netskope NSK100 Exam Questions
Questions for the NSK100 were updated on : Feb 20 ,2026
Page 1 out of 4. Viewing questions 1-15 out of 60
Question 1
You have an issue with the Netskope client connecting to the tenant.
In this scenario, what are two ways to collect the logs from the client machine? (Choose two.)
- A. from the Netskope client Ul About page
- B. from the command line using the nsdiag command
- C. from the Netskope client system tray icon
- D. from the Netskope client Ul Configuration page
Answer:
A, B
Explanation:
To collect the logs from the client machine when you have an issue with the Netskope client
connecting to the tenant, two ways that you can use are: from the Netskope client UI About page and
from the command line using the nsdiag command. From the Netskope client UI About page, you can
click on the “Collect Logs” button to generate a zip file containing all the relevant logs and
configuration files from the client machine. You can then send this zip file to Netskope support for
troubleshooting. From the command line, you can use the nsdiag command with various options to
collect different types of logs and diagnostic information from the client machine. For example, you
can use nsdiag -l to collect all logs, nsdiag -c to collect configuration files, nsdiag -t to collect traffic
statistics, etc. You can also use nsdiag -h to see all available options and usage instructions. You can
then send the output files to Netskope support for troubleshooting. Reference:
Netskope Client
Configuration overviewInstall and Test the Client - Netskope Knowledge Portal
Question 2
When would an administrator need to use a tombstone file?
- A. You use a tombstone file when a policy causes a file download to be blocked.
- B. You use a tombstone file when a policy causes a publicly shared file to be encrypted.
- C. You use a tombstone file when the policy causes a file to be moved to quarantine.
- D. You use a tombstone file when a policy causes a file to be moved to legal hold.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
A tombstone file is a placeholder file that replaces the original file when it is moved to quarantine by
a Netskope policy. The tombstone file contains information about the original file, such as its name,
size, type, owner, and the reason why it was quarantined. The tombstone file also provides a link to
the Netskope UI where the administrator or the file owner can view more details about the incident
and take appropriate actions, such as restoring or deleting the file. The purpose of using a tombstone
file is to preserve the metadata and location of the original file, as well as to notify the users about
the quarantine action and how to access the file if needed. Reference:
Threat Protection - Netskope
Knowledge PortalNetskope threat protection - Netskope
Question 3
How do you provision users to your customer's Netskope tenant? (Choose two.)
- A. Use Microsoft Intune.
- B. Use the AD Connector.
- C. Use SCIM.
- D. Use the Directory Importer.
Answer:
B, D
Explanation:
To provision users to your customer’s Netskope tenant, two methods that you can use are: use the
AD Connector and use SCIM. The AD Connector is a tool that allows you to synchronize users and
groups from your Active Directory (AD) domain to your Netskope tenant. The AD Connector runs as a
Windows service on a machine that has access to your AD domain controller. The AD Connector
periodically queries your AD domain for any changes in users and groups and updates them in your
Netskope tenant accordingly. The AD Connector also supports filtering users and groups based on
attributes or organizational units (OUs). SCIM stands for System for Cross-domain Identity
Management, which is a standard protocol for managing user identities across different applications
and services. SCIM allows you to provision users and groups from your identity provider (IdP), such
as Azure AD or Okta, to your Netskope tenant using APIs. SCIM also supports creating, updating,
deleting, and searching users and groups in your Netskope tenant based on your IdP’s
configuration. Reference:
Netskope AD ConnectorUser Provisioning with Azure AD
Question 4
You want to block access to sites that use self-signed certificates. Which statement is true in this
scenario?
- A. Certificate-related settings apply globally to the entire customer tenant.
- B. Certificate-related settings apply to each individual steering configuration level.
- C. Certificate-related settings apply to each individual client configuration level.
- D. Self-signed certificates must be changed to a publicly trusted CA signed certificate.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The statement that is true in this scenario is: Certificate-related settings apply to each individual
steering configuration level. Certificate-related settings are the options that allow you to configure
how Netskope handles SSL/TLS certificates for encrypted web traffic. For example, you can choose
whether to allow or block self-signed certificates, expired certificates, revoked certificates, etc. You
can also choose whether to enable SSL decryption for specific domains or categories. Certificate-
related settings apply to each individual steering configuration level, which means that you can have
different settings for different types of traffic or devices. For example, you can have one steering
configuration for managed devices and another one for unmanaged devices, and apply different
certificate-related settings for each one. This allows you to customize your security policies based on
your needs and preferences. Reference:
Netskope SSL DecryptionNetskope Steering Configuration
Question 5
When using an out-of-band API connection with your sanctioned cloud service, what are two
capabilities available to the administrator? (Choose two.)
