Snowflake DEA-C01 Exam Questions
Questions for the DEA-C01 were updated on : Feb 18 ,2026
Page 1 out of 5. Viewing questions 1-15 out of 65
Question 1
A Data Engineer wants to create a new development database (DEV) as a clone of the permanent
production database (PROD) There is a requirement to disable Fail-safe for all tables.
Which command will meet these requirements?
- A. CREATE DATABASE DEV CLONE PROD FAIL_SAFE=FALSE;
- B. CREATE DATABASE DEV CLONE PROD;
- C. CREATE TRANSIENT DATABASE DEV CLONE RPOD
- D. CREATE DATABASE DEV CLOSE PROD DATA_RETENTION_TIME_IN_DAYS =0L
Answer:
C
Explanation:
This option will meet the requirements of creating a new development database (DEV) as a clone of
the permanent production database (PROD) and disabling Fail-safe for all tables. By using the CREATE
TRANSIENT DATABASE command, the Data Engineer can create a transient database that does not
have Fail-safe enabled by default. Fail-safe is a feature in Snowflake that provides additional
protection against data loss by retaining historical data for seven days beyond the time travel
retention period. Transient databases do not have Fail-safe enabled, which means that they do not
incur additional storage costs for historical data beyond their time travel retention period. By using
the CLONE option, the Data Engineer can create an exact copy of the PROD database, including its
schemas, tables, views, and other objects.
Question 2
A company is building a dashboard for thousands of Analysts. The dashboard presents the results of a
few summary queries on tables that are regularly updated. The query conditions vary by tope
according to what data each Analyst needs Responsiveness of the dashboard queries is a top priority,
and the data cache should be preserved.
How should the Data Engineer configure the compute resources to support this dashboard?
- A. Assign queries to a multi-cluster virtual warehouse with economy auto-scaling Allow the system to automatically start and stop clusters according to demand.
- B. Assign all queries to a multi-cluster virtual warehouse set to maximized mode Monitor to determine the smallest suitable number of clusters.
- C. Create a virtual warehouse for every 250 Analysts Monitor to determine how many of these virtual warehouses are being utilized at capacity.
- D. Create a size XL virtual warehouse to support all the dashboard queries Monitor query runtimes to determine whether the virtual warehouse should be resized.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
This option is the best way to configure the compute resources to support this dashboard. By
assigning all queries to a multi-cluster virtual warehouse set to maximized mode, the Data Engineer
can ensure that there is enough compute capacity to handle thousands of concurrent queries from
different analysts. A multi-cluster virtual warehouse can scale up or down by adding or removing
clusters based on the load. A maximized scaling policy ensures that there is always at least one
cluster running and that new clusters are added as soon as possible when needed. By monitoring the
utilization and performance of the virtual warehouse, the Data Engineer can determine the smallest
suitable number of clusters that can meet the responsiveness requirement and minimize costs.
Question 3
Within a Snowflake account permissions have been defined with custom roles and role hierarchies.
To set up column-level masking using a role in the hierarchy of the current user, what command
would be used?
- A. CORRECT_ROLE
- B. IKVOKER_ROLE
- C. IS_RCLE_IN_SESSION
- D. IS_GRANTED_TO_INVOKER_ROLE
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The IS_ROLE_IN_SESSION function is used to set up column-level masking using a role in the
hierarchy of the current user. Column-level masking is a feature in Snowflake that allows users to
apply dynamic data masking policies to specific columns based on the roles of the users who access
them. The IS_ROLE_IN_SESSION function takes a role name as an argument and returns true if the
role is in the current user’s session, or false otherwise. The function can be used in a masking policy
expression to determine whether to mask or unmask a column value based on the role of the user.
For example:
CREATE OR REPLACE MASKING POLICY email_mask AS (val string) RETURNS string -> CASE WHEN
IS_ROLE_IN_SESSION(‘HR’) THEN val ELSE REGEXP_REPLACE(val, ‘(.).(.@.)’, ‘\1****\2’) END;
In this example, the IS_ROLE_IN_SESSION function is used to create a masking policy for an email
column. The masking policy returns the original email value if the user has the HR role in their
session, or returns a masked email value with asterisks if not.
Question 4
When would a Data engineer use table with the flatten function instead of the lateral flatten
combination?
