Snowflake SNOWPRO-CORE Exam Questions
Questions for the SNOWPRO-CORE were updated on : Feb 18 ,2026
Page 1 out of 42. Viewing questions 1-15 out of 629
Question 1
What can the Snowflake SCIM API be used to manage? (Select TWO).
- A. Integrations
- B. Network policies
- C. Session policies
- D. Roles
- E. Users
Answer:
D, E
Explanation:
The Snowflake SCIM (System for Cross-domain Identity Management) API is used for automated user
and role management. It enables integration with identity providers (IdPs) for the provisioning and
deprovisioning of user accounts and roles in Snowflake. This helps in managing access control and
permissions systematically and aligns with identity governance practices.
Reference:
Snowflake Documentation: Managing Users and Roles with SCIM API
Question 2
Which Snowflake feature can be used to find sensitive data in a table or column?
- A. Masking policies
- B. Data classification
- C. Row level policies
- D. External functions
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Data classification in Snowflake is a feature that allows organizations to identify and categorize data
stored in tables or columns based on its sensitivity level or content type. This feature can be used to
find sensitive data within the database by classifying data as confidential, personal, public, etc.,
making it easier to apply appropriate security measures, such as masking policies or row-level
security, to protect sensitive information.
Reference:
Snowflake Documentation: Data Classification
Question 3
What consideration should be made when loading data into Snowflake?
- A. Create small data files and stage them in cloud storage frequently.
- B. Create large data files to maximize the processing overhead for each file.
- C. The number of load operations That run in parallel can exceed the number of data files to be loaded.
- D. The number of data files that are processed in parallel is determined by the virtual warehouse.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
When loading data into Snowflake, one critical consideration is the parallel processing capability of
the virtual warehouse used for the data loading operation. The number of data files that can be
processed in parallel during a loading operation is determined by the size and resources of the virtual
warehouse. A larger warehouse can process more files simultaneously, improving the efficiency and
speed of data loading operations. Optimizing the size of the virtual warehouse according to the data
loading needs and the size and number of files to be loaded can significantly impact the overall
performance of the data loading process.
Reference:
Snowflake Documentation: Optimizing Data Loading
Question 4
What operations can be performed while loading a simple CSV file into a Snowflake table using the
COPY INTO command? (Select TWO).
- A. Performing aggregate calculations
- B. Reordering the columns
- C. Grouping by operations
- D. Converting the datatypes
- E. Selecting the first few rows
Answer:
B, D
Explanation:
When loading a simple CSV file into a Snowflake table using the COPY INTO command, you can
perform various transformations and adjustments on the data as part of the loading process.
Specifically, you can:
B . Reorder the columns: Specify the order of columns in the COPY INTO command to match the
structure of the target table if it differs from the order of columns in the source CSV file.
D . Convert the datatypes: Explicitly convert the datatypes of the data being loaded to match the
datatypes of the columns in the target table. This can be necessary when the source data's format
does not match the target table's expected datatype.
Reference:
Snowflake Documentation: Using the COPY INTO Command for Data Loading
Question 5
What is a feature of column-level security in Snowflake?
- A. Role access policies
- B. Network policies
- C. Internal tokenization
- D. External tokenization
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Column-level security in Snowflake is implemented through Role Access Policies. These policies allow
administrators to control access to specific columns of a table or view based on the role of the user
accessing the data. By applying a role access policy to a column, administrators can ensure that
sensitive information remains secure, and only users with the appropriate roles can view or query
the data in that column. This feature enhances the security model by providing fine-grained access
control at the column level.
Reference:
Snowflake Documentation: Implementing Column-level Security
Question 6
A Snowflake account administrator has set the resource monitors as shown in the diagram, with
actions defined for each resource monitor as "Notify & Suspend Immediately".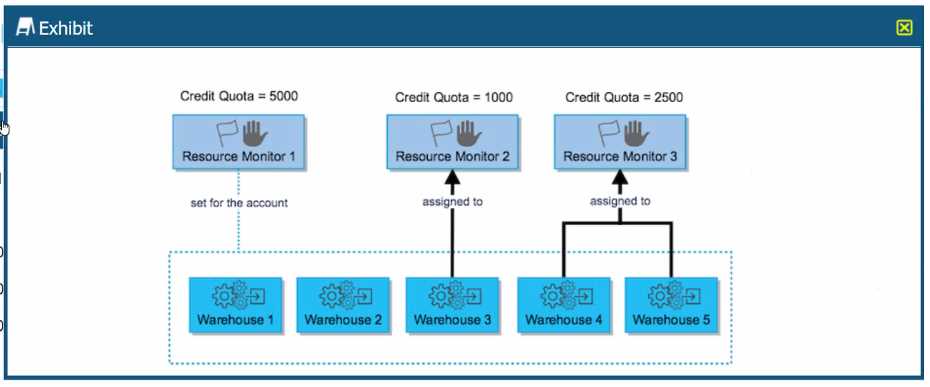
What is the MAXIMUM limit of credits that Warehouse 2 can consume?
