microsoft DP-420 Exam Questions
Questions for the DP-420 were updated on : Jul 05 ,2025
Page 1 out of 4. Viewing questions 1-15 out of 51
Question 1 Topic 1, Case Study 1Case Study Question View Case
You are troubleshooting the current issues caused by the application updates.
Which action can address the application updates issue without affecting the functionality of the application?
- A. Enable time to live for the con-product container.
- B. Set the default consistency level of account1 to strong.
- C. Set the default consistency level of account1 to bounded staleness.
- D. Add a custom indexing policy to the con-product container.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Bounded staleness is frequently chosen by globally distributed applications that expect low write latencies but require total
global order guarantee. Bounded staleness is great for applications featuring group collaboration and sharing, stock ticker,
publish-subscribe/queueing etc.
Scenario: Application updates in con-product frequently cause HTTP status code 429 "Too many requests". You discover
that the 429 status code relates to excessive request unit (RU) consumption during the updates.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cosmos-db/consistency-levels
Question 2 Topic 1, Case Study 1Case Study Question View Case
You need to select the partition key for con-iot1. The solution must meet the IoT telemetry requirements.
What should you select?
- A. the timestamp
- B. the humidity
- C. the temperature
- D. the device ID
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The partition key is what will determine how data is routed in the various partitions by Cosmos DB and needs to make sense
in the context of your specific scenario. The IoT Device ID is generally the "natural" partition key for IoT applications.
Scenario: The iotdb database will contain two containers named con-iot1 and con-iot2. Ensure that Azure Cosmos DB costs
for IoT-related processing are predictable.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/architecture/solution-ideas/articles/iot-using-cosmos-db
Topic 2, Case Study 2
Case Study
This is a case study. Case studies are not timed separately. You can use as much exam time as you would like to complete
each case. However, there may be additional case studies and sections on this exam. You must manage your time to ensure
that you are able to complete all questions included on this exam in the time provided.
To answer the questions included in a case study, you will need to reference information that is provided in the case study.
Case studies might contain exhibits and other resources that provide more information about the scenario that is described
in the case study. Each question is independent of the other questions in this case study.
At the end of this case study, a review screen will appear. This screen allows you to review your answers and to make
changes before you move to the next section of the exam. After you begin a new section, you cannot return to this section.
To start the case study
To display the first question in this case study, click the Next button. Use the buttons in the left pane to explore the content of
the case study before you answer the questions. Clicking these buttons displays information such as business requirements,
existing environment, and problem statements. If the case study has an All Information tab, note that the information
displayed is identical to the information displayed on the subsequent tabs. When you are ready to answer a question, click
the Question button to return to the question.
Overview
Litware, Inc. is a United States-based grocery retailer. Litware has a main office and a primary datacenter in Seattle. The
company has 50 retail stores across the United States and an emerging online presence. Each store connects directly to the
internet.
Existing environment. Cloud and Data Service Environments.
Litware has an Azure subscription that contains the resources shown in the following table.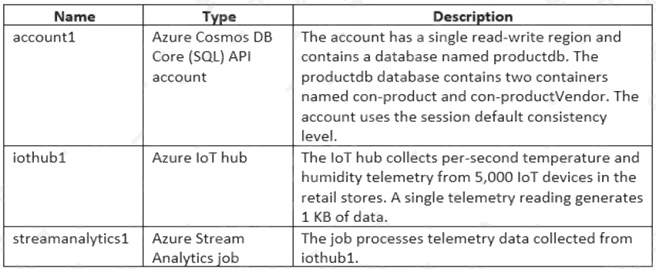
Each container in productdb is configured for manual throughput.
The con-product container stores the company's product catalog data. Each document in con-product includes a con-
productvendor value. Most queries targeting the data in con-product are in the following format.
SELECT * FROM con-product p WHERE p.con-productVendor - 'name'
Most queries targeting the data in the con-productVendor container are in the following format
SELECT * FROM con-productVendor pv ORDER BY pv.creditRating, pv.yearFounded
Existing environment. Current Problems.
Litware identifies the following issues:
Updates to product categories in the con-productVendor container do not propagate automatically to documents in the
con-product container.