- A. to quarantine malware
- B. to find sensitive content
- C. to block uploads
- D. to allow real-time access
Answer:
AB
Explanation:
When using an out-of-band API connection with your sanctioned cloud service, two capabilities
available to the administrator are: to quarantine malware and to find sensitive content. An out-of-
band API connection is a method of integrating Netskope with your cloud service provider using the
APIs exposed by the cloud service. This allows Netskope to access the data that is already stored in
the cloud service and perform retrospective inspection and enforcement of policies. One capability
that the administrator can use with an out-of-band API connection is to quarantine malware. This
means that Netskope can scan the files in the cloud service for malware, ransomware, phishing, and
other threats, and move them to a quarantine folder or delete them if they are found to be
malicious. Another capability that the administrator can use with an out-of-band API connection is to
find sensitive content. This means that Netskope can scan the files in the cloud service for sensitive
data, such as personal information, intellectual property, or regulated data, and apply data loss
prevention (DLP) policies to protect them. For example, Netskope can encrypt, redact, or watermark
the files that contain sensitive content, or notify the administrator or the file owner about the
exposure. Reference:
Netskope API ProtectionReal-time Control and Data Protection via Out-of-Band
API
Question 6
You want to set up a Netskope API connection to Box.
What two actions must be completed to enable this connection? (Choose two.)
- A. Install the Box desktop sync client.
- B. Authorize the Netskope application in Box.
- C. Integrate Box with the corporate IdP.
- D. Configure Box in SaaS API Data protection.
Answer:
BD
Explanation:
To set up a Netskope API connection to Box, two actions that must be completed are: authorize the
Netskope application in Box and configure Box in SaaS API Data protection. Authorizing the Netskope
application in Box allows Netskope to access the Box API and perform out-of-band inspection and
enforcement of policies on the data that is already stored in Box. Configuring Box in SaaS API Data
protection allows you to specify the Box instance details, such as domain name, admin email, etc.,
and enable features such as retroactive scan, event stream, etc. Reference:
Authorize Netskope
Introspection App on Box Enterprise - Netskope Knowledge PortalConfigure Box Instance in Netskope
UI - Netskope Knowledge Portal
Question 7
What are two pillars of CASB? (Choose two.)
- A. visibility
- B. compliance
- C. cloud native
- D. SASE
Answer:
A, B
Explanation:
Two pillars of CASB are visibility and compliance. CASB stands for Cloud Access Security Broker, which
is a solution that provides visibility and control over cloud services and web traffic, as well as data
and threat protection for cloud users and devices. Visibility is the capability to identify all cloud
services in use and assess their risk factors, such as security, auditability, business continuity, etc.
Compliance is the capability to ensure that cloud services and data meet the regulatory standards
and policies of the organization or industry, such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, etc. Reference:
What Is a
Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB)? | MicrosoftCASB Guide: What are the 4 Pillars of CASB? -
Security Service Edge
Question 8
Which three statements are correct about Netskope's NewEdge Security Cloud Network
Infrastructure? (Choose three.)
- A. It takes advantage of the public cloud by deploying security services on Google Cloud Platform.
- B. It includes direct peering with Microsoft and Google in every data center.
- C. It is a private security cloud network that is massively over provisioned, highly elastic, and built for scale.
- D. It delivers a single, unified network with no surcharges or reliance on public cloud infrastructure or virtual PoPs.
- E. It simplifies the administrator's job by limiting access to pre-defined availability zones.
Answer:
BCD
Explanation:
Netskope’s NewEdge Security Cloud Network Infrastructure is a global network that powers the
Netskope Security Cloud, providing real-time inline and out-of-band API-driven services for cloud and
web security. Three statements that are correct about Netskope’s NewEdge Security Cloud Network
Infrastructure are:
It includes direct peering with Microsoft and Google in every data center. This means that Netskope
has established high-speed, low-latency connections with these major cloud service providers,
ensuring optimal performance and user experience for their customers. Direct peering also reduces
the risk of network congestion, packet loss, or routing issues that may affect the quality of service.