- A. 0
- B. 1500
- C. 3500
- D. 5000
Answer:
B
Explanation:
In the provided exhibit, Warehouse 2 is under Resource Monitor 2, which has a credit quota of 1000
credits. However, it's important to note that warehouses can also draw from the account-level
resource monitor if they consume their dedicated monitor's quota. In this exhibit, Resource Monitor
1 is set for the account with a credit quota of 500 credits.
The exhibit does not clearly show whether Warehouse 2 is also subject to the account-level Resource
Monitor 1, but if we assume the typical case where all warehouses can draw from the account-level
monitor, the maximum limit of credits Warehouse 2 can consume would be the sum of its dedicated
resource monitor (Resource Monitor 2) and the account-level resource monitor (Resource Monitor
1).
Thus, Warehouse 2 can consume:
1000 credits from Resource Monitor 2
500 credits from Resource Monitor 1 (if applicable)
This gives a total of 1500 credits. Therefore, the maximum credit limit that Warehouse 2 can
consume, taking into account the possibility of the account-level monitor's contribution, would be
1500 credits.
However, without explicit confirmation that Warehouse 2 can use credits from Resource Monitor 1,
one would default to the specific resource monitor assigned to the warehouse, which is 1000 credits.
Given the available options, the closest and most accurate answer is B. 1500, as it represents the sum
of credits from both monitors that potentially apply to Warehouse 2.
Reference:
Snowflake Documentation on Resource Monitors: Managing Resource Monitors
Question 7
A Snowflake user needs to share unstructured data from an internal stage to a reporting tool that
does not have Snowflake access.
Which file function should be used?
- A. BUILD_SCOPED_FILE_URL
- B. BUILD_STAGE_FILE_URL
- C. GET_PRESIGNED_URL
- D. GET STAGE LOCATION
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The GET_PRESIGNED_URL function in Snowflake generates a presigned URL for a file stored in an
internal stage, allowing direct access to the file without requiring Snowflake access. This feature is
particularly useful for sharing unstructured data with external applications or tools that do not have
direct access to Snowflake. The presigned URL provides temporary access to the file, making it an
ideal solution for securely sharing unstructured data from an internal stage with a reporting tool or
any other external application.
Reference:
Snowflake Documentation: Generating Presigned URLs
Question 8
From what stage can a Snowflake user omit the FROM clause while loading data into a table?
- A. The user stage
- B. The table stage
- C. The internal named stage
- D. The external named stage
Answer:
B
Explanation:
In Snowflake, when loading data into a table using the COPY INTO command, the FROM clause can
be omitted if loading from the table's stage, also known as the table stage. The table stage is a
default location associated with each table where files can be temporarily stored for loading
operations. This simplifies the data loading process by allowing direct loading from files that have
been uploaded to the table's stage without specifying the stage explicitly in the COPY INTO
command.
Reference:
Snowflake Documentation: Loading Data into Tables
Question 9
Which statement accurately describes how a virtual warehouse functions?
- A. Increasing the size of a virtual warehouse will always improve data loading performance.
- B. Each virtual warehouse is an independent compute cluster that shares compute resources with other warehouses.
- C. Each virtual warehouse is a compute cluster composed of multiple compute nodes allocated by Snowflake from a cloud provider.
- D. All virtual warehouses share the same compute resources so performance degradation of one warehouse can significantly affect all the other warehouses.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
A virtual warehouse in Snowflake is an independent compute cluster that performs data processing
tasks such as executing SQL queries. Each virtual warehouse is dynamically allocated by Snowflake
from the cloud provider's resources and does not share compute resources with other warehouses.
This architecture ensures that the performance of one warehouse does not impact the performance
of another. Adjusting the size of a virtual warehouse affects its computational power by increasing or
decreasing the number of compute nodes, which can improve the performance of data processing
tasks depending on the workload.
Reference:
Snowflake Documentation: Understanding Virtual Warehouses
Question 10
Which SQL statement will require a virtual warehouse to run?