Application updates in con-product frequently cause HTTP status code 429 "Too many requests". You discover that the
429 status code relates to excessive request unit (RU) consumption during the updates.
Requirements. Planned Changes
Litware plans to implement a new Azure Cosmos DB Core (SQL) API account named account2 that will contain a database
named iotdb. The iotdb database will contain two containers named con-iot1 and con-iot2.
Litware plans to make the following changes:
Store the telemetry data in account2.
Configure account1 to support multiple read-write regions.
Implement referential integrity for the con-product container.
Use Azure Functions to send notifications about product updates to different recipients.
Develop an app named App1 that will run from all locations and query the data in account1.
Develop an app named App2 that will run from the retail stores and query the data in account2. App2 must be limited to a
single DNS endpoint when accessing account2. Requirements. Business Requirements
Litware identifies the following business requirements:
Whenever there are multiple solutions for a requirement, select the solution that provides the best performance, as long as
there are no additional costs associated. Ensure that Azure Cosmos DB costs for IoT-related processing are predictable.
Minimize the number of firewall changes in the retail stores.
Requirements. Product Catalog Requirements
Litware identifies the following requirements for the product catalog:
Implement a custom conflict resolution policy for the product catalog data.
Minimize the frequency of errors during updates of the con-product container.
Once multi-region writes are configured, maximize the performance of App1 queries against the data in account1.
Trigger the execution of two Azure functions following every update to any document in the con-product container.
Question 3 Topic 2, Case Study 2Case Study Question View Case
You configure multi-region writes for account1.
You need to ensure that App1 supports the new configuration for account1. The solution must meet the business
requirements and the product catalog requirements.
What should you do?
- A. Set the default consistency level of account1 to bounded staleness.
- B. Create a private endpoint connection.
- C. Modify the connection policy of App1.
- D. Increase the number of request units per second (RU/s) allocated to the con-product and con-productVendor containers.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
App1 queries the con-product and con-productVendor containers.
Note: Request unit is a performance currency abstracting the system resources such as CPU, IOPS, and memory that are
required to perform the database operations supported by Azure Cosmos DB.
Scenario:
Develop an app named App1 that will run from all locations and query the data in account1.
Once multi-region writes are configured, maximize the performance of App1 queries against the data in account1.
Whenever there are multiple solutions for a requirement, select the solution that provides the best performance, as long as
there are no additional costs associated.
Incorrect Answers:
A:
Bounded staleness relates to writes. App1 only do reads.
Note: Bounded staleness is frequently chosen by globally distributed applications that expect low write latencies but require
total global order guarantee. Bounded staleness is great for applications featuring group collaboration and sharing, stock
ticker, publish-subscribe/queueing etc.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cosmos-db/consistency-levels
Question 4 Topic 2, Case Study 2Case Study Question View Case
You need to provide a solution for the Azure Functions notifications following updates to con-product. The solution must
meet the business requirements and the product catalog requirements.
Which two actions should you perform? Each correct answer presents part of the solution.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
- A. Configure the trigger for each function to use a different leaseCollectionPrefix
- B. Configure the trigger for each function to use the same leaseCollectionName
- C. Configure the trigger for each function to use a different leaseCollectionName
- D. Configure the trigger for each function to use the same leaseCollectionPrefix
Answer:
A B
Explanation:
leaseCollectionPrefix: when set, the value is added as a prefix to the leases created in the Lease collection for this Function.
Using a prefix allows two separate Azure Functions to share the same Lease collection by using different prefixes.
Scenario: Use Azure Functions to send notifications about product updates to different recipients.
Trigger the execution of two Azure functions following every update to any document in the con-product container.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-functions/functions-bindings-cosmosdb-v2-trigger
Topic 3, Mixed Questions
Question 5 Topic 3, Mixed Questions
You have an application named App1 that reads the data in an Azure Cosmos DB Core (SQL) API account. App1 runs the
same read queries every minute. The default consistency level for the account is set to eventual.
You discover that every query consumes request units (RUs) instead of using the cache.
You verify the IntegratedCacheiteItemHitRate metric and the IntegratedCacheQueryHitRate metric. Both metrics have values
of 0.
You verify that the dedicated gateway cluster is provisioned and used in the connection string.
You need to ensure that App1 uses the Azure Cosmos DB integrated cache.