It is a private security cloud network that is massively over provisioned, highly elastic, and built for
scale. This means that Netskope owns and operates its own network infrastructure, without relying
on third-party providers or public cloud platforms. Netskope has invested over $150 million to build
the world’s largest and fastest security private cloud, with data centers in more than 65 regions and
growing. Netskope can dynamically scale its network capacity and resources to meet the growing
demand and traffic volume of its customers, without compromising on security or performance.
It delivers a single, unified network with no surcharges or reliance on public cloud infrastructure or
virtual PoPs. This means that Netskope provides a consistent and transparent network service to its
customers, regardless of their location or device. Netskope does not charge any additional fees or
hidden costs for accessing its network services, unlike some other providers that may impose
surcharges based on geography or bandwidth usage. Netskope also does not use virtual points of
presence (PoPs) that are hosted on public cloud platforms, which may introduce latency, complexity,
or security risks.
Reference:
Netskope NewEdgeNetskope NewEdge Data SheetNetskope SASE
Question 9
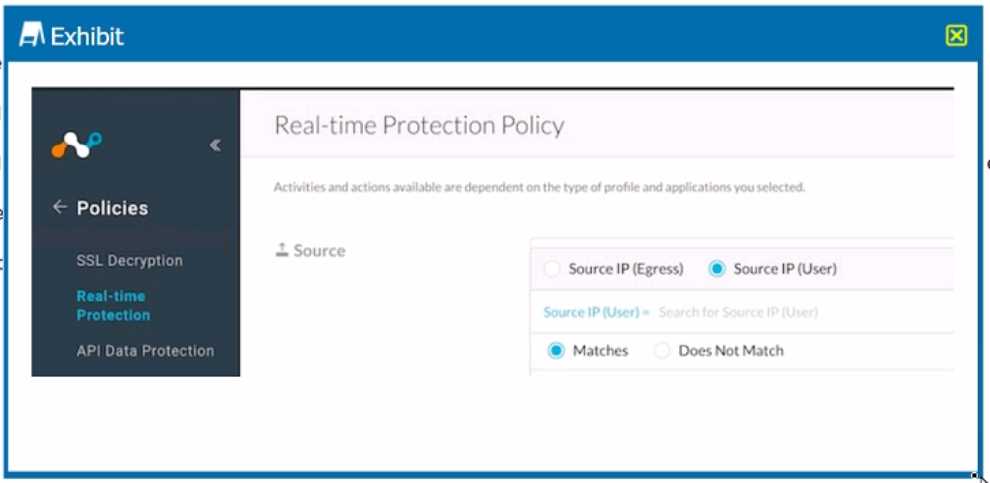
Click the Exhibit button.
Referring to the exhibit, which statement accurately describes the difference between Source IP
(Egress) and Source IP (User) address?
- A. Source IP (Egress) is the IP address of the destination Web server while Source IP (User) is the IP address assigned to your network.
- B. Source IP (Egress) is the IP address assigned to the endpoint host IP address while Source IP (User) is the public IP address of your Internet edge router.
- C. You must always leave the source IP fields blank and configure the user identity as a source criteria.
- D. Source IP (Egress) is the public IP address of your Internet edge router while Source IP (User) is the address assigned to the endpoint.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The statement that accurately describes the difference between Source IP (Egress) and Source IP
(User) address is: Source IP (Egress) is the public IP address of your Internet edge router while Source
IP (User) is the address assigned to the endpoint. Source IP (Egress) is the IP address that is visible to
external networks when you send traffic from your network to the Internet. It is usually the IP
address of your Internet edge router or gateway that performs NAT (Network Address Translation).
Source IP (User) is the IP address that is assigned to your endpoint device, such as a laptop or a
smartphone, within your network. It is usually a private IP address that is not routable on the
Internet. You can use these two criteria to filter traffic based on where it originates from within your
network or outside your network. Reference:
Source Address / Source Port vs Destination Address /
Destination PortHow to explain Source IP Address, Destination IP Address & Service in easy way
Question 10
What are two primary advantages of Netskope's Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) architecture?
(Choose two.
