python institute PCPP-32-101 Exam Questions
Questions for the PCPP-32-101 were updated on : Feb 20 ,2026
Page 1 out of 3. Viewing questions 1-15 out of 45
Question 1
Which of the following methods allow you to load a configuration using ConfigParser? (Select two
answers.)
- A. read
- B. read_dict
- C. read_conf
- D. read_str
Answer:
AD
Explanation:
ConfigParser is a built-in library in Python that allows you to read and write configuration files. The
read method is used to read the configuration file which can be in any of the supported file formats,
such as INI, YAML, and JSON. The read_dict method is used to read the configuration from a Python
dictionary. The read_conf and read_str options are not valid methods in the ConfigParser module.
Therefore, the correct options to load a configuration using ConfigParser are A. read and D.
read_string.
Reference:
Official
Python
documentation
on
ConfigParser:
https://docs.python.org/3/library/configparser.html
Question 2
What will be the content of the co/ors.csv file when you run the following code?
A)
B)
C)
D)
An exception will be raised.
- A. Option A
- B. Option B
- C. Option C
- D. Option D
Answer:
B
Question 3
What is the result of the following code?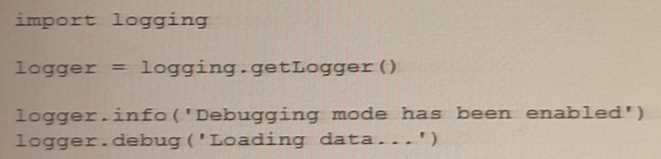
What is the result of the following code?
- A. Nothing will be displayed
- B. Loading data...
- C. Debugging mode has been enabled
- D. Debugging mode has been enabled Loading data...
Answer:
B
Explanation:
This statement is true because the code uses the logging module to create a logger object and set its
level to logging.INFO. The logging module provides a way of reporting events that occur during the
execution of a program. The logging level determines which events are reported and which are
ignored. The logging module defines five levels of severity: DEBUG, INFO, WARNING, ERROR, and
CRITICAL. The lower the level, the more events are reported.
The code then uses the logger object to log two messages: one with the level logging.DEBUG and
one with the level logging.INFO. The logger object only reports the messages that have a level equal
or higher than its own level. Therefore, the message with the level logging.DEBUG is ignored, while
the message with the level logging.INFO is reported. The default format for reporting messages is
“level name: message”. Therefore, the output of the code is:
INFO: Loading data…
Question 4
Select the true statements about the sqirte3 module. (Select two answers.)
- A. The sqlite3 module provides an interface compliant with the DB-API 2.0.
- B. The special name memory is used to create a database in RAM.
- C. The sqhte3 module does not support transactions.
- D. The fetchall method returns an empty list when no rows are available
Answer:
AB
Explanation:
A. The sqlite3 module in python provides an interface compliant to the DB-API 2.0. Thus, it follows a
standard performance metric that allows for consistency in database programming with python.
B. The special name 'memory' is used to create a database in RAM using the sqlite3 module. Thus,
when you use it as the name of the database file while opening a connection, it creates a temporary
database that exists only in memory.
Reference: Official Python documentation on sqlite3:
https://docs.python.org/3/library/sqlite3.html
Question 5
Which one of the following methods allows you to debug an XML tree in the xml.etree ELementTree
module?
- A. debug
- B. dump
- C. log
- D. parse
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The dump() method in the xml.etree.ElementTree module allows you to output a debug
representation of an XML tree to a file or standard output. This method is useful for analyzing the
structure of the tree and tracking down errors.
Reference:
Official
Python
documentation
on
the
ElementTree
module:
https://docs.python.org/3/library/xml.etree.elementtree.html
Question 6
Which of the following constants will be used if you do riot define the quoting argument in the writer
method provided by the csv module?
- A. csv.QUOTE_MINIMAL
- B. csv.QUOTE_NONE
- C. svQUOTE_ALL
- D. csv.QUOTE_NONNUMERIC
Answer:
A
Explanation:
If you do not define the quoting argument in the writer method provided by the csv module, the
default quoting behavior is set to QUOTE_MINIMAL. This means that fields containing special
characters such as the delimiter or newline character will be quoted, while fields that do not contain
special characters will not be quoted.
Reference:
Official
Python
documentation
on
the
csv
module:
https://docs.python.org/3/library/csv.html
Question 7
Select the true statements about the sqlite3 module. (Select two answers.)