What should you configure?
- A. the indexing policy of the Azure Cosmos DB container
- B. the consistency level of the requests from App1
- C. the connectivity mode of the App1 CosmosClient
- D. the default consistency level of the Azure Cosmos DB account
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Because the integrated cache is specific to your Azure Cosmos DB account and requires significant CPU and memory, it
requires a dedicated gateway node. Connect to Azure Cosmos DB using gateway mode.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cosmos-db/integrated-cache-faq
Question 6 Topic 3, Mixed Questions
HOTSPOT
You provision Azure resources by using the following Azure Resource Manager (ARM) template.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:
Answer:

Explanation:
Box 1: No
An alert is triggered when the DB key is regenerated, not when it is used.
Note: The az cosmosdb keys regenerate command regenerates an access key for a Azure Cosmos DB database account.
Box 2: No
Only an SMS action will be taken.
Emailreceivers is empty so no email action is taken.
Box 3: Yes
Yes, an alert is triggered when the DB key is regenerated.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/cli/azure/cosmosdb/keys
Question 7 Topic 3, Mixed Questions
HOTSPOT
You have an Azure Cosmos DB Core (SQL) API account named account1 that has the
disableKeyBasedMetadataWriteAccess property enabled.
You are developing an app named App1 that will be used by a user named DevUser1 to create containers in account1.
DevUser1 has a non-privileged user account in the Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) tenant.
You need to ensure that DevUser1 can use App1 to create containers in account1.
What should you do? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area: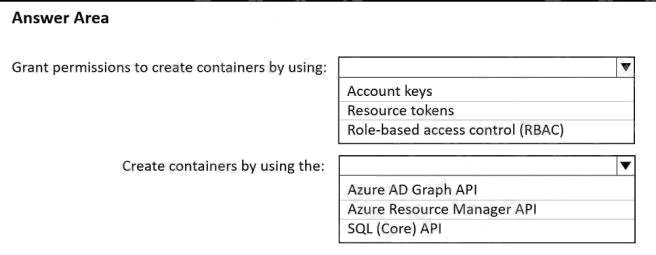
Answer:
Explanation:
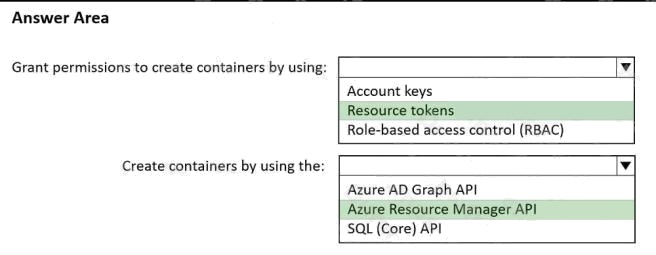
Box 1: Resource tokens
Resource tokens provide access to the application resources within a database. Resource tokens:
Provide access to specific containers, partition keys, documents, attachments, stored procedures, triggers, and UDFs.
Box 2: Azure Resource Manager API
You can use Azure Resource Manager to help deploy and manage your Azure Cosmos DB accounts, databases, and
containers.
Incorrect Answers:
The Microsoft Graph API is a RESTful web API that enables you to access Microsoft Cloud service resources.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cosmos-db/secure-access-to-data https://docs.microsoft.com/en-
us/rest/api/resources/
Question 8 Topic 3, Mixed Questions
HOTSPOT
You have an Azure Cosmos DB Core (SQL) account that has a single write region in West Europe.
You run the following Azure CLI script.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:
Answer:

Explanation:
Box 1: Yes
The Automatic failover option allows Azure Cosmos DB to failover to the region with the highest failover priority with no user
action should a region become unavailable.
Box 2: No
West Europe is used for failover. Only North Europe is writable.
To Configure multi-region set UseMultipleWriteLocations to true.
Box 3: Yes
Provisioned throughput with single write region costs $0.008/hour per 100 RU/s and provisioned throughput with multiple
writable regions costs $0.016/per hour per 100 RU/s.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cosmos-db/sql/how-to-multi-master https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cosmos-
db/optimize-cost-regions
Question 9 Topic 3, Mixed Questions
You are developing an application that will use an Azure Cosmos DB Core (SQL) API account as a data source.
