NetApp NS0-521 Exam Questions
Questions for the NS0-521 were updated on : Feb 18 ,2026
Page 1 out of 5. Viewing questions 1-15 out of 65
Question 1
What is the maximum size for a LUN in NetApp ONTAP 9.14.1 software?
- A. 16TiB
- B. 64TiB
- C. 128TiB
- D. 300TiB
Answer:
C
Explanation:
In NetApp ONTAP 9.14.1 software, the maximum size for a LUN is 128TiB. This limit ensures that
large datasets can be stored and managed efficiently within a single LUN, catering to the needs of
high-capacity SAN environments
Question 2
An administrator runs the vserver nvme namespace convert-from-iun command on a NetApp ASA
cluster to increase host performance.
What is modified by the convert command?
- A. FlexVol
- B. FlexClone
- C. LUN clone
- D. Metadata
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The vserver nvme namespace convert-from-lun command in a NetApp ASA cluster is used to convert
a LUN to an NVMe namespace to increase host performance. This process involves modifying the
metadata of the storage object to make it compatible with the NVMe protocol, allowing for faster
access and reduced latency
Question 3
Which two NetApp features provide synchronous data replication between two sites for SAN
workloads with automatic failover in case of a site disaster? (Choose two.)
- A. SnapMirror active sync
- B. SnapMirror SVM
- C. SnapMirror Synchronous
- D. MetroCluster IP
Answer:
CD
Explanation:
For synchronous data replication between two sites with automatic failover in case of a site disaster
for SAN workloads, the two NetApp features that provide these capabilities are SnapMirror
Synchronous and MetroCluster IP.
SnapMirror Synchronous: This feature provides volume-granular, synchronous replication with zero
RPO (Recovery Point Objective), ensuring that data is mirrored in real-time to a secondary site. This
setup supports automatic failover, maintaining data availability even during site failures
MetroCluster IP: This solution provides synchronous replication and combines high availability and
disaster recovery capabilities. MetroCluster IP uses IP networking to extend the distance over which
replication can occur and supports automatic failover and failback, making it suitable for critical SAN
workloads
Question 4
An administrator needs to ensure that Snapshot copies of database files across multiple FCP LUNs are
taken at the same point in time.
Which two configurations enable the administrator to achieve this? (Choose two.)
- A. Create each LUN within the same FlexVol volume.
- B. Create a consistency group that uses FlexGroup volumes.
- C. Create a consistency group that uses FlexVol volumes.
- D. Create each LUN within the same FlexGroup volume.
Answer:
C, D
Explanation:
To ensure that Snapshot copies of database files across multiple FCP LUNs are taken at the same
point in time, the following configurations can be used:
Create a consistency group that uses FlexVol volumes: This setup ensures that snapshots of all
volumes in the consistency group are taken simultaneously.
Create each LUN within the same FlexGroup volume: This configuration allows for a unified snapshot
across multiple LUNs within the FlexGroup, ensuring data consistency.
For more details, see:
NetApp Documentation on Consistency Groups
NetApp FlexGroup Overview
Question 5
An SVM is created for FCP traffic. LUNs must be created to share with ESXi hosts for datastores.
Which two items must be configured after the LUN is created, for this to happen? (Choose two.)
- A. Create an igroup with the ESXi hosts' WWPNs.
- B. Create an igroup with the ESXi hosts' WWNNs.
- C. Configure CHAP authentication.
- D. Map the LUNs to the igroup.
Answer:
A, D
Explanation:
For configuring LUNs to share with ESXi hosts for datastores in an SVM created for FCP traffic, the
following steps are necessary after creating the LUN:
Create an igroup with the ESXi hosts' WWPNs: This step involves defining an initiator group that
includes the WWPNs of the ESXi hosts that need access to the LUN.
Map the LUNs to the igroup: This step assigns the LUN to the created igroup, allowing the ESXi hosts
to access the LUN.
For further details, refer to:
NetApp Documentation on LUN and igroup Configuration
Question 6
An administrator upgraded their NetApp ONTAP software from release 9.10.1 to 9.13.1 on a NetApp
All SAN Array (ASA) cluster and is creating a new iSCSI SVM.
