nokia 4A0-AI1 Exam Questions
Questions for the 4A0-AI1 were updated on : Feb 20 ,2026
Page 1 out of 6. Viewing questions 1-15 out of 80
Question 1
Which of the following is the proper Postman syntax to access an Intent based off an Intent Type
named port-ethernet-intent and with target comportment 10.10.10.1 and 1/1/2?
A)
B)
C)
D)
- A. Option A
- B. Option B
- C. Option C
- D. Option D
Answer:
C
Question 2
What happens if you select "Modify" under "Behavior" in the WebUI and successfully modify
anintent?
- A. The Intent is updated in the Intent Manager database and no other actions are performed.
- B. The Intent is updated in the Intent Manager database and compared with the configuration on the target node.
- C. The Intent is updated in the Intent Manager database and synchronized.
- D. The version number of the Intent is increased and multiple copies of the Intent are stored In the Intent Manager.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
According to the NSP Intent Manager Application Help12, if you select “Modify” under “Behavior” in
the WebUI and successfully modify an intent, the intent is updated in the Intent Manager database
and compared with the configuration on the target node. This will change the intended configuration
for the audit and synchronize operations
Question 3
An Intent Type has to be in which state for Intent Manager to provision a request?
- A. Phased-out
- B. Draft
- C. Released
- D. Draft or Released
Answer:
C
Explanation:
According to the NSP Intent Manager Application Help, an intent type has to be in Released state for
Intent Manager to provision a request. An intent type can be in Draft, Released or Phased-out state.
A Draft state means that the intent type is under development and cannot be used for
provisioning. A Phased-out state means that the intent type is no longer supported and cannot be
used for provisioning
Question 4
Which of the following is NOT a category of files found in the Intent-type resources directory?
- A. Framework files
- B. Configuration files
- C. API services files
- D. Template files
Answer:
A
Explanation:
According to the NSP Intent Manager Application Help1, an intent type consists of four components:
general metadata, target, YANG model and script. The resources component is used to store files that
are required by the script component1. Therefore, A. Framework files is NOT a category of files found
in the intent-type resources directory.
Question 5
Which of the following files contains helper functions that can be leveraged by the scripts of many
different Intent types?
- A. Framework
- B. Mapping script
- C. Tern plate-mapping
- D. Configuration template
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The Framework file contains helper functions that can be leveraged by the scripts of many different
Intent types.
The Framework file is a JavaScript file that provides common utility functions for Intent operations. It
is located in the /opt/nokia/nsp/intent/scripts directory on the NSP server. It can be imported by
other script files using the require() function.
For example, a Framework file could contain:
function getNfmpTemplate(templateName) { // logic for getting an NFM-P template by name }
function getMdTemplate(templateName) { // logic for getting an MD template by name }
Question 6
Which of the following files contains all the back end implementations required for Intent
configurations to be performed?
- A. script-content.js
- B. meta-info.json
- C. yang-patch.json
- D. util.js
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The script-content.js file contains all the back end implementations required for Intent configurations
to be performed.
The script-content.js file is a JavaScript file that defines the logic for creating, updating, deleting and
synchronizing intents. It also defines the validation rules and error handling mechanisms for intents.
For example, a script-content.js file could contain:
function createIntent(intent) { // logic for creating an intent }
function updateIntent(intent) { // logic for updating an intent }
Question 7
Whatare the main sections of an abstract YANG module file?
- A. Arguments and statements
- B. Structures and statements
- C. Arguments and leaves
- D. Structure and arguments
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The main sections of an abstract YANG module file are arguments and statements.
An argument is a string that provides additional information about a statement. A statement is a
keyword followed by an argument and optionally enclosed by braces ({ }) containing substatements.
For example, an abstract YANG module file could start with:
module ibn-intent { namespace “urn:nokia.com:ibn:intent”; prefix ibn;
This defines the module name, namespace and prefix as arguments for the module, namespace and
prefix statements respectively.
