Juniper JN0-683 Exam Questions
Questions for the JN0-683 were updated on : Feb 18 ,2026
Page 1 out of 5. Viewing questions 1-15 out of 65
Question 1
Exhibit.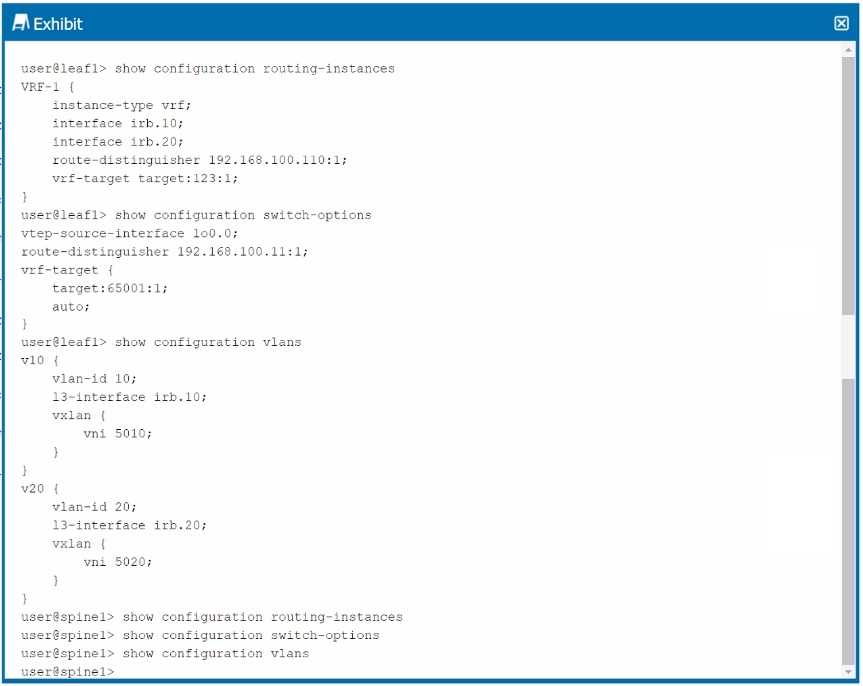
Referring to the exhibit, which statement Is true?
- A. A PBB-EVPN architecture is being used.
- B. An ERB architecture is being used.
- C. An OTT architecture is being used.
- D. A CRB architecture is being used.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Understanding Network Architectures:
ERB (Edge Routed Bridging) architecture involves routing at the network's edge (leaf nodes), while
traffic between leaf nodes is switched. This is commonly used in VXLAN-EVPN setups.
Analysis of the Exhibit:
The exhibit shows configurations related to routing instances, VXLAN, and VLANs, with VNIs being
used for each VLAN. This setup is characteristic of an ERB architecture where each leaf device
handles Layer 3 routing for its connected devices.
Conclusion:
Option B: Correct—The configuration shown corresponds to an ERB architecture where routing
occurs at the network's edge (leaf devices).
Question 2
You are asked to set up an IP fabric that supports Al or ML workloads. You have chosen to use lossless
Ethernet in this scenario, which statement is correct about congestion management?
- A. The switch experiencing the congestion notifies the source device.
- B. Only the source and destination devices need ECN enabled.
- C. ECN marks packets based on WRED settings.
- D. ECN is negotiated only among the switches that make up the IP fabric for each queue.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Understanding Lossless Ethernet and Congestion Management:
Lossless Ethernet is crucial for AI and ML workloads, where packet loss can significantly degrade
performance. To implement lossless Ethernet, congestion management protocols like ECN (Explicit
Congestion Notification) are used.
Role of ECN in Congestion Management:
Option A: In an IP fabric that supports lossless Ethernet, when a switch experiences congestion, it can
mark packets using ECN. This marking notifies the source device of the congestion, allowing the
source to reduce its transmission rate, thereby preventing packet loss.
