oracle 1Z0-820 Exam Questions
Questions for the 1Z0-820 were updated on : Jun 28 ,2025
Page 1 out of 9. Viewing questions 1-15 out of 131
Question 1
Identify the two security features incorporated in the Oracle Solaris 11 Cryptographic Framework.
- A. Layer 5 IP address encryptions
- B. Internet protocol security
- C. Diffie-Kerberos coaxial key encryption
- D. Signed cryptographic plugins (providers)
- E. Kernel support for signed antivirus plugins
Answer:
D, E
Explanation:
The framework enables providers of cryptographic services to have their services used by many
consumers in the Oracle Solaris operating system. Another name for providers is plugins. The
framework allows three types of plugins:
* User-level plugins - Shared objects that provide services by using PKCS #11 libraries, such as
pkcs11_softtoken.so.1.
* Kernel-level plugins - Kernel modules that provide implementations of cryptographic algorithms in
software, such as AES.
Many of the algorithms in the framework are optimized for x86 with the SSE2 instruction set and for
SPARC hardware.
* Hardware plugins - Device drivers and their associated hardware accelerators. The Niagara chips,
the ncp and n2cp device drivers, are one example. A hardware accelerator offloads expensive
cryptographic functions from the operating system. The Sun Crypto Accelerator 6000 board is one
example.
Reference: Oracle Solaris Cryptographic Framework
http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E19963-01/html/821-1456/scf-10.html
Question 2
Review the ZFS dataset output that is displayed on your system:
Which four correctly describe the output?
- A. /data/file4 has been added.
- B. The link /data/file3 has been added.
- C. /data/file3 has been renamed to /data/file13.
- D. /data/file4 has been modified and is now larger.
- E. /data/file1 has been deleted.
- F. /data/file1 has been modified and is now smaller.
- G. /data/file5 has been modified.
- H. /data/file3 (a link) has been removed.
Answer:
A, C, E, G
Explanation:
A: + Indicates the file/directory was added in the later dataset
C: R Indicates the file/directory was renamed in the later dataset
E: - Indicates the file/directory was removed in the later dataset
G: M Indicates the file/directory was modified in the later dataset
Note: Identifying ZFS Snapshot Differences (zfs diff)
You can determine ZFS snapshot differences by using the zfs diff command.
The following table summarizes the file or directory changes that are identified by the zfs diff
command.
File or Directory Change Identifier
* File or directory is modified or file or directory link changed
M
* File or directory is present in the older snapshot but not in the newer snapshot
* File or directory is present in the newer snapshot but not in the older snapshot
+
* File or directory is renamed
R
Question 3
Which five statements describe options available for installing the Oracle Solaris 11operating system
using the installation media?
- A. You can perform a text or LiveCD installation locally or over the network.
- B. The text Installer does not install the GNOME desktop. The GNOME desktop package must he added after you have installed the operating system.
- C. The LiveCD Installation cannot be used to install multiple instances of Oracle Solaris.
- D. The LiveCD installer cannot be used if you need to preserve a specific Solaris Volume Table of Contents (VTOC) slice in your current operating system.
- E. The LiveCD Installer is for x86 platforms only.
- F. The GUI installer cannot be used to upgrade your operating system from Solaris 10.
- G. If you are installing Oracle Solaris 11 on an x86-based system that will have more than one operating system installed in it, you cannot partition your disk during the installation process.
- H. The LiveCD installer can be used for SPARC or x86 platforms.
Answer:
BCDEF
Explanation:
A: If the network is setup to perform automated installations, you can perform a text installation over
the network by setting up an install service on the network and selecting a text installation when the
client system boots.
B: After a fresh install of Solaris 11 express, only the console mode is activated.
To add Gnome, simply do :
$ sudo pkg install slim_install
This will install additional packages that are not installed by default.
D: The text installer advantages over the GUI installer include:
* In addition to modifying partitions, the text installer enables you to create and modify VTOC slices
within the Solaris partition.
F: How do I upgrade my Solaris 10 or lower systems to Solaris 11?
Unfortunately, you CAN'T. There is no direct upgrade installer or other tool that will allow you to
upgrade from earlier releases of Solaris to Solaris 11. This is primarily due to the vast changes in the
packaging mechanism in Solaris 10.
Incorrect answers:
E: Both installers can be used to install Oracle Solaris on the x86 platform. The text installer can also
be used to install Oracle Solaris on the SPARC platform.