- A. no on-premises hardware required for policy enforcement
- B. Bayesian spam filtering
- C. Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
- D. single management console
Answer:
A, D
Explanation:
Two primary advantages of Netskope’s Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) architecture are: no on-
premises hardware required for policy enforcement and single management console. Netskope’s
SASE architecture delivers network and security services as cloud-based services that can be
accessed from any location and device. This eliminates the need for on-premises hardware
appliances such as firewalls, proxies, VPNs, etc., that are costly to maintain and scale. Netskope’s
SASE architecture also provides a single management console that allows administrators to configure
and monitor all the network and security services from one place. This simplifies IT operations and
reduces complexity and overhead. Reference:
Netskope SASEWhat is SASE?
Question 11
Exhibit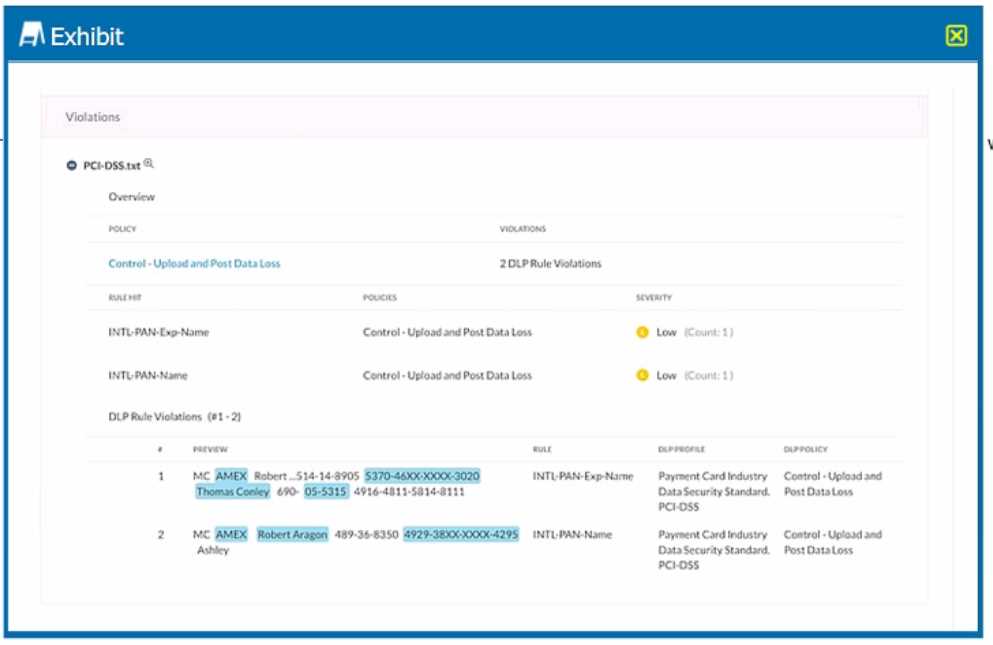
Which portion of the interface shown in the exhibit allows an administrator to set severity, assign
ownership, track progress, and perform forensic analysis with excerpts of violating content?
- A. Skope IT-> Alerts
- B. Incidents -> DLP
- C. API-enabled Protection -> Inventory
- D. Reports -> New Report
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The portion of the interface shown in the exhibit that allows an administrator to set severity, assign
ownership, track progress, and perform forensic analysis with excerpts of violating content is
Incidents -> DLP. The Incidents dashboard provides a comprehensive view of all the incidents that
have occurred in your cloud environment, such as DLP violations, malware infections, anomalous
activities, etc. You can filter the incidents by various criteria, such as app name, incident type,
severity, user name, etc. You can also drill down into each incident to see more details, such as file
name, file path, file owner, file size, file type, etc. You can also assign an owner to an incident, change
its status and severity, add notes or comments, and view the excerpts of the violating content that
triggered the DLP policy. Reference:
Netskope Incidents Dashboard
Question 12
You want to prevent Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attacks on an encrypted website or application. In
this scenario, which method would you use?
- A. Use a stronger encryption algorithm.
- B. Use certificate pinning.
- C. Use a proxy for the connection.
- D. Use a weaker encryption algorithm.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
To prevent Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attacks on an encrypted website or application, one method
that you can use is certificate pinning. Certificate pinning is a technique that restricts which
certificates are considered valid for a particular website or application, limiting risk. Instead of
allowing any trusted certificate to be used, operators "pin" the certificate authority (CA) issuer(s),
public keys or even end-entity certificates of their choice. Certificate pinning helps to prevent MITM
attacks by validating the server certificates against a hardcoded list of certificates in the website or
application. If an attacker tries to intercept or modify the traffic using a fraudulent or compromised
certificate, it will be rejected by the website or application as invalid, even if it is signed by a trusted
CA. Reference:
Certificate pinning - IBMCertificate and Public Key Pinning | OWASP Foundation
Question 13
You need to provide a quick view under the Skope IT Applications page showing only risky shadow IT
cloud applications being used.
