Splunk SPLK-1002 Exam Questions
Questions for the SPLK-1002 were updated on : Feb 18 ,2026
Page 1 out of 20. Viewing questions 1-15 out of 297
Question 1
Which of the following can be saved as an event type?
- A. index=server_496 sourcetype=BETA_534 code=610
- B. index=server_49c sourcetype=BETA_534 code=610 | stats count by code
- C. index=server_496 sourcetype=BETA_534 code=610 | where code > 200
- D. index=server_496 sourcetype=BETA_534 code=610 [| inputlookup append=t servercode.csv]
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Step-by-Step
Event types in Splunk are predefined searches that match specific patterns in the event data.
Only raw searches (without transforming commands like stats, where, or inputlookup) can be saved
as an event type.
Option A is a basic search string and can be saved as an event type.
Option B includes stats count by code, which transforms the data and cannot be used.
Option C includes where code > 200, which modifies results after they are returned, making it
ineligible.
Option D includes a subsearch with inputlookup, which is not valid for event types.
Reference: Splunk Docs - Event Types
Question 2
When using the timechart command, what optional argument is used to specify the interval of
_time?
- A. bin
- B. by
- C. span
- D. over
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Step-by-Step
The timechart command in Splunk is used to generate time-series visualizations of data.
The span argument is used to specify the interval (or bin size) for the _time field.
Example usage:
css
CopyEdit
index=_internal | timechart span=1h count
This command will create a timechart where _time is grouped into 1-hour intervals.
bin is used in the bin command to group numerical or time-based fields but is not specific to
timechart.
by is used to split results by a specific field but does not define the interval.
over is not a valid argument for timechart.
Reference: Splunk Docs - timechart command
Question 3
Consider the following search: index=web sourcetype=access_combined
The log shows several events that share the same jsessionid value (sd497k117o2f098). View the
events as a group.
From the following list, which search groups events by JSESSIONID?
- A. index=web sourcetype=access_combined | transaction JSESSIONID | search SD497K117O2F098
- B. index=web sourcetype=access_combined JSESSIONID <sd497kl!7o2f098>
- C. index=web sourcetype=access_combined | highlight JSESSIONID 'search SD497K117O2F098
- D. index=web sourcetype=access_combined SD497K117O2F098 | table JSESSIONID
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The objective is to group all events that share the same JSESSIONID value and filter them by a
specific JSESSIONID.
Option A: This uses the transaction command with the JSESSIONID field to group all events sharing
the same session ID and filters for the specific value SD497K117O2F098. This is correct.
Option B: The syntax here is invalid because JSESSIONID <value> is not a proper search syntax.
Option C: The highlight command only highlights fields or values in events; it does not group them.
Option D: While this filters for events containing SD497K117O2F098, it does not group them by
JSESSIONID.
Reference:
Splunk Docs: Transaction Command
Question 4
Which of the following can a field alias be applied to?
- A. Tags
- B. Indexes
- C. Sourcetypes
- D. Event types
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Field aliases in Splunk are used to map field names in event data to alternate names to make them
easier to understand or consistent across datasets.
Option A (Tags): Field aliases are not directly applied to tags. Tags are used for categorizing events or
field values.
Option B (Indexes): Field aliases cannot be applied to indexes. Indexes are physical storage locations
for events in Splunk.
Option C (Sourcetypes): This is correct. Field aliases can be defined at the sourcetype level to ensure
consistent naming across events of the same sourcetype.
Option D (Event types): Event types are saved searches, and field aliases do not apply here directly.
Reference:
Splunk Docs: Field Aliases
Question 5
What does the fillnull command do in this search?
index=main sourcetype=http_log | fillnull value="Unknown" src
- A. Set the values of the src field to null when it is "Unknown".
- B. Set all fields with the value of "Unknown" to null.
- C. Set the values of the src field to "Unknown" if it is null.
- D. Set all fields that are null to "Unknown".
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The fillnull command in Splunk is used to replace null (missing) field values with a specified value.
Explanation of options:
A: Incorrect, as fillnull does not set fields to null; it fills null values with a specific value.
B: Incorrect, as the command only affects the specified field (src in this case).
C: Correct, as the fillnull command explicitly sets null values in the src field to "Unknown".
D: Incorrect, as only the src field is affected, not all fields.
Example:
If the src field is null for some events, fillnull will populate "Unknown" in those cases.
Reference: Splunk Docs - Fillnull Command
Question 6
Which of the following can be saved as an event type?
- A. index=server sourcetype=BETA_718 code=UB9 | stats count by code
- B. index=server_494 sourcetype=BETA_718 code=889
- C. index=server_494 sourcetype=BETA_718 code=839 stats where code > 203
- D. index=server_494 sourcetype=BETA_718 code=839 | inputlookup append=t servercode.csv
Answer:
B
Explanation:
An event type in Splunk is essentially a saved search with specific conditions. It must meet the
following criteria:
The search cannot include transforming commands like stats, inputlookup, or where.
It should define a clear pattern of events to match.
Explanation of each option:
A: Includes stats count by code, which is a transforming command. This cannot be saved as an event
type.
B: Contains only search criteria (index, sourcetype, and code). This can be saved as an event type.
C: Includes stats and a conditional filter (where), which are not valid for event types.
D: Includes inputlookup, a transforming command, so it cannot be saved as an event type.
Reference: Splunk Docs - Event Types
Question 7
Brad created a tag called "SpecialProjectX". It is associated with several field/value pairs, such as
team=support, location=Austin, and release=Fuji. What search should Brad run to filter results for
SpecialProjectX events related to the Support Team?
- A. tag=SpecialProjectX
- B. tag::team=SpecialProjectX
- C. tag::Support-SpecialProjectX
- D. tag!=Fuji,Austin
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Tags in Splunk allow users to assign multiple field-value pairs to a common label.