You need to create a report that displays the top five most ordered fruits as shown in the following table.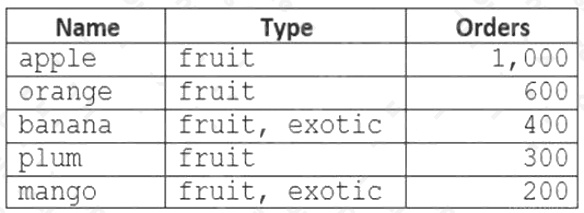
A collection that contains aggregated data already exists. The following is a sample document:
{
"name": "apple",
"type": ["fruit", "exotic"],
"orders": 10000 }
Which two queries can you use to retrieve data for the report? Each correct answer presents a complete solution.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
- A. Option A
- B. Option B
- C. Option C
- D. Option D
Answer:
B D
Explanation:
ARRAY_CONTAINS returns a Boolean indicating whether the array contains the specified value. You can check for a partial
or full match of an object by using a boolean expression within the command.
Incorrect Answers:
A: Default sorting ordering is Ascending. Must use Descending order. C: Order on Orders not on Type.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cosmos-db/sql/sql-query-array-contains
Question 10 Topic 3, Mixed Questions
HOTSPOT
You have a database in an Azure Cosmos DB Core (SQL) API account.
You plan to create a container that will store employee data for 5,000 small businesses. Each business will have up to 25
employees. Each employee item will have an emailAddress value.
You need to ensure that the emailAddress value for each employee within the same company is unique.
To what should you set the partition key and the unique key? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area: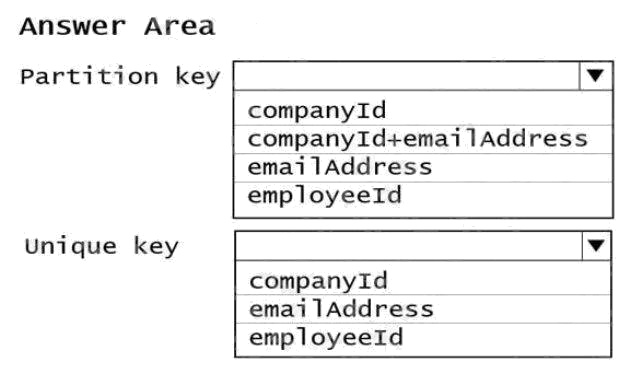
Answer:
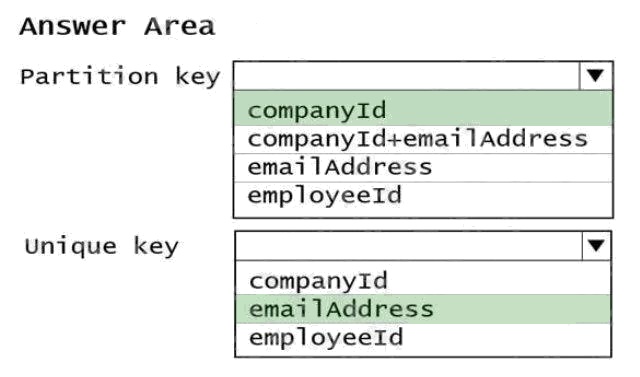
Explanation:
Box 1: CompanyID
After you create a container with a unique key policy, the creation of a new or an update of an existing item resulting in a
duplicate within a logical partition is prevented, as specified by the unique key constraint. The partition key combined with the
unique key guarantees the uniqueness of an item within the scope of the container.
For example, consider an Azure Cosmos container with Email address as the unique key constraint and CompanyID as the
partition key. When you configure the user's email address with a unique key, each item has a unique email address within a
given CompanyID. Two items can't be created with duplicate email addresses and with the same partition key value. Box 2:
emailAddress
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cosmos-db/unique-keys
Question 11 Topic 3, Mixed Questions
HOTSPOT
You have a container named container1 in an Azure Cosmos DB Core (SQL) API account. The container1 container has 120
GB of data.
The following is a sample of a document in container1.
The orderId property is used as the partition key.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:
Answer:

Explanation:
Box 1: Yes
Records with different OrderIDs will match.