- A. The fetchalt method returns None when no rows are available
- B. The execute method allows you to perform several queries at once
- C. The execute method is provided by the Cursor class
- D. The fetchone method returns None when no rows are available
Answer:
CD
Explanation:
C. The execute method is provided by the Cursor class
This statement is true because the execute method is one of the methods of the Cursor class in the
sqlite3 module. The Cursor class represents an object that can execute SQL statements and fetch
results from a database connection. The execute method takes an SQL query as an argument and
executes it against the database. For example, cur = conn.cursor (); cur.execute (“SELECT * FROM
table”) creates and executes a cursor object that selects all rows from a table.
D. The fetchone method returns None when no rows are available
This statement is true because the fetchone method is another method of the Cursor class in the
sqlite3 module. The fetchone method fetches the next row of a query result set and returns it as a
single tuple or None if no more rows are available. For example, row = cur.fetchone () fetches and
returns one row from the cursor object or None if there are no more rows.
Question 8
A socket object is usually created by which one of the following invocations?
- A. socket. socket (socket_domain, socket_type)
- B. socket = socket. socket (socket_number)
- C. socket = socket. socket (socket_domain, socket_type, server_address)
- D. socket = socket.socket(server address)
Answer:
A
Explanation:
A socket object is usually created using the socket() constructor provided by the socket module in
Python. The correct invocation is socket.socket(socket_domain, socket_type). This creates a new
socket object with the specified socket domain and type.
Reference:
Official
Python
documentation
on
socket
programming:
https://docs.python.org/3/library/socket.html
Question 9
Select the true statements about the following invocation:
(Select two answers.)
- A. It addresses a service deployed at localhost (the host where the code is run).
- B. It addresses a service whose timeout is set to 3000 ms.
- C. It addresses a service located at the following address local.host.com.
- D. It addresses a service listening at port 3000.
Answer:
AD
Explanation:
A. It addresses a service deployed at localhost (the host where the code is run).
This statement is true because localhost is a special hostname that refers to the local machine or the
current host where the code is run. It is equivalent to using the IP address 127.0.0.1, which is the
loopback address of the network interface. By using localhost as the hostname, the invocation
addresses a service that is deployed on the same machine as the client.
D. It addresses a service listening at port 3000.
This statement is true because port 3000 is the part of the URL that follows the colon after the
hostname. It specifies the port number where the service is listening for incoming requests. A port
number is a 16-bit integer that identifies a specific process or application on a host. By using port
3000, the invocation addresses a service that is listening at that port.
B. It addresses a service whose timeout is set to 3000 ms.
This statement is false because timeout is not a part of the URL, but a parameter that can be passed
to the requests.get () function in Python. Timeout specifies how long to wait for the server to send
data before giving up. It is measured in seconds, not milliseconds. By using timeout=3, the invocation
sets the timeout to 3 seconds, not 3000 ms.
C. It addresses a service located at the following address local.host.com.
This statement is false because local.host.com is not the same as localhost. Local.host.com is a fully
qualified domain name (FQDN) that consists of three parts: local, host, and com. It requires DNS
resolution to map it to an IP address. Localhost, on the other hand, is a special hostname that does
not require DNS resolution and always maps to 127.0.0.1. By using localhost as the hostname, the
invocation does not address a service located at local.host.com.
Reference:
: https://docs.python.org/3/library/requests.html : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Localhost :
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Port_(computer_networking)
:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fully_qualified_domain_name
Question 10
In the JSON processing context, the term serialization:
- A. names a process in which Python data is turned into a JSON string.
- B. names a process in which a JSON string is turned into Python data.
- C. refers to nothing, because there is no such thing as JSON serialization.
- D. names a process in which a JSON string is remodeled and transformed into a new JSON string
Answer:
A
Explanation:
In the JSON processing context, the term serialization: A. names a process in which Python data is
turned into a JSON string.
Serialization refers to the process of converting a data object, such as a Python object, into a format
that can be easily transferred over a network or stored in a file. In the case of JSON, serialization
refers to converting Python data into a string representation using the JSON format. This string can
be sent over a network or stored as a file, and later deserialized back into the original Python data
object.
Reference: Official Python documentation on json:
https://docs.python.org/3/library/json.html#json-
serialization
Question 11
What is ElementTree?
- A. A Python built-in module that contains functions used for creating HTML files.