Conclusion:
Option A: Correct—The switch experiencing congestion notifies the source device via ECN marking.
Question 3
Which three statements are correct about VXLAN control planes? (Choose three.)
- A. EVPN is inefficient and does not scale well.
- B. Both multicast and EVPN can facilitate MAC learning.
- C. Multicast is not agile and requires manual VNI mapping.
- D. EVPN enables fast convergence and updates.
- E. Multicast does not require as many resources.
Answer:
BDE
Explanation:
VXLAN Control Planes:
VXLAN (Virtual Extensible LAN) uses different control planes to handle MAC learning and traffic
forwarding. The control planes include multicast and EVPN (Ethernet VPN).
Multicast and EVPN Comparison:
Option B: Both multicast and EVPN can be used for MAC learning in a VXLAN environment. Multicast
is a more traditional approach, while EVPN is more advanced and supports distributed MAC learning.
Option D: EVPN offers benefits such as fast convergence and rapid updates, making it more efficient
and scalable for modern data center environments.
Option E: Multicast does not require as many resources because it relies on traditional Layer 3
multicast mechanisms to distribute broadcast, unknown unicast, and multicast (BUM) traffic.
However, it can be less flexible and less scalable compared to EVPN.
Conclusion:
Option B: Correct—Both control planes facilitate MAC learning.
Option D: Correct—EVPN provides fast convergence and updates.
Option E: Correct—Multicast is resource-efficient but less flexible.
Question 4
You are asked for TX and RX traffic statistics for each interface to which an application server is
attached. The statistics need to be reported every five seconds. Using the Junos default settings,
which telemetry method would accomplish this request?
- A. gNMI
- B. SNMP
- C. Native Sensors
- D. OpenConfig
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Telemetry Methods in Junos:
Telemetry is used to collect and report data from network devices. For high-frequency statistics
reporting, such as every five seconds, you need a telemetry method that supports this level of
granularity and real-time monitoring.
Junos Native Sensors:
Option C: Native Sensors in Junos provide detailed, high-frequency telemetry data, including TX and
RX traffic statistics for interfaces. They are designed to offer real-time monitoring with customizable
sampling intervals, making them ideal for the five-second reporting requirement.
Conclusion:
Option C: Correct—Native Sensors in Junos are capable of providing the required high-frequency
telemetry data every five seconds.
Question 5
You are implementing seamless stitching between two data centers and have a proposed
configuration for a border leaf device.
In this scenario, which two statements are correct? {Choose two.)
- A. The translation-vni must match in both data centers.
- B. The translation-vni must be different in each data center.
- C. The ESI must be different in each data center.
- D. The ESI must match in both data centers.
Answer:
BD
Explanation:
Understanding Seamless Stitching:
Seamless stitching is used in EVPN to interconnect two data centers, allowing for consistent Layer 2
and Layer 3 connectivity across them. This is often achieved by translating VNIs (Virtual Network
Identifiers) between the data centers.
Translation-VNI:
Option B: The translation VNI must be different in each data center to ensure that traffic can be
correctly routed and distinguished as it crosses between the data centers. This differentiation helps
to maintain the integrity of the traffic flows and prevents any potential overlap or conflict in VNIs.
Ethernet Segment Identifier (ESI):
Option D: The ESI must match in both data centers to ensure that the same Ethernet segment (which
could be multihomed) is recognized consistently across the data centers. Matching ESIs are crucial for
maintaining a unified view of the Ethernet segment across the interconnected fabric.
Conclusion:
Option B: Correct—Translation VNIs must be unique to each data center for proper traffic distinction.
Option D: Correct—Matching ESIs are necessary to maintain consistent Ethernet segment
identification across both data centers.