Which automatic feature can be used with iSCSI?
- A. LIF failover
- B. LUN mapping
- C. CHAP authentication
- D. igroup creation
Answer:
A
Explanation:
In NetApp ONTAP 9.13.1, one of the automatic features that can be used with iSCSI is LIF failover.
This feature ensures that in the event of a network failure or a node issue, the Logical Interface (LIF)
will automatically fail over to another available port, maintaining connectivity and minimizing
disruption to iSCSI traffic.
For more information, refer to:
NetApp ONTAP 9.13.1 Features
Question 7
A customer Is setting up a two-node cluster to serve (SCSI LUNs. How many interfaces should be
created?
- A. One iSCSI LIF per node
- B. One ISCSI LIF per SVM
- C. Two iSCSI LIFs per node
- D. Two ISCSI LIFs per SVM
Answer:
C
Explanation:
For a two-node cluster serving iSCSI LUNs, it is recommended to create two iSCSI LIFs per node. This
configuration provides redundancy and load balancing, ensuring that each node can handle failover
scenarios effectively and maintain high availability for the iSCSI connections.
For more details, see:
NetApp Documentation on iSCSI LIF Configuration
Question 8
A customer has a two-node NetApp AFF ASA cluster in an environment with a Cisco Fibre Channel
SAN and Cisco UCS Servers. The customer wants to upgrade the UCS Server BIOS and the Cisco NX-
OS system running on the switches.
Which NetApp resource should be consulted to check compatibility with the new versions?
- A. Interoperability Matrix Tool (IMT)
- B. BlueXP digital advisor
- C. Hardware Universe
- D. Active IQ Config Advisor
Answer:
A
Explanation:
When planning to upgrade the UCS Server BIOS and Cisco NX-OS system running on the switches in a
NetApp AFF ASA cluster environment, the Interoperability Matrix Tool (IMT) is the recommended
resource to check compatibility with the new versions. The IMT provides detailed compatibility
information for various hardware and software components, ensuring that the planned upgrades will
not cause any interoperability issues.
For further details, refer to:
NetApp Interoperability Matrix Tool
Question 9
During maintenance of A NetApp AFF ONTAP cluster, which two steps are needed to move the SAN
UFs to new nodes that are members of a portset? (Choose two.)
- A. Remove the LIF from the portset.
- B. Disable the SLM feature for the node that hosts the LIF.
- C. Disable the zoning of the LIF WWPN.
- D. Take the SAN LIF offline.
Answer:
A, D
Explanation:
To move SAN LIFs to new nodes that are members of a portset during maintenance of a NetApp AFF
ONTAP cluster, you should take the following steps:
Remove the LIF from the portset: This ensures that the LIF is no longer associated with the current
node, preparing it for the move to the new node.
Take the SAN LIF offline: This step is necessary to make configuration changes without causing
disruption to the SAN hosts. Once offline, the LIF can be moved to the new node and reconfigured as
needed.
These actions help maintain the integrity and performance of the SAN environment during the
migration of LIFs.
For more details, see:
NetApp Documentation on Moving SAN LIFs
NetApp Community on Moving LIFs
Question 10
An administrator is planning a SAN implementation and needs to validate that the ESXI host and
NetApp ONTAP software releases are supported.
Which tool is used to accomplish this?
- A. NetApp Interoperabilty Matrix Tool
- B. NetApp Active IQ Config Advisor
- C. NetApp Hardware Universe
- D. Broadcom SAN Health
Answer:
A
Explanation:
To validate that the ESXi host and NetApp ONTAP software releases are supported, the NetApp
Interoperability Matrix Tool (IMT) should be used. The IMT provides comprehensive compatibility
information, ensuring that all components of the SAN environment will work together seamlessly.
For further details, refer to:
NetApp Interoperability Matrix Tool
Question 11
A customer wants to Implement a NetApp AFF system at a small remote site that has two ESXi
servers that require SAN storage from the NetApp ONTAP based storage system. The servers will be
directly connected, because the customer does not want to deploy any switches.
Which protocol should the customer use?