- A. When TABLE with FLATTEN requires another source in the from clause to refer to
- B. When TABLE with FLATTEN requires no additional source m the from clause to refer to
- C. When the LATERAL FLATTEN combination requires no other source m the from clause to refer to
- D. When table with FLATTEN is acting like a sub-query executed for each returned row
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The TABLE function with the FLATTEN function is used to flatten semi-structured data, such as JSON
or XML, into a relational format. The TABLE function returns a table expression that can be used in
the FROM clause of a query. The TABLE function with the FLATTEN function requires another source
in the FROM clause to refer to, such as a table, view, or subquery that contains the semi-structured
data. For example:
SELECT t.value:city::string AS city, f.value AS population FROM cities t, TABLE(FLATTEN(input =>
t.value:population)) f;
In this example, the TABLE function with the FLATTEN function refers to the cities table in the FROM
clause, which contains JSON data in a variant column named value. The FLATTEN function flattens the
population array within each JSON object and returns a table expression with two columns: key and
value. The query then selects the city and population values from the table expression.
Question 5
A Data Engineer is evaluating the performance of a query in a development environment.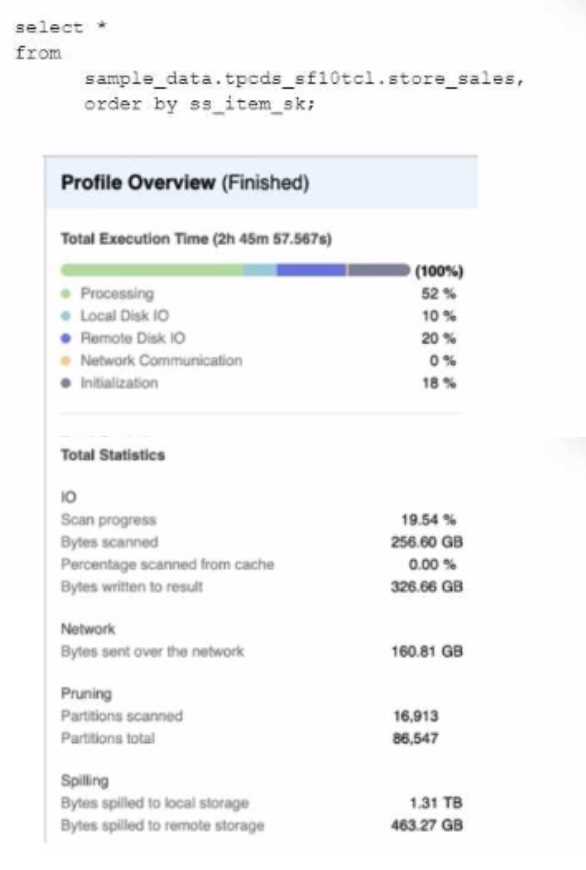
Based on the Query Profile what are some performance tuning options the Engineer can use? (Select
TWO)
- A. Add a LIMIT to the ORDER BY If possible
- B. Use a multi-cluster virtual warehouse with the scaling policy set to standard
- C. Move the query to a larger virtual warehouse
- D. Create indexes to ensure sorted access to data
- E. Increase the max cluster count
Answer:
A, C
Explanation:
The performance tuning options that the Engineer can use based on the Query Profile are:
Add a LIMIT to the ORDER BY If possible: This option will improve performance by reducing the
amount of data that needs to be sorted and returned by the query. The ORDER BY clause requires
sorting all rows in the input before returning them, which can be expensive and time-consuming. By
adding a LIMIT clause, the query can return only a subset of rows that satisfy the order criteria,
which can reduce sorting time and network transfer time.
Create indexes to ensure sorted access to data: This option will improve performance by reducing the
amount of data that needs to be scanned and filtered by the query. The query contains several
predicates on different columns, such as o_orderdate, o_orderpriority, l_shipmode, etc. By creating
indexes on these columns, the query can leverage sorted access to data and prune unnecessary
micro-partitions or rows that do not match the predicates. This can reduce IO time and processing
time.
The other options are not optimal because:
Use a multi-cluster virtual warehouse with the scaling policy set to standard: This option will not
improve performance, as the query is already using a multi-cluster virtual warehouse with the scaling
policy set to standard. The Query Profile shows that the query is using a 2XL warehouse with 4
clusters and a standard scaling policy, which means that the warehouse can automatically scale up or
down based on the load. Changing the warehouse size or the number of clusters will not affect the
performance of this query, as it is already using the optimal resources.