Question 6
Exhibit.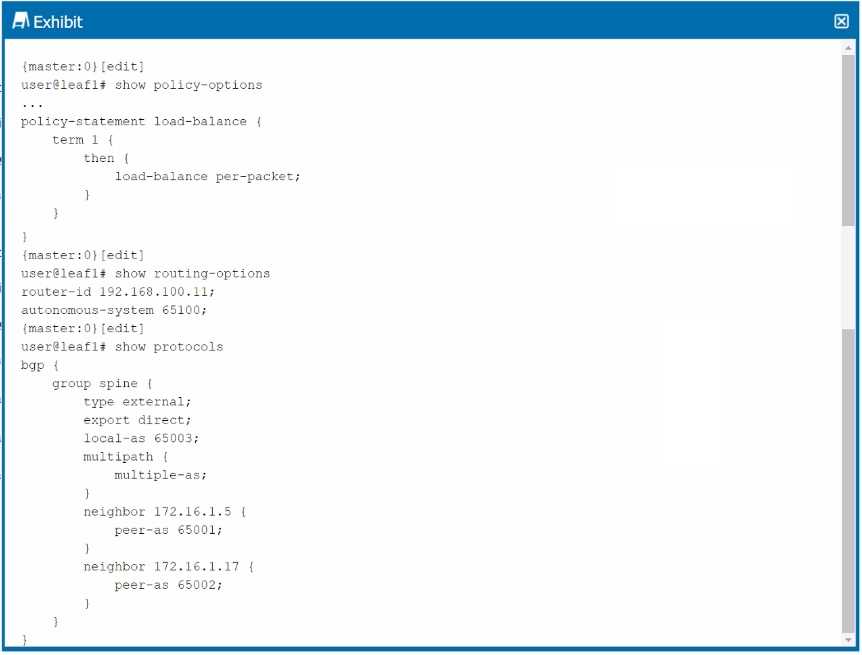
You are troubleshooting an IP fabric (or your data center. You notice that your traffic is not being load
balanced to your spine devices from your leaf devices. Referring to the configuration shown in the
exhibit, what must be configured to solve this issue?
- A. The load-balance policy must be applied to the forwarding table under the routing-options hierarchy.
- B. The multipast multiple -as configuration must be configured for each peer in the BGP spine group.
- C. The load-balance policy must be applied as an export policy to your BGP
- D. The load-balance policy must have a from statement that matches on protocol bgp.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
IP Fabric Load Balancing:
In the provided configuration, traffic is not being load-balanced to the spine devices. The issue likely
relates to how BGP routes are being selected and whether Equal-Cost Multi-Path (ECMP) is
functioning correctly.
Multipath Multiple-AS:
Option B: The multipath multiple-as configuration is essential when using BGP in an IP fabric where
devices belong to different Autonomous Systems (AS). This setting allows BGP to consider multiple
paths (even across different AS numbers) as equal cost, enabling ECMP and proper load balancing
across spine devices.
Conclusion:
Option B: Correct—The multipath multiple-as configuration is necessary for achieving ECMP and
effective load balancing in a multi-AS BGP environment.