In this scenario, which two filter combinations would you use to accomplish this task? (Choose two.)
- A. Sanctioned = No
- B. User Device Type = Windows Device
- D. CCL = Medium. Low, Poor
Answer:
A, D
Explanation:
To provide a quick view under the Skope IT Applications page showing only risky shadow IT cloud
applications being used, you can use two filter combinations: Sanctioned = No and CCL = Medium,
Low, Poor. The Sanctioned filter allows you to select whether you want to see only sanctioned or
unsanctioned apps in your organization. Sanctioned apps are those that are approved and managed
by your IT department, while unsanctioned apps are those that are used without authorization or
oversight by your employees. Shadow IT refers to the use of unsanctioned apps that may pose
security or compliance risks for your organization. The CCL filter allows you to select the Cloud
Confidence Level (CCL) ratings of the apps you want to see. The CCL rating is a measure of how
enterprise-ready a cloud app is based on various criteria such as security, auditability, business
continuity, etc. The CCL rating ranges from Excellent to Poor, with Excellent being the most secure
and compliant and Poor being the least. Risky cloud apps are those that have a low CCL rating, such
as Medium, Low, or Poor. By applying these two filters, you can narrow down the list of apps to only
those that are unsanctioned and have a low CCL rating, which indicates that they are risky shadow IT
cloud applications being used in your organization. Reference:
SkopeIT ApplicationsNetskope Cloud
Confidence Index
Question 14
In which scenario would you use a SAML reverse proxy?
- A. When the API-enabled protection exceeds the Cloud App API usage limits and cannot be used anymore.
- B. When the organization wants to perform inline inspection of cloud application traffic for roaming users that do not have the Netskope agent installed.
- C. When there are multiple SAML IdPs in use and the SAML reverse proxy can help federate them all together.
- D. When PAC files or explicit proxies can be used to steer traffic to the Netskope platform.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
A SAML reverse proxy is a service that acts as an intermediary between a SAML service provider (SP)
and one or more SAML identity providers (IdPs). It can perform various functions, such as
authentication, authorization, load balancing, caching, etc. One scenario where you would use a
SAML reverse proxy is when there are multiple SAML IdPs in use and the SAML reverse proxy can
help federate them all together. For example, suppose you have an internal application that needs to
authenticate users from different domains or organizations, each with their own SAML IdP. Instead of
configuring the application to trust each IdP separately, you can use a SAML reverse proxy to act as a
single SP for the application and a single IdP for the users. The SAML reverse proxy can then redirect
the users to their respective IdPs for authentication and relay the SAML assertions back to the
application. This way, you can simplify the integration and management of multiple SAML IdPs and
provide a seamless user experience. Reference:
SAML Reverse ProxyWhat is application proxy &
SAML SSO?
Question 15
Which two use cases would be considered examples of Shadow IT within an organization? (Choose
two.)
- A. a sanctioned Salesforce account used by a contractor to upload non-sensitive data
- B. a sanctioned Wetransfer being used by a corporate user to share sensitive data
- C. an unsanctioned Microsoft 365 OneDrive account being used by a corporate user to upload sensitive data
- D. an unsanctioned Google Drive account used by a corporate user to upload non-sensitive data
Answer:
C, D
Explanation:
Shadow IT is the term for the unauthorized use of IT resources and functions by employees within an
organization. It can include cloud services, software, and hardware that are not approved or
managed by the IT department. Two use cases that would be considered examples of shadow IT
within an organization are: an unsanctioned Microsoft 365 OneDrive account being used by a
corporate user to upload sensitive data and an unsanctioned Google Drive account used by a
corporate user to upload non-sensitive data. In both cases, the corporate user is using a personal
cloud storage service that is not sanctioned by the organization to store work-related data. This can
introduce security risks, such as data leakage, data loss, compliance violations, malware infections,
etc. The IT department may not have visibility or control over these cloud services or the data stored
in them. Reference:
What is shadow IT? | CloudflareWhat is Shadow IT? | IBM