- A. FCP
- B. NFS
- C. FCoE
- D. iSCSI
Answer:
D
Explanation:
For a small remote site with two ESXi servers requiring SAN storage and no switches, the
recommended protocol is iSCSI. iSCSI allows for direct connectivity between the servers and the
NetApp ONTAP storage system using standard Ethernet infrastructure, which is suitable for
environments without Fibre Channel switches.
For more information, see:
NetApp iSCSI Configuration Guide
Question 12
A customer has a two-node NetApp ONTAP cluster that Is hosting FC LUNs for 64 SAN hosts. An
administrator is tasked to add 40 more hosts to the environment.
What two actions would the administrator need to take to avoid potential performance problems
with the environment? (Choose two.)
- A. Configure additional FC ports on existing hosts.
- B. Configure additional FC target ports.
- C. Configure additional SAN LIFs.
- D. Configure a higher queue depth on the target ports.
Answer:
BC
Explanation:
When adding 40 more hosts to a two-node NetApp ONTAP cluster that is already hosting 64 SAN
hosts, the following actions are necessary to avoid potential performance problems:
Configure additional FC target ports: Increasing the number of Fibre Channel (FC) target ports on the
storage nodes will help distribute the I/O load more evenly, reducing the risk of bottlenecks.
Configure additional SAN LIFs: Adding more SAN Logical Interfaces (LIFs) will ensure that the
increased number of hosts can connect efficiently, improving load balancing and path management.
These actions help maintain optimal performance and prevent congestion in the SAN environment.
For more detailed guidance, refer to:
NetApp SAN Host Configuration Overview
NetApp Best Practices for SAN(
NetApp
)(
NetApp
)
Question 13
Click the Exhibit button.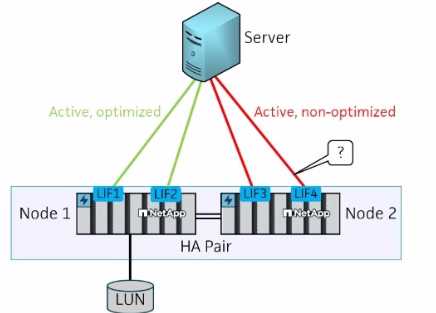
A customer is testing a newly installed NetApp AFF A400 all-flash HA storage system. An SVM for FCP
with a LUN on Node 1 has been configured, and a server has been connected as shown in the exhibit.
For testing, the engineer plans to do a storage failover of Node 1.
After the failover, what is the expected status of the marked path?
- A. Unavailable
- B. Active/Optimized
- C. Active/Nonoptimized
- D. Offline
Answer:
C
Explanation:
In the scenario where a storage failover is performed on Node 1 in an HA pair, the path marked in the
exhibit would become Active/Nonoptimized. After the failover, the LIFs from Node 1 that were active
and optimized will switch to Node 2. Paths that were previously optimized will become nonoptimized
because they are now served through the partner node.
For more details, see:
NetApp Documentation on ALUA
Question 14
A four-node NetApp ONTAP SAN cluster has been deployed. After installation, the engineer wants to
verify cabling.
Which NetApp tool should the engineer use?
- A. NetApp Host Utilities package
- B. Active IQ Config Advisor
- C. Interoperability Matrix Tool
- D. Hardware Universe
Answer:
B
Explanation:
To verify the cabling of a four-node NetApp ONTAP SAN cluster after installation, the recommended
tool is Active IQ Config Advisor. This tool provides detailed checks for proper configuration, including
cabling verification, and helps ensure that best practices are followed for optimal performance and
reliability.
For further details, see:
NetApp Active IQ Config Advisor
Question 15
During expansion planning for a 10-node cluster running NetApp ONTAP 9.14.1 software, which uses
SAN and NAS, how many additional nodes can be added to this cluster?
- A. 4
- B. 6
- C. 2
- D. 8
Answer:
B
Explanation:
NetApp ONTAP 9.14.1 supports up to a 16-node cluster for SAN and NAS configurations. Given a
current 10-node cluster, you can add up to 6 additional nodes to reach the maximum supported node
count. This expansion capability ensures scalability for growing storage needs while maintaining high
availability and performance.
For more information, refer to:
NetApp Storage Limits Documentation(
NetApp
)