- A. SELECT COUNT{*) FROM TBL_EMPLOYEE;
- B. ALTER TABLE TBL_EMPLOYEE ADD COLUMN EMP_REGI0N VARCHAR(20);
- C. INSERT INTO TBL_EMPLOYEE(EMP_ID, EMP_NAME, EMP_SALARY, DEPT) VALUES(1,'Adam*,20000,* Finance');
- D. CREATE OR REPLACE TABLE TBL_EMPLOYEE ( EMP_ID NUMBER, EMP_NAME VARCHAR(30), EMP_SALARY NUMBER, DEPT VARCHAR{20) );
Answer:
C
Explanation:
A virtual warehouse in Snowflake is used to perform data processing tasks that require
computational resources, such as queries that modify data or perform significant computation. Of
the options provided:
C . INSERT INTO TBL_EMPLOYEE(EMP_ID, EMP_NAME, EMP_SALARY, DEPT)
VALUES(1,'Adam',20000,'Finance'); This SQL statement performs a data modification operation
(DML) by inserting a new record into the TBL_EMPLOYEE table, which requires computational
resources provided by a virtual warehouse to execute.
Reference:
Snowflake Documentation: Understanding Virtual Warehouses
Question 11
A user wants to upload a file to an internal Snowflake stage using a put command.
Which tools and or connectors could be used to execute this command? (Select TWO).
- A. SnowCD
- B. SnowSQL
- C. SQL API
- D. Python connector
- E. Snowsight worksheets
Answer:
B, E
Explanation:
To upload a file to an internal Snowflake stage using a PUT command, you can use:
B . SnowSQL: SnowSQL, the command-line client for Snowflake, supports the PUT command,
allowing users to upload files directly to Snowflake stages from their local file systems.
E . Snowsight worksheets: Snowsight, the web interface for Snowflake, provides a user-friendly
environment for executing SQL commands, including the PUT command, through its interactive
worksheets.
Reference:
Snowflake Documentation: Loading Data into Snowflake using SnowSQL
Snowflake Documentation: Using Snowsight
Topic 5, Exam pool E
Question 12
In Snowflake, the use of federated authentication enables which Single Sign-On (SSO) workflow
activities? (Select TWO).
- A. Authorizing users
- B. Initiating user sessions
- C. Logging into Snowflake
- D. Logging out of Snowflake
- E. Performing role authentication
Answer:
B C
Explanation:
Federated authentication in Snowflake allows users to use their organizational credentials to log in to
Snowflake, leveraging Single Sign-On (SSO). The key activities enabled by this setup include:
B . Initiating user sessions: Federated authentication streamlines the process of starting a user
session in Snowflake by using the existing authentication mechanisms of an organization.
C . Logging into Snowflake: It simplifies the login process, allowing users to authenticate with their
organization's identity provider instead of managing separate credentials for Snowflake.
Reference:
Snowflake Documentation: Configuring Federated Authentication
Question 13
Which DDL/DML operation is allowed on an inbound data share?
- A. ALTER TA3LE
- B. INSERT INTO
- C. MERGE
- D. SELECT
Answer:
D
Explanation:
In Snowflake, an inbound data share refers to the data shared with an account by another account.
The only DDL/DML operation allowed on an inbound data share is SELECT. This restriction ensures
that the shared data remains read-only for the consuming account, maintaining the integrity and
ownership of the data by the sharing account.
Reference:
Snowflake Documentation: Using Data Shares
Question 14
What is one of the characteristics of data shares?
- A. Data shares support full DML operations.
- B. Data shares work by copying data to consumer accounts.
- C. Data shares utilize secure views for sharing view objects.
- D. Data shares are cloud agnostic and can cross regions by default.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Data sharing in Snowflake allows for live, read-only access to data across different Snowflake
accounts without the need to copy or transfer the data. One of the characteristics of data shares is
the ability to use secure views. Secure views are used within data shares to restrict the access of
shared data, ensuring that consumers can only see the data that the provider intends to share,
thereby preserving privacy and security.
Reference:
Snowflake Documentation: Understanding Secure Views in Data Sharing
Question 15
What compute resource is used when loading data using Snowpipe?
- A. Snowpipe uses virtual warehouses provided by the user.
- B. Snowpipe uses an Apache Kafka server for its compute resources.
- C. Snowpipe uses compute resources provided by Snowflake.
- D. Snowpipe uses cloud platform compute resources provided by the user.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Snowpipe is Snowflake's continuous data ingestion service that allows for loading data as soon as it's
available in a cloud storage stage. Snowpipe uses compute resources managed by Snowflake,
separate from the virtual warehouses that users create for querying data. This means that Snowpipe
operations do not consume the computational credits of user-created virtual warehouses, offering an
efficient and cost-effective way to continuously load data into Snowflake.
Reference:
Snowflake Documentation: Understanding Snowpipe