Increase the max cluster count: This option will not improve performance, as the query is not limited
by the max cluster count. The max cluster count is a parameter that specifies the maximum number
of clusters that a multi-cluster virtual warehouse can scale up to. The Query Profile shows that the
query is using a 2XL warehouse with 4 clusters and a standard scaling policy, which means that the
warehouse can automatically scale up or down based on the load. The default max cluster count for a
2XL warehouse is 10, which means that the warehouse can scale up to 10 clusters if needed.
However, the query does not need more than 4 clusters, as it is not CPU-bound or memory-bound.
Increasing the max cluster count will not affect the performance of this query, as it will not use more
clusters than necessary.
Question 6
Company A and Company B both have Snowflake accounts. Company A's account is hosted on a
different cloud provider and region than Company B's account Companies A and B are not in the
same Snowflake organization.
How can Company A share data with Company B? (Select TWO).
- A. Create a share within Company A's account and add Company B's account as a recipient of that share
- B. Create a share within Company A's account, and create a reader account that is a recipient of the share Grant Company B access to the reader account
- C. Use database replication to replicate Company A's data into Company B's account Create a share within Company B's account and grant users within Company B's account access to the share
- D. Create a new account within Company A's organization in the same cloud provider and region as Company B's account Use database replication to replicate Company A's data to the new account Create a share within the new account and add Company B's account as a recipient of that share
- E. Create a separate database within Company A's account to contain only those data sets they wish to share with Company B Create a share within Company A's account and add all the objects within this separate database to the share Add Company B's account as a recipient of the share
Answer:
AE
Explanation:
The ways that Company A can share data with Company B are:
Create a share within Company A’s account and add Company B’s account as a recipient of that
share: This is a valid way to share data between different accounts on different cloud platforms and
regions. Snowflake supports cross-cloud and cross-region data sharing, which allows users to create
shares and grant access to other accounts regardless of their cloud platform or region. However, this
option may incur additional costs for network transfer and storage replication.
Create a separate database within Company A’s account to contain only those data sets they wish to
share with Company B Create a share within Company A’s account and add all the objects within this
separate database to the share Add Company B’s account as a recipient of the share: This is also a
valid way to share data between different accounts on different cloud platforms and regions. This
option is similar to the previous one, except that it uses a separate database to isolate the data sets
that need to be shared. This can improve security and manageability of the shared data. The other
options are not valid because:
Create a share within Company A’s account, and create a reader account that is a recipient of the
share Grant Company B access to the reader account: This option is not valid because reader
accounts are not supported for cross-cloud or cross-region data sharing. Reader accounts are
Snowflake accounts that can only consume data from shares created by their provider account.
Reader accounts must be on the same cloud platform and region as their provider account.
Use database replication to replicate Company A’s data into Company B’s account Create a share
within Company B’s account and grant users within Company B’s account access to the share: This
option is not valid because database replication cannot be used for cross-cloud or cross-region data
sharing. Database replication is a feature in Snowflake that allows users to copy databases across
accounts within the same cloud platform and region. Database replication cannot copy databases
across different cloud platforms or regions.
Create a new account within Company A’s organization in the same cloud provider and region as
Company B’s account Use database replication to replicate Company A’s data to the new account
Create a share within the new account and add Company B’s account as a recipient of that share:
This option is not valid because it involves creating a new account within Company A’s organization,
which may not be feasible or desirable for Company A. Moreover, this option is unnecessary, as
Company A can directly share data with Company B without creating an intermediate account.
Question 7
A secure function returns data coming through an inbound share
What will happen if a Data Engineer tries to assign usage privileges on this function to an outbound
share?
- A. An error will be returned because the Engineer cannot share data that has already been shared
- B. An error will be returned because only views and secure stored procedures can be shared
- C. An error will be returned because only secure functions can be shared with inbound shares
- D. The Engineer will be able to share the secure function with other accounts
Answer:
A
Explanation:
An error will be returned because the Engineer cannot share data that has already been shared. A
secure function is a Snowflake function that can access data from an inbound share, which is a share
that is created by another account and consumed by the current account. A secure function can only
be shared with an inbound share, not an outbound share, which is a share that is created by the
current account and shared with other accounts. This is to prevent data leakage or unauthorized
access to the data from the inbound share.