The correct syntax to filter by tag is tag::<field>=<tag_name>.
tag::team=SpecialProjectX will filter results where team=support is associated with the tag
SpecialProjectX.
tag=SpecialProjectX searches for all events associated with SpecialProjectX, not just the support
team.
tag::Support-SpecialProjectX is incorrect syntax.
tag!=Fuji,Austin is incorrect since it does not filter using the SpecialProjectX tag.
Reference: Splunk Docs - Tags
Question 8
When using the eval command, which of these characters can be used to concatenate a string and a
number into a single value?
- A. & (ampersand)
- B. + (plus)
- C. - (tilde)
- D. . (period)
Answer:
D
Explanation:
In Splunk, the eval command is often used for manipulating field values, including concatenation.
The correct way to concatenate a string and a number is to use the . (period) operator. This operator
joins different types of data into a single string value.
For example:
eval concatenated_value = "value_" . 123
Result: concatenated_value will be value_123.
Other operators:
& is not a valid operator in eval for concatenation.
+ is used for arithmetic addition, not concatenation.
- is also not a concatenation operator.
Reference: Splunk Docs - Eval Command
Question 9
What is a benefit of installing the Splunk Common Information Model (CIM) add-on?
- A. It permits users to create workflow actions to align with industry standards.
- B. It provides users with a standardized set of field names and tags to normalize data.
- C. It allows users to create 3-D models of their data and export these visualizations.
- D. It enables users to itemize their events based on the results of the Search Job Inspector.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
It provides users with a standardized set of field names and tags to normalize data.
The Splunk CIM add-on provides a standardized set of field names and data models, which allows
users to normalize and categorize data from various sources into a common format. This helps with
data interoperability and enables faster, more consistent reporting and searching across different
data sources.
Reference:
Splunk Documentation - Common Information Model (CIM)
Question 10
Which of the following can be saved as an event type?
- A. index=server_48 sourcetype=BETA_881 code=220
- B. index=server_48 sourcetype=BETA_881 code=220 | stats count by code
- C. index=server_48 sourcetype=BETA_881 code=220 | inputlookup append=t servercode.csv
- D. index=server_48 sourcetype=BETA_881 code=220 | stats where code > 220
Answer:
A
Explanation:
An event type is a classification of events based on a search query, which allows for a static set of
search criteria. In this case, option A (index=server_48 sourcetype=BETA_881 code=220) represents a
simple search without transforming commands (e.g., stats, inputlookup). Event types cannot include
transforming commands such as stats or lookup.
Reference:
Splunk Documentation - Event Types
Question 11
Two separate results tables are being combined using the join command. The outer table has the
following values: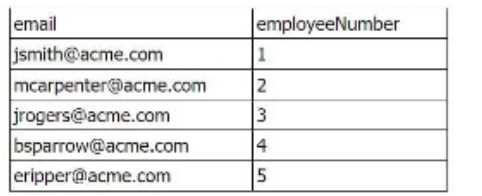
The inner table has the following values: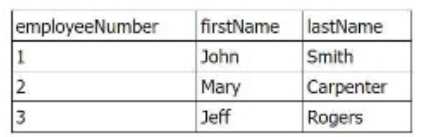
The line of SPL used to join the tables is: join employeeNumber type=outer
How many rows are returned in the new table?
- A. Three
- B. Eight
- C. Five
- D. Zero
Answer:
C
Explanation:
In this case, the outer join is applied, which means that all rows from the outer (left) table will be
included, even if there are no matching rows in the inner (right) table. The result will include all five
rows from the outer table, with the matched data from the inner table where employeeNumber
matches. Rows without matching employeeNumber values will have null values for the fields from
the inner table.
Reference:
Splunk Documentation - Join Command
Question 12
A search contains example(100,200). What is the name of the macro?
- A. example(2)
- B. example(var1,var2)
- C. example($,$)
- D. example[2]
Answer:
B
Explanation:
In Splunk, macros that accept arguments are defined with placeholders for those arguments in the
format example(var1, var2). In the search example(100,200), "100" and "200" are the values passed
for var1 and var2 respectively.
Reference:
Splunk Docs – Macros
Question 13
What happens to the original field name when a field alias is created?
- A. The original field name is not affected by the creation of a field alias.
- B. The original field name is replaced by the field alias within the index.
- C. The original field name is italicized to indicate that it is not an alias.
- D. The original field name still exists in the index but is not visible to the user at search time.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Creating a field alias in Splunk does not modify or remove the original field. Instead, the alias allows
the same data to be accessed using a different field name without affecting the original field.
Reference:
Splunk Docs - Field aliases
=================
Question 14
Which of the following can be saved as an event type?
- A. index=server_485 sourcetype=BETA_726 code=917 ['inputlookup append=t servercode.csv]
- B. index=server_485 sourcetype=BETA_726 code=917 | stats where code > 200
- C. index=server_485 sourcetype=BETA_726 code=917
- D. index=server_485 sourcetype=BETA_726 code=917 | stats count by code
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Event types in Splunk are saved as static search strings. The example index=server_485
sourcetype=BETA_726 code=917 is a simple search that can be saved as an event type, as it does not
contain dynamic processing commands like stats or inputlookup, which are not valid for event types.
Reference:
Splunk Docs - Event types
=================
Question 15
How do event types help a user search their data?
- A. Event types can optimize data storage.
- B. Event types improve dashboard performance.
- C. Event types improve search performance.
- D. Event types categorize events based on a search string.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Event types allow users to assign labels to events based on predefined search strings. This helps
categorize data and makes it easier to reference specific sets of events in future searches.
Reference:
Splunk Docs - Event types