Question 7
Exhibit.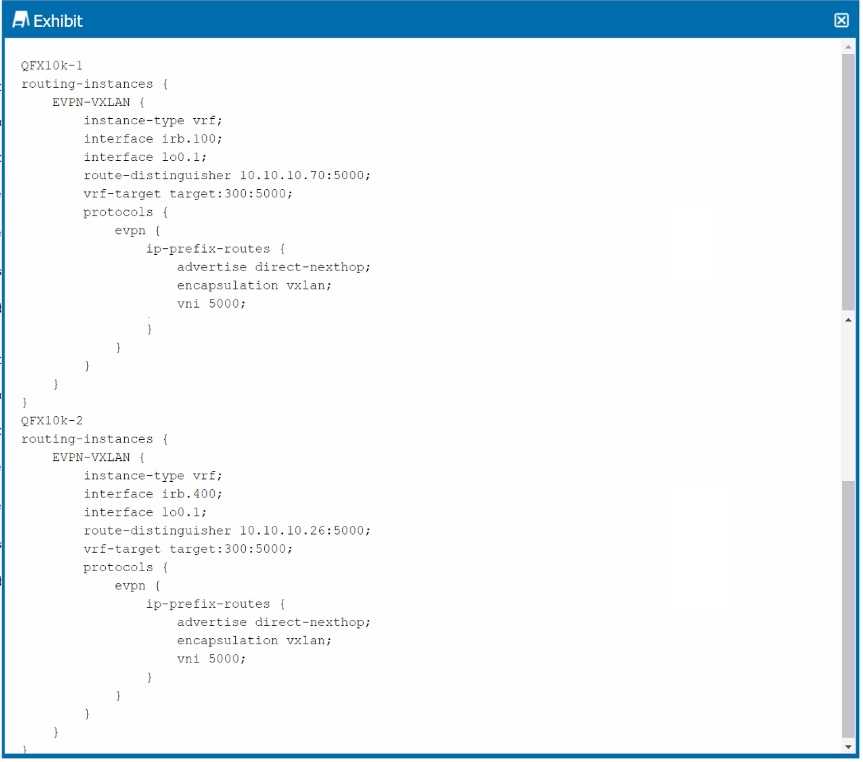
You have a sample configuration for connecting two sites through EVPN-VXLAN by exchanging IP
prefix routes.
Referring to the exhibit, which two statements regarding the configuration are true? {Choose two.)
- A. The advertise direct-nexthop option enables the receiver to resolve the next-hop route using only information carried in the Type 5 route.
- B. The advertise direct-nexthop option enables the receiver to resolve the next-hop route using only information carried in the Type 2 route.
- C. The VNI must match on all devices for the same customer.
- D. The VNI should be unique on all devices for each customer site.
Answer:
AC
Explanation:
EVPN-VXLAN Configuration:
The configuration provided in the exhibit shows an EVPN-VXLAN setup where IP prefix routes are
exchanged between two sites. The advertise direct-nexthop option and the VNI (Virtual Network
Identifier) settings are crucial in this context.
Advertise Direct-Nexthop:
Option A: The advertise direct-nexthop option ensures that the next-hop route is resolved using only
the information carried in the EVPN Type 5 route. Type 5 routes are used for IP prefix advertisement
in EVPN, which is key to enabling Layer 3 interconnectivity between different VXLAN segments.
VNI Consistency:
Option C: For the same customer across different devices, the VNI must be consistent. This
consistency ensures that all devices can correctly map traffic to the appropriate VXLAN segment,
maintaining seamless Layer 2 and Layer 3 connectivity.
Question 8
You are asked to interconnect Iwo data centers using a method that provides EVPN Type 2
connectivity, is highly scalable, and limits VXLAN tunnels between border leaf devices. What will
satisfy these requirements?
- A. over the top full-mesh interconnect
- B. EVPN Type 2 stretch
- C. IP VPN
- D. Type 2 seamless stitching
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Requirement Analysis:
The scenario requires a solution to interconnect two data centers that supports EVPN Type 2
connectivity. The solution must be highly scalable and must minimize the number of VXLAN tunnels
between border leaf devices.
Understanding Type 2 Seamless Stitching:
Option D: Type 2 seamless stitching is a method used in EVPN to provide Layer 2 connectivity (such as
MAC address mobility) across different VXLAN segments. It is scalable because it allows only
necessary tunnels to be established between border leaf devices, reducing the overhead of
maintaining a full mesh of VXLAN tunnels.
Conclusion:
Option D: Correct—Type 2 seamless stitching satisfies the requirement by enabling scalable, efficient
interconnection of two data centers with minimal VXLAN tunnels.