Question 8
What is a characteristic of the use of external tokenization?
- A. Secure data sharing can be used with external tokenization
- B. External tokenization cannot be used with database replication
- C. Pre-loading of unmasked data is supported with external tokenization
- D. External tokenization allows (he preservation of analytical values after de-identification
Answer:
D
Explanation:
External tokenization is a feature in Snowflake that allows users to replace sensitive data values with
tokens that are generated and managed by an external service. External tokenization allows the
preservation of analytical values after de-identification, such as preserving the format, length, or
range of the original values. This way, users can perform analytics on the tokenized data without
compromising the security or privacy of the sensitive data.
Question 9
Which functions will compute a 'fingerprint' over an entire table, query result, or window to quickly
detect changes to table contents or query results? (Select TWO).
- A. HASH (*)
- B. HASH_AGG(*)
- C. HASH_AGG(<expr>, <expr>)
- D. HASH_AGG_COMPARE (*)
- E. HASH COMPARE(*)
Answer:
B, C
Explanation:
The functions that will compute a ‘fingerprint’ over an entire table, query result, or window to
quickly detect changes to table contents or query results are:
HASH_AGG(*): This function computes a hash value over all columns and rows in a table, query
result, or window. The function returns a single value for each group defined by a GROUP BY clause,
or a single value for the entire input if no GROUP BY clause is specified.
HASH_AGG(<expr>, <expr>): This function computes a hash value over two expressions in a table,
query result, or window. The function returns a single value for each group defined by a GROUP BY
clause, or a single value for the entire input if no GROUP BY clause is specified. The other functions
are not correct because:
HASH (*): This function computes a hash value over all columns in a single row. The function returns
one value per row, not one value per table, query result, or window.
HASH_AGG_COMPARE (): This function compares two hash values computed by HASH_AGG() over
two tables or query results and returns true if they are equal or false if they are different. The
function does not compute a hash value itself, but rather compares two existing hash values.
HASH COMPARE(): This function compares two hash values computed by HASH() over two rows and
returns true if they are equal or false if they are different. The function does not compute a hash
value itself, but rather compares two existing hash values.
Question 10
A Data Engineer needs to load JSON output from some software into Snowflake using Snowpipe.
Which recommendations apply to this scenario? (Select THREE)
- A. Load large files (1 GB or larger)
- B. Ensure that data files are 100-250 MB (or larger) in size compressed
- C. Load a single huge array containing multiple records into a single table row
- D. Verify each value of each unique element stores a single native data type (string or number)
- E. Extract semi-structured data elements containing null values into relational columns before loading
- F. Create data files that are less than 100 MB and stage them in cloud storage at a sequence greater than once each minute
Answer:
B, D, F
Explanation:
The recommendations that apply to this scenario are:
Ensure that data files are 100-250 MB (or larger) in size compressed: This recommendation will
improve Snowpipe performance by reducing the number of files that need to be loaded and
increasing the parallelism of loading. Smaller files can cause performance degradation or errors due
to excessive metadata operations or network latency.
Verify each value of each unique element stores a single native data type (string or number): This
recommendation will improve Snowpipe performance by avoiding data type conversions or errors
when loading JSON data into variant columns. Snowflake supports two native data types for JSON
elements: string and number. If an element has mixed data types across different files or records,
such as string and boolean, Snowflake will either convert them to string or raise an error, depending
on the FILE_FORMAT option.
Create data files that are less than 100 MB and stage them in cloud storage at a sequence greater
than once each minute: This recommendation will minimize Snowpipe costs by reducing the number
of notifications that need to be sent to Snowpipe for auto-ingestion. Snowpipe charges for
notifications based on the number of files per notification and the frequency of notifications. By
creating smaller files and staging them at a lower frequency, fewer notifications will be needed.