G: Both installers enable you to select, create, or modify disk partitions during an installation.
H: Both installers can be used to install Oracle Solaris on the x86 platform. The text installer can also
be used to install Oracle Solaris on the SPARC platform.
Reference: Oracle Solaris 11 Information Library, Comparing Installation Options
Question 4
When setting up Automated Installer (AI) clients, an interactive tool can be used to generate a
custom system configuration profile. The profile will specify the time zone, data and time, user and
root accounts, and name services used for an AI client installation. This interactive tool will prompt
you to enter the client information and an SC profile (XML) will be created.
Which interactive tool can be used to generate this question configuration?
- A. sys-unconfig
- B. installadm set-criteria
- C. sysconfig create-profile
- D. installadm create-profile
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Use the installadm set-criteria command to update the client criteria associated with an AI manifest
that you already added to a service using installadm add-manifest.
Use the installadm add-manifest command to add a custom AI manifest to an install service.
The value of manifest is a full path and file name with .xml extension. The manifest file contains an AI
manifest (installation instructions). The manifest file can also reference or embed an SC manifest
(system configuration instructions).
Incorrect answers:
A: The sys-unconfig command is used to restore a system's configuration to
an "as-manufactured" state, ready to be reconfigured again.
C: You can use the sysconfig create-profile command to create a new system configuration profile.
Thesysconfigcommand affects all functional groupings in the Solaris instance.
D: Use the installadm create-profile command to add a system configuration profile to an install
service. The create-profile subcommand validates profiles before adding them to the install service.
Specify criteria so that appropriate clients select that configuration profile. If no criteria are specified,
all clients use this profile.
Question 5
Review the zonestat command:
zonestate - q physical - memory -R high -z -p -p zones 10 24h 60m
Select the option that correctly describes the information that is displayed by this command.
- A. It is a sample of dbzones physical memory usage taken every hour over a 24-hour period. Only the top 10 samplings of peak memory usage are displayed. All other utilization data is eliminated.
- B. It is a sample of dbzones CPU, virtual memory, and networking utilization. Physical memory is executed from the report. The sampling is taken every 10 minutes over a 24-hour period and peak utilization id displayed each hour.
- C. It is a sample of dbzones CPU, virtual memory, and networking utilization. Physical memory is executed from the report. The sampling is taken every 10 minutes over a 24-hour period and displayed each hour.
- D. It is a sample of dbzones physical memory usage taken every 10 seconds and 24-hour period. Only peak virtual memory usage and CPU utilization are displayed each hour. All other Utilization data is eliminated.
- E. It is a sample of dbzones physical memory usage taken every 10 seconds and 24-hour period. Only peak memory usage is displayed each hour. All other utilization data is eliminated.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
* (Not A, B, C): interval (here 10 seconds): Specifies the length in seconds to pause between each
interval report.
* duration (here 24 h)
* -R report[,report] (here high)
Print a summary report.
high Print a summary report detailing the highest usage of each resource and zone during any
interval of thezonestatutility invocation.
Note: The zonestat utility reports on the cpu, memory, and resource control utilization of the
currently running zones. Each zone's utilization is reported both as a percentage of system resources
and the zone's configured limits.
The zonestat utility prints a series of interval reports at the specified interval. It optionally also prints
one or more summary reports at a specified interval.
The default output is a summary of cpu, physical, and virtual memory utilization. The -r option can be
used to choose detailed output for specific resources.
Question 6
You are configuring NFS on a server. Select the two statements that are true.
- A. Resources listed in /etc/dfs/dfstab are automatically shared on boot up.
- B. A directory cannot be shared if a subdirectory below it is already shared.
- C. Renaming a share created with the zfs set share command is not supported.
- D. NFS and SMB protocols cannot be used simultaneously to share the same directory.
Answer:
A, C
Explanation:
A: ZFS can automatically share file systems by setting the sharenfs property. Using this property, you
do not have to modify the /etc/dfs/dfstab file when a new file system is shared. The sharenfs
property is a comma-separated list of options to pass to the share command. The value on is an alias
for the default share options, which provides read/write permissions to anyone. The value off
indicates that the file system is not managed by ZFS and can be shared through traditional means,
such as the /etc/dfs/dfstab file. All file systems whose sharenfs property is not off are shared during
boot.
Incorrect answers:
D: A share can define options for both NFS and SMB sharing.
Question 7
You have already generated a 256-bit AES raw key and named the keystore file /mykey. You need to
use the key to create an encrypted file system.