Question 9
Exhibit.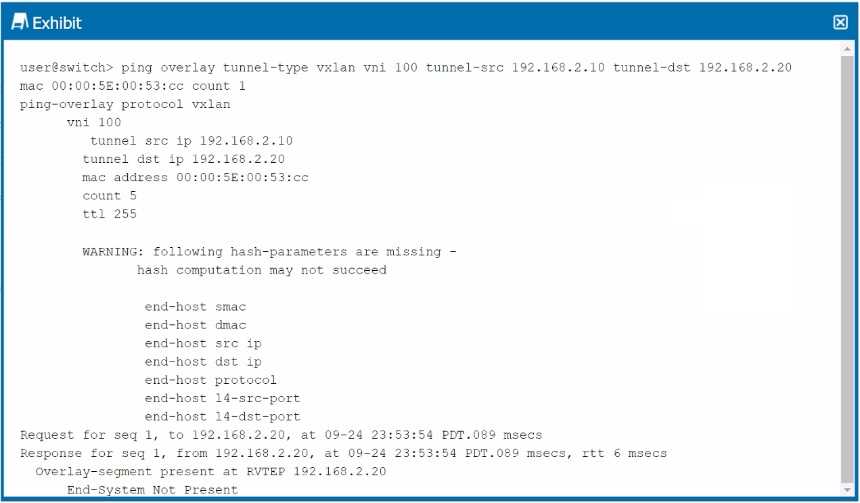
Referring to the exhibit, which statement is correct?
- A. VNI 100 is not configured on the remote VTEP.
- B. The MAC address is unknown and not in the forwarding table of the remote VTEP.
- C. The remote VTEP is not responding.
- D. The MAC address is known but not reachable by the remote VTEP
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Analyzing the Exhibit Output:
The command ping overlay tunnel-type vxlan is used to test the VXLAN tunnel between two VTEPs
(VXLAN Tunnel Endpoints). The output shows a warning about missing hash parameters, but more
importantly, it displays the result: End-System Not Present.
Understanding the Response:
The message End-System Not Present indicates that the remote VTEP (192.168.2.20) did not find the
MAC address 00:00:5E:00:53:CC in its forwarding table. This typically means that the MAC address is
unknown to the remote VTEP, and as a result, it could not forward the packet to the intended
destination.
Conclusion:
Option B: Correct—The MAC address is unknown and is not in the forwarding table of the remote
VTEP, which is why the system reports that the "End-System" is not present.
Question 10
You are deploying a Clos IP fabric with an oversubscription ratio of 3:1.
In this scenario, which two statements are correct? (Choose two.)
- A. The oversubscription ratio remains the same when you remove spine devices.
- B. The oversubscription ratio decreases when you add spine devices.
- C. The oversubscription ratio increases when you remove spine devices.
- D. The oversubscription ratio remains the same when you add spine devices.
Answer:
BC
Explanation:
Understanding Oversubscription in a Clos Fabric:
The oversubscription ratio in a Clos IP fabric measures the ratio of the amount of edge (leaf)
bandwidth to the core (spine) bandwidth. An oversubscription ratio of 3:1 means that there is three
times more edge bandwidth compared to core bandwidth.
Impact of Adding/Removing Spine Devices:
Option C: If you remove spine devices, the total available core bandwidth decreases, while the edge
bandwidth remains the same. This results in an increase in the oversubscription ratio because there
is now less core bandwidth to handle the same amount of edge traffic.
Option B: Conversely, if you add spine devices, the total core bandwidth increases. This decreases the
oversubscription ratio because more core bandwidth is available to handle the edge traffic.
Conclusion:
Option C: Correct—Removing spine devices increases the oversubscription ratio.
Option B: Correct—Adding spine devices decreases the oversubscription ratio.