Question 11
How can the following relational data be transformed into semi-structured data using the LEAST
amount of operational overhead?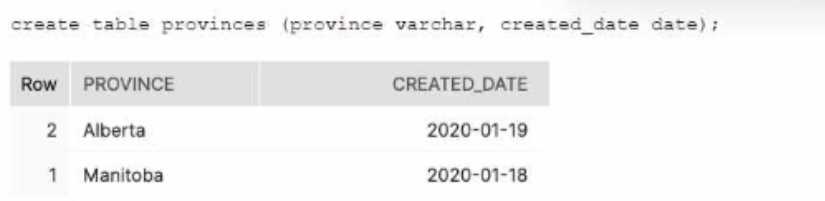
- A. Use the to_json function
- B. Use the PAESE_JSON function to produce a variant value
- C. Use the OBJECT_CONSTRUCT function to return a Snowflake object
- D. Use the TO_VARIANT function to convert each of the relational columns to VARIANT.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
This option is the best way to transform relational data into semi-structured data using the least
amount of operational overhead. The OBJECT_CONSTRUCT function takes a variable number of key-
value pairs as arguments and returns a Snowflake object, which is a variant type that can store JSON
data. The function can be used to convert each row of relational data into a JSON object with the
column names as keys and the column values as values.
Question 12
A company built a sales reporting system with Python, connecting to Snowflake using the Python
Connector. Based on the user's selections, the system generates the SQL queries needed to fetch the
data for the report First it gets the customers that meet the given query parameters (on average
1000 customer records for each report run) and then it loops the customer records sequentially
Inside that loop it runs the generated SQL clause for the current customer to get the detailed data for
that customer number from the sales data table
When the Data Engineer tested the individual SQL clauses they were fast enough (1 second to get the
customers 0 5 second to get the sales data for one customer) but the total runtime of the report is
too long
How can this situation be improved?
- A. Increase the size of the virtual warehouse
- B. Increase the number of maximum clusters of the virtual warehouse
- C. Define a clustering key for the sales data table
- D. Rewrite the report to eliminate the use of the loop construct
Answer:
D
Explanation:
This option is the best way to improve the situation, as using a loop construct to run SQL queries for
each customer is very inefficient and slow. Instead, the report should be rewritten to use a single SQL
query that joins the customer and sales data tables and applies the query parameters as filters. This
way, the report can leverage Snowflake’s parallel processing and optimization capabilities and reduce
the network overhead and latency.
Question 13
The following is returned from SYSTEMCLUSTERING_INFORMATION () for a table named orders with
a date column named O_ORDERDATE: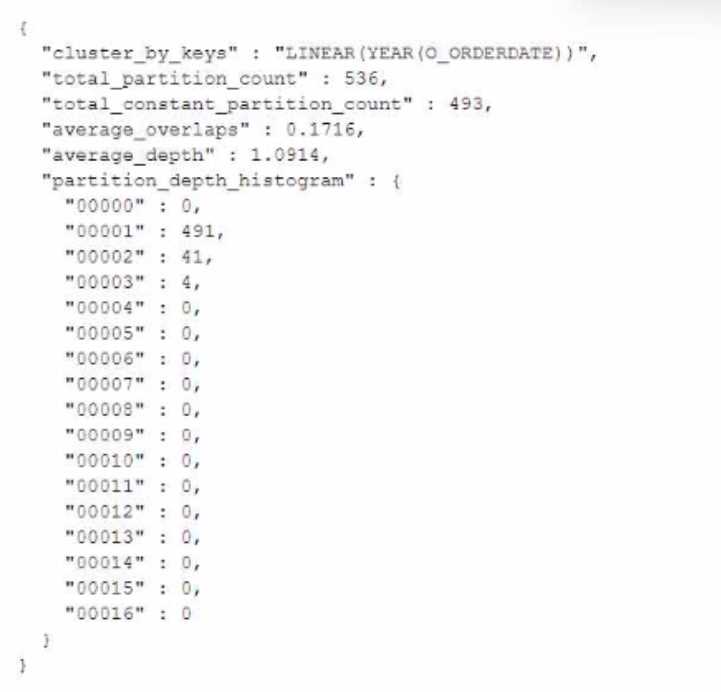
What does the total_constant_partition_count value indicate about this table?
- A. The table is clustered very well on_ORDERDATE, as there are 493 micro-partitions that could not be significantly improved by reclustering
- B. The table is not clustered well on O_ORDERDATE, as there are 493 micro-partitions where the range of values in that column overlap with every other micro partition in the table.