Question 8
Which of the following can only be viewed by making a RESTCONF call to query an existing intent?
- A. abstract YANG model
- B. ibn:intent model
- C. template-mappings
- D. metadata
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The template-mappings can only be viewed by making a RESTCONF call to query an existing intent.
The template-mappings are a set of key-value pairs that map the abstract YANG model attributes to
concrete NFM-P templates and parameters. They are not exposed in the UI or the ibn:intent model,
but they are stored internally in the NSP database.
For example, a template-mapping could be: /network=IP/service=VPN -> nsp-ip-vpn-template.
Question 9
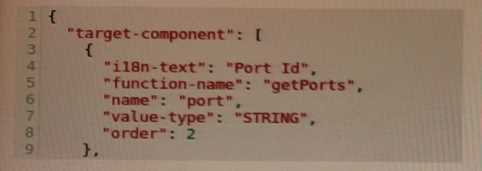
Based on the exhibit, which attribute of the target-component determines the component name
displayed in the UI?
- A. i18n-text
- B. function-name
- C. name
- D. order
Answer:
A
Explanation:
According to the NSP Network Services Platform Release 20.9 User Guide1, the attribute of the
target-component that determines the component name displayed in the UI is i18n-text.
The i18n-text attribute specifies a key for a localized text string that is displayed as a label for this
component in the UI. The actual text string is retrieved from a resource bundle file based on the
user’s locale.
For example, if i18n-text is “Port Id”, then the UI will display “Port Id” as the component name.
Question 10
Which character is used to separate the attributes of a Target with multiple attributes?
- A. -
- B. /
- C. #
- D. \
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The character used to separate the attributes of a Target with multiple attributes is /.
For example, a Target with multiple attributes could be: /network=IP/service=VPN.
Question 11
Which tab(s) does the metadata in the meta-info.Json file appear in the "Edit Intent Type" window of
the Intent Manager UI?
- A. Target
- B. Resources
- C. General and Resources
- D. General and Target
Answer:
C
Explanation:
According to the NSP Network Services Platform Release 20.6 Intent Manager Application Help1, an
intent type consists of four components: general metadata, target, YANG model and script. The
metadata in the meta-info.Json file appears in the General and Resources panels of the Edit Intent
Type window
Question 12
What are the possible data types capable of being assigned to the value type attributes of the target-
component?
- A. String
- B. Boolean
- C. Boolean and String
- D. Number and String
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The value type attributes of the target-component can be assigned either a boolean or a string data
type. The boolean data type can be used to indicate whether a certain attribute is enabled or not,
while the string data type can be used to store textual information. Numbers and other data types
are not supported.
Question 13
Which of the following is the master configuration that is synchronized with the network
configuration and is stored in the database as the source of truth?
- A. Intent Type
- B. Intent
- C. Metadata
- D. YANG module
Answer:
B
Explanation:
An Intent is the master configuration that is synchronized with the network configuration and is
stored in the database as the source of truth. Intent Types define the type of Intent, such as a
network service or a configuration change, while Metadata is used to store additional information
about the Intent, such as its version or author. YANG modules are used to define the data model for a
particular technology.
Question 14
Which of the following is NOT an Intent Type life-cycle state?
- A. Draft
- B. Released
- C. Phased-Out
- D. Created
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Intent Types have four life-cycle states: Draft, Released, Phased-Out, and Deleted. The Created state
is not a life-cycle state for Intent Types; instead, it is an intermediate state used to create an Intent
before it is moved to a life-cycle state.
Question 15
Which of the following operations CANNOT be performed on an Intent?
- A. Synchronize
- B. Audit
- C. Phase-out
- D. Mark as misaligned
Answer:
C
Explanation:
some of the operations that can be performed on an Intent are:
Create
Synchronize
Audit
Update
Delete
Therefore, based on this source, the answer that CANNOT be performed on an Intent is C. Phase-out.