Box 2: Yes
Records with different OrderIDs will match.
Box 3: No
Only records with one specific OrderId will match
Question 12 Topic 3, Mixed Questions
You are designing an Azure Cosmos DB Core (SQL) API solution to store data from IoT devices. Writes from the devices will
be occur every second.
The following is a sample of the data.
You need to select a partition key that meets the following requirements for writes:
Minimizes the partition skew
Avoids capacity limits Avoids hot partitions

What should you do?
- A. Use timestamp as the partition key.
- B. Create a new synthetic key that contains deviceId and sensor1Value.
- C. Create a new synthetic key that contains deviceId and deviceManufacturer.
- D. Create a new synthetic key that contains deviceId and a random number.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Use a partition key with a random suffix. Distribute the workload more evenly is to append a random number at the end of
the partition key value. When you distribute items in this way, you can perform parallel write operations across partitions.
Incorrect Answers:
A: You will also not like to partition the data on DateTime, because this will create a hot partition. Imagine you have
partitioned the data on time, then for a given minute, all the calls will hit one partition. If you need to retrieve the data for a
customer, then it will be a fan-out query because data may be distributed on all the partitions.
B: Senser1Value has only two values.
C: All the devices could have the same manufacturer.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cosmos-db/sql/synthetic-partition-keys
Question 13 Topic 3, Mixed Questions
You maintain a relational database for a book publisher. The database contains the following tables.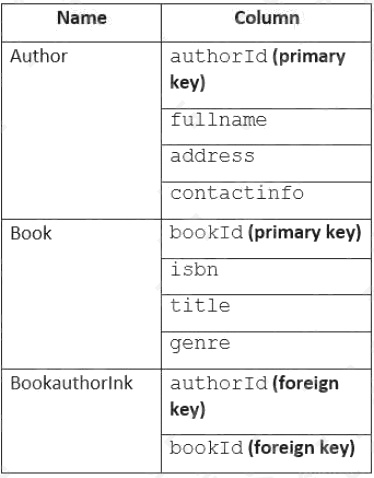
The most common query lists the books for a given authorId.
You need to develop a non-relational data model for Azure Cosmos DB Core (SQL) API that will replace the relational
database. The solution must minimize latency and read operation costs.
What should you include in the solution?
- A. Create a container for Author and a container for Book. In each Author document, embed bookId for each book by the author. In each Book document embed authorId of each author.
- B. Create Author, Book, and Bookauthorlnk documents in the same container.
- C. Create a container that contains a document for each Author and a document for each Book. In each Book document, embed authorId.
- D. Create a container for Author and a container for Book. In each Author document and Book document embed the data from Bookauthorlnk.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Store multiple entity types in the same container.
Question 14 Topic 3, Mixed Questions
You have an Azure Cosmos DB Core (SQL) API account.
You run the following query against a container in the account.
SELECT
IS_NUMBER("1234") AS A,
IS_NUMBER(1234) AS B,
IS_NUMBER({prop: 1234}) AS C
What is the output of the query?
- A. [{"A": false, "B": true, "C": false}]
- B. [{"A": true, "B": false, "C": true}]
- C. [{"A": true, "B": true, "C": false}]
- D. [{"A": true, "B": true, "C": true}]
Answer:
A
Explanation:
IS_NUMBER returns a Boolean value indicating if the type of the specified expression is a number. "1234" is a string, not a
number.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cosmos-db/sql/sql-query-is-number
Question 15 Topic 3, Mixed Questions
You need to implement a trigger in Azure Cosmos DB Core (SQL) API that will run before an item is inserted into a
container.
Which two actions should you perform to ensure that the trigger runs? Each correct answer presents part of the solution.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
- A. Append pre to the name of the JavaScript function trigger.
- B. For each create request, set the access condition in RequestOptions.
- C. Register the trigger as a pre-trigger.
- D. For each create request, set the consistency level to session in RequestOptions.
- E. For each create request, set the trigger name in RequestOptions.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
C: When triggers are registered, you can specify the operations that it can run with.
F: When executing, pre-triggers are passed in the RequestOptions object by specifying PreTriggerInclude and then passing
the name of the trigger in a List object.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cosmos-db/sql/how-to-use-stored-procedures-triggers-udfs