Which command should you use to create a ZFS encrypted file system named pool1/encrypt using
the /mykey keystore?
- A. zfs create - o encryption = /mykey pool1/encrypt
- B. zfs create - o encryption = 256-ccm - o keysource = raw, file : ///my key pool1/encrypt
- C. zfs create - o encryption = AES keysource = /mykey pool1/encrypt
- D. zfs create - o encryption = on keystore = /mykey pool1/encrypt
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Example: Encrypting a ZFS File System by Using a Raw Key
In the following example, an aes-256-ccm encryption key is generated by using the pktool command
and is written to a file, /cindykey.file.
# pktool genkey keystore=file outkey=/cindykey.file keytype=aes keylen=256
Then, the /cindykey.file is specified when the tank/home/cindy file system is created.
# zfs create -o encryption=aes-256-ccm -o keysource=raw,file:///cindykey.file tank/home/cindys
Reference: Oracle Solaris ZFS Administration Guide, Examples of Encrypting ZFS File Systems
Question 8
You need to set up an Oracle Solaris 11 host as an iSCSI target so that the host's disk can be accessed
over a storage network. The disk device is c3t4d0.
Which six options describe the steps that need to be taken on this host to enable an iSCSI target?
- A. Create a ZFS file system named iscsi/target.
- B. Create a zpool named iscsi with disk device c3t4d0
- C. Create zfs volume named iscsi/target.
- D. Use the stmfadm command to create a LUN using /dev/zvol/rdsk/iscsi/target.
- E. Use the stmfadm command to create a LUN using iscsi/target.
- F. Use the stmfadm command to make the LUN viewable.
- G. Use the stmfadm command to make the volume viewable.
- H. Enable the svc:/network/iscsi/target:default Service.
- I. Use the itadm command to create the iSCSI target.
Answer:
B, C, D, F, H, I
Explanation:
How to Create an iSCSI LUN
The following steps are completed on the system that is providing the storage device.
1.Create a ZFS storage pool.
Example: target# zpool create sanpool mirror c2t3d0 c2t4d0
(C)2. Create a ZFS volume to be used as a SCSI LUN.
(D)3. Create a LUN for the ZFS volume.
Example:
target# stmfadm create-lu /dev/zvol/rdsk/sanpool/vol1
Logical unit created: 600144F0B5418B0000004DDAC7C10001
4. Confirm that the LUN has been created.
Example
target# stmfadm list-lu
LU Name: 600144F0B5418B0000004DDAC7C10001
(F) 5. Add the LUN view.
This command makes the LUN accessible to all systems.
target# stmfadm add-view 600144F0B5418B0000004DDAC7C10001
How to Create the iSCSI Target
This procedure assumes that you are logged in to the local system will contains the iSCSI target.
Note: The stmfadm command manages SCSI LUNs. Rather than setting a special iSCSI property on the
ZFS volume, create the volume and use stmfadm to create the LUN.
(H) 1. Enable the iSCSI target service.
target# svcadm enable -r svc:/network/iscsi/target:default
(I) 2. Create the iSCSI target.
target# itadm create-target
Reference: Oracle Solaris Administration: Devices and File Systems, Configuring iSCSI Devices With
COMSTAR
Question 9
Identify the Automated Installer’s (AI) equivalent to jumpStart’s finish scripts and sysidcfg files.
- A. Manifest files
- B. SMF system configuration profile files
- C. Installadm create - client
- D. IPS software package repository
- E. installadm create-service
- F. svccfg - s application/pkg/server setprop sysidcfg
Answer:
B
Explanation:
ComparingsysidcfgFile Keywords to System Configuration Profile Directives
The following table comparessysidcfgfile keywords with example AI system configuration profile
specifications.
sysidcfgFile Keyword
System Configuration Profile Directives
Etc.
Reference: http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E23824_01/html/E21799/config-1.html
Question 10
You need to update an OS image on a client. The pkg publishers command displays the wrong
publisher with the wrong update:
PUBLISHER
TYPE
STATUS URI
Solaris
origin
online
http://pkg.oracle.com/solaris/release
The update is available on the updated publisher:
PUBLISHER
TYPE
STATUS URI
Solaris
origin
online
http://sysA.example.com
Select the option that describes the procedure used to update the OS image on the system from the
updated publisher.