- B. A Python library that contains an API used for parsing and manipulating JSON files.
- C. A Python library that contains functions and tools used for manipulating text files in GUI Programming.
- D. A Python built-in module that contains functions used for parsing and creating XML data.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
ElementTree is a Python built-in module that provides a simple and efficient API for parsing and
creating XML data. It allows you to access and manipulate XML data in a very straightforward way,
making it easy to write XML processing applications.
Reference:
Official
Python
documentation
on
ElementTree:
https://docs.python.org/3/library/xml.etree.elementtree.html
This statement is true because ElementTree is a module in the standard library of Python that
provides an API for working with XML data. The module supports parsing XML from strings or files,
creating XML trees from scratch or modifying existing ones, searching and iterating over XML
elements, and writing XML data to strings or files.
Question 12
Select the true statements about the json.-dumps () function. (Select two answers.)
- A. It returns a JSON string.
- B. It returns a Python entity.
- C. It takes a JSON string as its argument
- D. It takes Python data as its argument.
Answer:
AD
Explanation:
The json.dumps() function is used to convert a Python object into a JSON string 1. It takes Python
data as its argument, such as a dictionary or a list, and returns a JSON string.
Reference:
Official
Python
documentation
on
json.dumps():
https://docs.python.org/3/library/json.html#json.dumps
A. It returns a JSON string.
This statement is true because the json.dumps () function takes a Python object as its argument and
returns a JSON-formatted string that represents the object. For example, json.dumps ([1, 2, 3])
returns ‘[1, 2, 3]’.
D. It takes Python data as its argument.
This statement is true because the json.dumps () function accepts any Python object that can be
serialized into JSON, such as lists, dictionaries, strings, numbers, booleans, or None. For example,
json.dumps ({“name”: “Alice”, “age”: 25}) returns ‘{“name”: “Alice”, “age”: 25}’.
Question 13
Select the true statement about the socket. gaierror exception.
- A. It is raised when a timeout occurs on a socket.
- B. It is raised when a system function returns a system-related error.
- C. It is raised when an address-related error caused by the repr () function occurs.
- D. It is raised when an address-related error caused by the getaddrinfo () and getnameinfo () functions occurs.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The socket.gaierror exception is raised when an address-related error caused by the getaddrinfo()
and getnameinfo() functions occurs. These functions are used to translate hostnames to IP addresses
and vice versa, and the gaierror exception is raised if they fail to perform this translation.
Reference:
Official
Python
documentation
on
socket.gaierror:
https://docs.python.org/3/library/socket.html#socket.gaierror
Question 14
Select the true statements about sockets. (Select two answers)
- A. A socket is a connection point that enables a two-way communication between programs running in a network.
- B. A socket is always the secure means by which computers on a network can safely communicate, without the risk of exposure to an attack
- C. A socket is a connection point that enables a one-way communication only between remote processes
- D. A socket can be used to establish a communication endpoint for processes running on the same or different machines.
Answer:
AD
Explanation:
A. A socket is a connection point that enables a two-way communication between programs running
in a network.
This statement is true because a socket is a software structure that serves as an endpoint for sending
and receiving data across a network. A socket is defined by an application programming interface
(API) for the networking architecture, such as TCP/IP.
A socket can be used to establish a
communication channel between two programs running on the same or different network nodes12
.
B. A socket is always the secure means by which computers on a network can safely communicate,
without the risk of exposure to an attack.
This statement is false because a socket by itself does not provide any security or encryption for the
data transmitted over the network. A socket can be vulnerable to various types of attacks, such as
eavesdropping, spoofing, hijacking, or denial-of-service.
To ensure secure communication, a socket
can use additional protocols or mechanisms, such as SSL/TLS, SSH, VPN, or firewall3
.
C. A socket is a connection point that enables a one-way communication only between remote
processes.
This statement is false because a socket can enable both one-way and two-way communication
between processes running on the same or different network nodes. A socket can be used for
connection-oriented or connectionless communication, depending on the type of protocol used.
For
example, TCP is a connection-oriented protocol that provides reliable and bidirectional data transfer,
while UDP is a connectionless protocol that provides unreliable and unidirectional data transfer12
.
D. A socket can be used to establish a communication endpoint for processes running on the same or
different machines.
This statement is true because a socket can be used for inter-process communication (IPC) within a
single machine or across different machines on a network.