Question 11
Exhibit.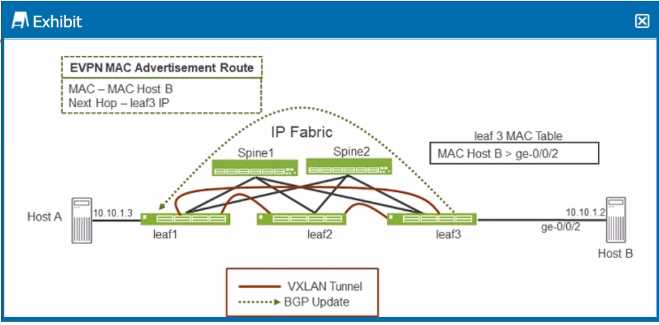
Referring to the exhibit, when Host A sends an ARP request for Host B's IP address, which Junos
feature does leaf1 require to send an ARP response back to Host A without having to send a
broadcast frame over the fabric?
- A. proxy ARP
- B. proxy NDP
- C. GARP
- D. DAD
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Scenario Overview:
In the exhibit, Host A is trying to resolve Host B's IP address (10.10.1.2) through ARP (Address
Resolution Protocol). Normally, an ARP request would be broadcasted over the network, and the
host owning the IP address (Host B) would respond.
Role of Proxy ARP:
Option A: Proxy ARP allows a router or switch (in this case, leaf1) to respond to ARP requests on
behalf of another host. Leaf1, knowing the MAC address of Host B through the EVPN MAC
advertisement, can reply to Host A's ARP request directly without broadcasting the request across
the entire network fabric. This feature reduces unnecessary traffic and increases network efficiency.
Conclusion:
Option A: Correct—Proxy ARP enables leaf1 to respond to Host A's ARP request for Host B's IP
without broadcasting over the IP fabric, thus providing the ARP response locally.
Question 12
Exhibit.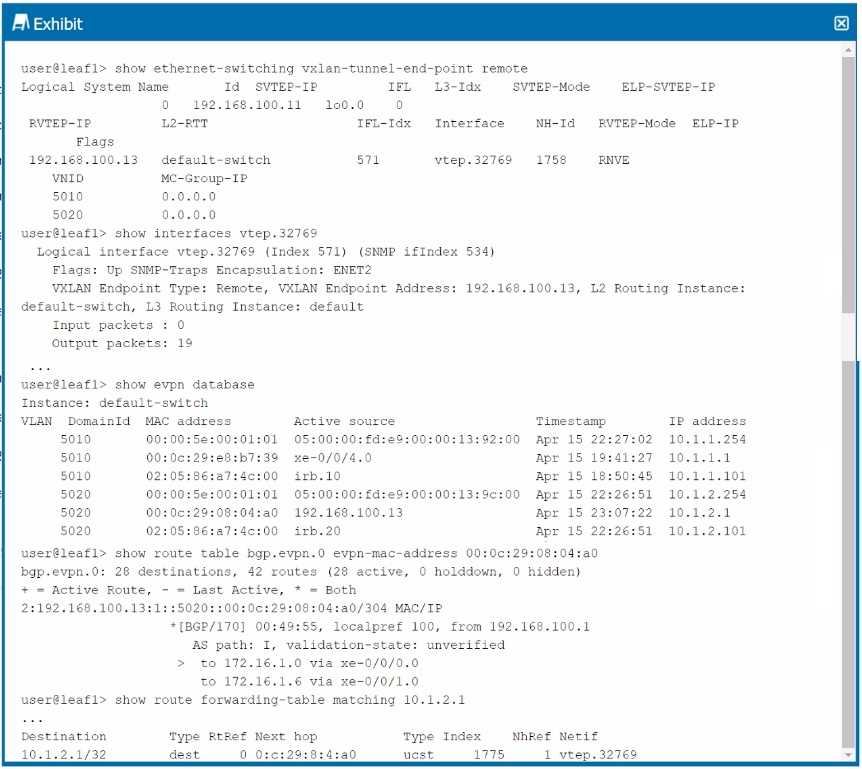
Referring to the exhibit, Host1 (10.1.1.1) is failing to communicate with Host2 (10.1.2.1) in a data
center that uses an ERB architecture. What do you determine from the output?