- A. Copy the repository from the ISO image onto the local client. Configure the repository on the client by using the svccfg - s command so that the Solaris publisher is connected to the new repository. Refresh the application/pkg/server service. Issue the pkgrepo refresh command to refresh the repository catalog
- B. Configure the publisher on the client using the svcfg - s command so that the Solaris publisher is connected to the repository at http://sysA.example.com Refresh the application/pkg/server service. Issue the pkgrepo refresh command to repository catalog
- C. Use the pkg set-publisher command to change the URL of the publisher Solaris to http://sysA.example.com. Issue the pkg update command to update the OS image.
- D. Add the new publisher http://sysA.example.com Solaris Use the pkg set-publisher command to set the publisher search order and place http://sysA.example.com of http://pkg.oracle.com/solaris/release Issue the pkg publisher command to view the publishers. Set the new publisher to sticky. Issue the pkg update command to update the OS image.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
You can use the pkg set-publisher command to change a publisher URI.
Changing a Publisher Origin URI
To change the origin URI for a publisher, add the new URI and remove the old URI. Use the -g option
to add a new origin URI. Use the -G option to remove the old origin URI.
# pkg set-publisher -g http://pkg.example.com/support \
-G <http://pkg.example.com/release example.com>
Note: You can use either the install or update subcommand to update a package.
The install subcommand installs the package if the package is not already installed in the image. If
you want to be sure to update only packages that are already installed, and not install any new
packages, then use the update subcommand.
Reference: Oracle Solaris 11 Express Image Packaging System Guide, Managing Package Publishers
Question 11
alice is a user account used by Alice on a Solaris 11 system.
sadmin is a role account on the same system.
Your task is to add the command /usr/sbin/cryptoadm to the Network management profile, so that
Alice can execute it, while assuming the sadmin role.
Select the three activities necessary to accomplish this.
- A. To the file /etc/security/prof_attr, add the line: Network Management: solaris:cmd:RO::/usr/sbin/cryptoadm:euid=0
- B. To the file /etc/security/auth_attr, add the line: Network Management: solaris:cmd:RO::/usr/sbin/cryptoadm:euid=0
- C. To the file /etc/security/exec_attr.d/local-entriies, add the line: Network Management: solaris:cmd:RO::/usr/sbin/cryptoadm:euid=0
- D. Run the roles alice to ensure that alice may assume the role sadmin.
- E. Run the command profiles sadmin to ensure that the role sadmin includes the network Management profile.
- F. Run the command profiles alice to ensure that the Alice has permissions to access the Network management profile.
- G. Run the command profiles Network management to ensure that the Network management profile includes the sadmin role.
Answer:
C, D, G
Explanation:
C: /etc/security/exec_attr is a local database that specifies
the execution attributes associated with profiles. The
exec_attr file can be used with other sources for execution
profiles, including the exec_attr NIS map and NIS+ table.
A profile is a logical grouping of authorizations and com-
mands that is interpreted by a profile shell to form a
secure execution environment.
Incorrect answers:
A: etc/security/prof_attr is a local source for execution profile names, descriptions, and other
attributes of execution profiles. The prof_attr file can be used with other profile sources, including
the prof_attr NIS map.
B: /etc/security/auth_attr is a local source for authorization names and descriptions. The auth_attr
file can be used with other authorization sources, including the auth_attr NIS map and NIS+ table.
An authorization is a right assigned to users that is checked by certain privileged programs to
determine whether users can execute restricted functionality.
Reference: man exec_attr
Question 12
Select the two statements that correctly describe the operation of NWAM.
- A. If a location is explicitly enabled, it remains active until explicitly changed.
- B. Wireless security keys can be configured by using the nwammgr command.
- C. NWAM stores profile information in /etc/ipadm/ipadm.conf and /etc/dladm/datalink.conf.
- D. Multiple locations may be automatically activated in systems with multiple network interface cards.
- E. Interface NCU Properties "float" and are automatically attached to the highest priority Link NCU Property.
- F. If the DefaultFixed NCP is enabled, persistent configuration, stored in /etc/ipadm.conf and /etc/dladm/datalink.conf is used.
Answer:
A, D
Explanation:
A: Conditional and system locations can be manually
activated, which means that the location remains active until explicitly disabled.