- C. The data in O_ORDERDATE does not change very often as there are 493 micro-partitions containing rows where that column has not been modified since the row was created
- D. The data in O_ORDERDATE has a very low cardinality as there are 493 micro-partitions where there is only a single distinct value in that column for all rows in the micro-partition
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The total_constant_partition_count value indicates the number of micro-partitions where the
clustering key column has a constant value across all rows in the micro-partition. However, this does
not necessarily mean that the table is clustered well on that column, as there could be other micro-
partitions where the range of values in that column overlap with each other. This is the case for the
orders table, as the clustering depth is 1, which means that every micro-partition overlaps with every
other micro-partition on O_ORDERDATE. This indicates that the table is not clustered well on
O_ORDERDATE and could benefit from reclustering.
Question 14
Assuming a Data Engineer has all appropriate privileges and context which statements would be
used to assess whether the User-Defined Function (UDF), MTBATA3ASZ. SALES
.REVENUE_BY_REGION, exists and is secure? (Select TWO)
- A. SHOW DS2R FUNCTIONS LIKE 'REVEX'^BYJIESION' IN SCHEMA SALES;
- B. SELECT IS_SECURE FROM SNOWFLAKE. INFCRXATION_SCKZMA. FUNCTIONS WHERE FUNCTI0N_3CHEMA = 'SALES' AND FUNCTI CN_NAXE = •ftEVEXUE_BY_RKXQH4;
- C. SELECT IS_SEC"JRE FROM INFOR>LVTICN_SCHEMA. FUNCTIONS WHERE FUNCTION_SCHEMA = 'SALES1 AND FUNGTZON_NAME = ' REVENUE_BY_REGION';
- D. SHOW EXTERNAL FUNCTIONS LIKE ‘REVENUE_BY_REGION’ IB SCHEMA SALES;
- E. SHOW SECURE FUNCTIONS LIKE 'REVENUE 3Y REGION' IN SCHEMA SALES;
Answer:
AB
Explanation:
The statements that would be used to assess whether the UDF, MTBATA3ASZ. SALES
.REVENUE_BY_REGION, exists and is secure are:
SHOW DS2R FUNCTIONS LIKE ‘REVEX’^BYJIESION’ IN SCHEMA SALES;: This statement will show
information about the UDF, including its name, schema, database, arguments, return type, language,
and security option. If the UDF does not exist, the statement will return an empty result set.
SELECT IS_SECURE FROM SNOWFLAKE. INFCRXATION_SCKZMA. FUNCTIONS WHERE
FUNCTI0N_3CHEMA = ‘SALES’ AND FUNCTI CN_NAXE = •ftEVEXUE_BY_RKXQH4;: This statement will
query the SNOWFLAKE.INFORMATION_SCHEMA.FUNCTIONS view, which contains metadata about
the UDFs in the current database. The statement will return the IS_SECURE column, which indicates
whether the UDF is secure or not. If the UDF does not exist, the statement will return an empty result
set. The other statements are not correct because:
SELECT IS_SEC"JRE FROM INFOR>LVTICN_SCHEMA. FUNCTIONS WHERE FUNCTION_SCHEMA =
‘SALES1 AND FUNGTZON_NAME = ’ REVENUE_BY_REGION’;: This statement will query the
INFORMATION_SCHEMA.FUNCTIONS view, which contains metadata about the UDFs in the current
schema. However, the statement has a typo in the schema name (‘SALES1’ instead of ‘SALES’), which
will cause it to fail or return incorrect results.
SHOW EXTERNAL FUNCTIONS LIKE ‘REVENUE_BY_REGION’ IB SCHEMA SALES;: This statement will
show information about external functions, not UDFs. External functions are Snowflake functions
that invoke external services via HTTPS requests and responses. The statement will not return any
results for the UDF.
SHOW SECURE FUNCTIONS LIKE ‘REVENUE 3Y REGION’ IN SCHEMA SALES;: This statement is invalid
because there is no such thing as secure functions in Snowflake. Secure functions are a feature of
some other databases, such as PostgreSQL, but not Snowflake. The statement will cause a syntax
error.
Question 15
What kind of Snowflake integration is required when defining an external function in Snowflake?
- A. API integration
- B. HTTP integration
- C. Notification integration
- D. Security integration
Answer:
A
Explanation:
An API integration is required when defining an external function in Snowflake. An API integration is
a Snowflake object that defines how Snowflake communicates with an external service via HTTPS
requests and responses. An API integration specifies parameters such as URL, authentication
method, encryption settings, request headers, and timeout values. An API integration is used to
create an external function object that invokes the external service from within SQL queries.