A socket can use different types of
addresses to identify the processes involved in the communication, such as IP address and port
number for network sockets, or file name or path for Unix domain sockets12
.
Reference:
1:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Network_socket 2:
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/socket-in-
computer-network/ 3
:
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/what-is-a-network-socket-computer-
networks
Question 15
Select the true statements about the connection-oriented and connectionless types of
communication. (Select two answers.)
- A. In the context of TCP/IP networks, the communication side that initiates a connection is called the client, whereas the side that answers the client is called the server
- B. Connectionless communications are usually built on top of TCP
- C. Using walkie-talkies is an example of a connection-oriented communication
- D. A phone call is an example of a connection-oriented communication
Answer:
AD
Explanation:
A. In the context of TCP/IP networks, the communication side that initiates a connection is called the
client, whereas the side that answers the client is called the server.
This statement is true because TCP/IP networks use a client-server model to establish connection-
oriented communications. The client is the device or application that requests a service or resource
from another device or application, which is called the server. The server responds to the client’s
request and provides the service or resource. For example, when you browse a website using a web
browser, the browser acts as a client and sends a request to the web server that hosts the
website.
The web server acts as a server and sends back the requested web page to the browser1
.
B. Connectionless communications are usually built on top of TCP.
This statement is false because TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) is a connection-oriented protocol
that requires establishing and terminating a connection before and after sending data.
Connectionless communications are usually built on top of UDP (User Datagram Protocol), which is a
connectionless protocol that does not require any connection setup or teardown. UDP simply sends
data packets to the destination without checking if they are received or not
.
C. Using walkie-talkies is an example of a connection-oriented communication.
This statement is false because using walkie-talkies is an example of a connectionless
communication. Walkie-talkies do not establish a dedicated channel or connection between the
sender and receiver before transmitting data. They simply broadcast data over a shared frequency
without ensuring that the receiver is ready or available to receive it.
The sender does not know if the
receiver has received the data or not3
.
D. A phone call is an example of a connection-oriented communication.
This statement is true because a phone call is an example of a connection-oriented communication.
A phone call requires setting up a circuit or connection between the caller and callee before
exchanging voice data. The caller and callee can hear each other’s voice and know if they are
connected or not.
The phone call also requires terminating the connection when the conversation is
over4
.
Reference:
1:
https://www.techtarget.com/searchnetworking/definition/client-server 2:
https://www.javatpoint.com/connection-oriented-vs-connectionless-service 3
:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Walkie-talkie
: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Telephone_call
A is true because in the context of TCP/IP networks, the communication side that initiates a
connection is called the client, and the side that answers the client is called the server. This is the
basis for establishing a connection-oriented communication.
D is true because a phone call is an example of a connection-oriented communication. Like TCP/IP, a
phone call establishes a connection between two devices (in this case, two phones) before
communication can occur.
A is true because in the context of TCP/IP networks, the communication side that initiates a
connection is called the client, and the side that answers the client is called the server. This is the
basis for establishing a connection-oriented communication.
D is true because a phone call is an example of a connection-oriented communication. Like TCP/IP, a
phone call establishes a connection between two devices (in this case, two phones) before
communication can occur.
B is false because connectionless communications are usually built on top of UDP, not TCP. UDP is a
connectionless protocol that does not establish a connection before sending data.
C is false because using walkie-talkies is an example of a connectionless communication. Walkie-
talkies do not establish a connection before communication begins, and messages are simply
broadcasted to all devices within range.
Here is a sample code in Python using the socket module to create a TCP server and client to
demonstrate the connection-oriented communication:
Server-side code:
import socket
HOST = '127.0.0.1'
PORT = 8080
with socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) as s:
s.bind((HOST, PORT))
s.listen()
conn, addr = s.accept()
with conn:
print('Connected by', addr)
while True:
data = conn.recv(1024)
if not data:
break
conn.sendall(data)
Client-side code:
import socket
HOST = '127.0.0.1'
PORT = 8080
with socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) as s:
s.connect((HOST, PORT))
s.sendall(b'Hello, world')
data = s.recv(1024)
print('Received', repr(data))
The server listens for incoming connections on port 8080, and when a connection is established, it
prints the address of the client that has connected. The server then continuously receives data from
the client and sends it back to the client until the connection is closed.
The client establishes a connection with the server and sends the message "Hello, world" encoded as
bytes. It then waits for a response from the server and prints the data it receives.