D: A location comprises certain elements of a network configuration, for example a name service
and firewall settings, that are applied together, when required. You can create multiple locations
for various uses. For example, one location can be used when you are connected at the office by
using the company intranet. Another location can be used at home when you are connected to
the public Internet by using a wireless access point. Locations can be activated manually or
automatically, according to environmental conditions, such as the IP address that is obtained
by a network connection.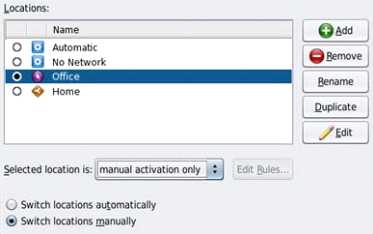
Incorrect answers:
Note: The Network Auto-Magic (NWAM) feature simplifies basic network configuration by
automatically addressing basic Ethernet and WiFi configurations, such as connecting to your wired or
wireless network at startup and displaying notifications about the status of your currently active
network connection from the desktop. NWAM is also designed to simplify some of the more complex
networking tasks, such as the creation and management of system-wide network profiles, for
example, the configuration of name services, IP Filter and IP Security (IPsec).
Reference: Oracle Solaris Administration: Network Interfaces and NetworkVirtualization, Activating
and Deactivating Profiles
Reference: Oracle Solaris Administration: Network Interfaces and NetworkVirtualization,Creating and
Managing Locations
Question 13
On server A, you enter the following command to add a static route to serverA
route -p add -host 192.168.1.101 192.168.1.101 -static
What is the purpose of this command?
- A. to temporarily bypass IP Filter rules
- B. to specify an IPMP target IP address to in.mpathd
- C. to specify routing to an adjacent network when in.rdisc is not used
- D. to specify routing to an adjacent network when in.routed is not used
- E. to ensure the IP address for serverB is not flushed from the ARP cache
- F. to optimize link aggregation using a direct connection between two systems
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Note: # route -p add -host destination-IP gateway-IP -static
wheredestination-IPandgateway-IPare IPv4 addresses of the host to be used as a target.
For example, you would type the following to specify the target system 192.168.10.137, which is on
the same subnet as the interfaces in IPMP group itops0:
$ route -p add -host 192.168.10.137 192.168.10.137 -static
This new route will be automatically configured every time the system is restarted. If you want to
define only a temporary route to a target system for probe-based failure detection, then do not use
the -p option.
Question 14
Before booting test zone a non-global zone, you want to connect to the zones console so that you
can watch the boot process.
Choose the command used to connect to testzones console.
- A. zoneadm -C testzone
- B. zoneadm -console testzone
- C. zlogin - z testzone console
- D. zlogin - z testzone - C
- E. zlogin -C testzone
- F. zoneadm - testzone - c
Answer:
E
Explanation:
The following options are supported:
-C
Connects to the zone console. Connects to the zone console.
Note:
After you install a zone, you must log in to the zone to complete its application environment. You
might log in to the zone to perform administrative tasks as well. Unless the-Coption is used to
connect to the zone console, logging in to a zone usingzloginstarts a new task. A task cannot span
two zones
Incorrect answers:
B: No option -console.
C, D: No option -z.
Reference: man zlogin
Question 15
Consider the following rule file for use with the Basic Audit Reporting Tool (BART).
CHECK all
IGNORE dirmtime
/etc/security
/etc/notices
IGNORE contents
/export/home
IGNORE mtime size contents
/var
CHECK
You are using BART to detect inappropriate changes to the file system.
Identify the two correct statements describing the attributes recorded.
- A. /var/dhcp Attribute: size uid gid mode acl
- B. /etc/hosts Attributes: size uid gid mode acl intime dest
- C. /var/spool/mqueue Attribute: size uid gid mode acl dirmtime
- D. /etc/security/exec_attr Attribute: size uid mode acl mtime devnode
- E. /export/home/kate/.profile Attributes: uid gid mode acl dirmtime
- F. /export/home/rick/.profile Attributes: size uid gid mode acl mtime contents
Answer:
D, F
Explanation:
D: According to line /etc/security
F: According to line /export/home
Not E: According to line IGNORE dirmtime
Note: In default mode, the bart compare command, as shown in the following example, checks all
the files installed on the system, with the exception of modified directory timestamps (dirmtime):
CHECK all
IGNORE dirmtime
Note 2: The Basic Audit Reporting Tool (BART) feature of Oracle Solaris enables you to
comprehensively validate systems by performing file-level checks of a system over time. By creating
BART manifests, you can easily and reliably gather information about the components of the
software stack that is installed on deployed systems.
BART is a useful tool for integrity management on one system or on a network of systems.
Reference: Oracle Solaris Administration: Security Services, BART Manifests, Rules Files, and Reports
(Reference)