head cluster captain when collection content changes.
- B. The search head cluster captain is also the KV Store Primary when collection content changes.
- C. The KV Store Collection will not allow for changes to content if there are more than 50 search heads in the cluster.
- D. Each search head in the cluster independently updates its KV store collection when collection content changes.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
According to the Splunk documentation1
, in a search head cluster, the KV Store Primary is the same
node as the search head cluster captain. The KV Store Primary is responsible for coordinating the
replication of KV Store data across the cluster members. When any node receives a write request, the
KV Store delegates the write to the KV Store Primary. The KV Store keeps the reads local, however.
This ensures that the KV Store data is consistent and available across the cluster.
Reference:
About the app key value store
KV Store and search head clusters
Question 14
Which Splunk component is mandatory when implementing a search head cluster?
- A. Captain Server
- B. Deployer
- C. Cluster Manager
- D. RAFT Server
Answer:
B
Explanation:
This is a mandatory Splunk component when implementing a search head cluster, as it is responsible
for distributing the configuration updates and app bundles to the cluster members1
.
The deployer is
a separate instance that communicates with the cluster manager and pushes the changes to the
search heads1
. The other options are not mandatory components for a search head cluster.
Option A,
Captain Server, is not a component, but a role that is dynamically assigned to one of the search heads
in the cluster2
.
The captain coordinates the replication and search activities among the cluster
members2
.
Option C, Cluster Manager, is a component for an indexer cluster, not a search head
cluster3
.
The cluster manager manages the replication and search factors, and provides a web
interface for monitoring and managing the indexer cluster3
.
Option D, RAFT Server, is not a
component, but a protocol that is used by the search head cluster to elect the captain and maintain
the cluster state4
. Therefore, option B is the correct answer, and options A, C, and D are incorrect.
1: Use the deployer to distribute apps and configuration updates 2: About the captain 3: About the
cluster manager 4
: How a search head cluster works
Question 15
When designing the number and size of indexes, which of the following considerations should be
applied?
- A. Expected daily ingest volume, access controls, number of concurrent users
- B. Number of installed apps, expected daily ingest volume, data retention time policies
- C. Data retention time policies, number of installed apps, access controls
- D. Expected daily ingest volumes, data retention time policies, access controls
Answer:
D
Explanation:
When designing the number and size of indexes, the following considerations should be applied:
Expected daily ingest volumes: This is the amount of data that will be ingested and indexed by the
Splunk platform per day. This affects the storage capacity, the indexing performance, and the license
usage of the Splunk deployment.
The number and size of indexes should be planned according to the
expected daily ingest volumes, as well as the peak ingest volumes, to ensure that the Splunk
deployment can handle the data load and meet the business requirements12
.
Data retention time policies: This is the duration for which the data will be stored and searchable by
the Splunk platform. This affects the storage capacity, the data availability, and the data compliance
of the Splunk deployment.
The number and size of indexes should be planned according to the data
retention time policies, as well as the data lifecycle, to ensure that the Splunk deployment can retain
the data for the desired period and meet the legal or regulatory obligations13
.
Access controls: This is the mechanism for granting or restricting access to the data by the Splunk
users or roles. This affects the data security, the data privacy, and the data governance of the Splunk
deployment.
The number and size of indexes should be planned according to the access controls, as
well as the data sensitivity, to ensure that the Splunk deployment can protect the data from
unauthorized or inappropriate access and meet the ethical or organizational standards14
.
Option D is the correct answer because it reflects the most relevant and important considerations for
designing the number and size of indexes.
Option A is incorrect because the number of concurrent
users is not a direct factor for designing the number and size of indexes, but rather a factor for
designing the search head capacity and the search head clustering configuration5
. Option B is
incorrect because the number of installed apps is not a direct factor for designing the number and
size of indexes, but rather a factor for designing the app compatibility and the app performance.
Option C is incorrect because it omits the expected daily ingest volumes, which is a crucial factor for
designing the number and size of indexes.
Reference:
:
Splunk Validated Architectures 2: [Indexer capacity planning] 3: [Set a retirement and archiving
policy for your indexes] 4: [About securing Splunk Enterprise] 5
: [Search head capacity planning] :
[App installation and management overview]