- A. The traffic is failing because load balancing is not configured correctly.
- B. The traffic is entering the VXLAN tunnel.
- C. Host1 and Host2 are directly connected to leaf1.
- D. The irb.20 interface is not configured on leaf1.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Understanding the Problem:
Host1 (10.1.1.1) is failing to communicate with Host2 (10.1.2.1) within an EVPN-VXLAN environment
using ERB architecture.
Analysis of the Exhibit:
The provided output includes information from the show route forwarding-table matching command
for IP 10.1.2.1. The next hop is shown as vtep.32769, which indicates that the traffic destined for
10.1.2.1 is being forwarded into the VXLAN tunnel with the correct VTEP (VXLAN Tunnel Endpoint).
Conclusion:
Option B: Correct—The traffic from Host1 is entering the VXLAN tunnel, as evidenced by the next hop
pointing to a VTEP. However, the issue could lie elsewhere, possibly with the remote VTEP, routing
configurations, or the receiving leaf/spine devices.
Question 13
Exhibit.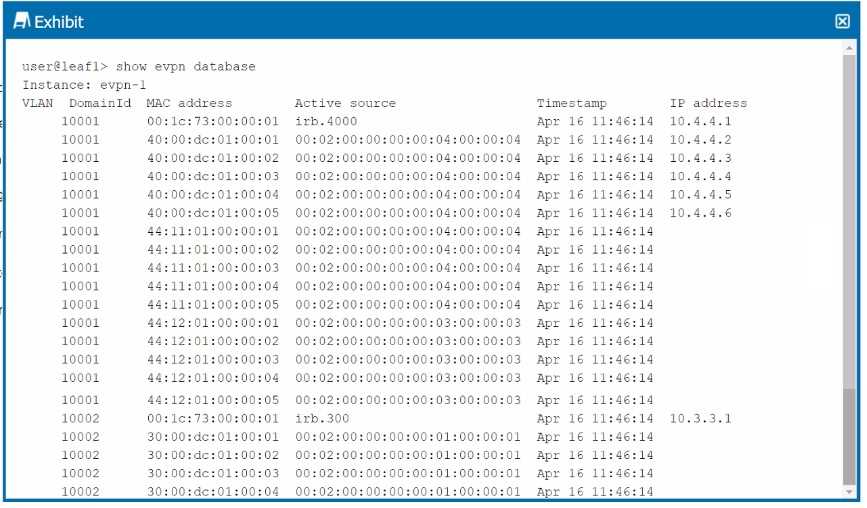
The exhibit shows the truncated output of the show evpn database command.
Given this output, which two statements are correct about the host with MAC address
40:00:dc:01:00:04? (Choose two.)
- A. The host is assigned IP address 10.4.4.5.
- B. The host is originating from irb.300.
- C. The host is located on VN110002.
- D. The host is originating from an ESI LAG.
Answer:
AD
Explanation:
Understanding the Output:
The show evpn database command output shows the MAC address, VLAN, active source, timestamp,
and IP address associated with various hosts in the EVPN instance.
Analysis of the MAC Address:
Option A: The MAC address 40:00:dc:01:00:04 is associated with the IP address 10.4.4.5, as indicated
by the output in the IP address column. This confirms that this host has been assigned the IP
10.4.4.5.
Option D: The active source for the MAC address 40:00:dc:01:00:04 is listed as
00:02:00:00:00:04:00:04:00:00:04:00:04, which indicates that the host is connected via an ESI
(Ethernet Segment Identifier) LAG (Link Aggregation Group). This setup is typically used in multi-
homing scenarios to provide redundancy and load balancing across multiple physical links.
Conclusion:
Option A: Correct—The host with MAC 40:00:dc:01:00:04 is assigned IP 10.4.4.5.
Option D: Correct—The host is originating from an ESI LAG, as indicated by the active source value.
Question 14
Exhibit.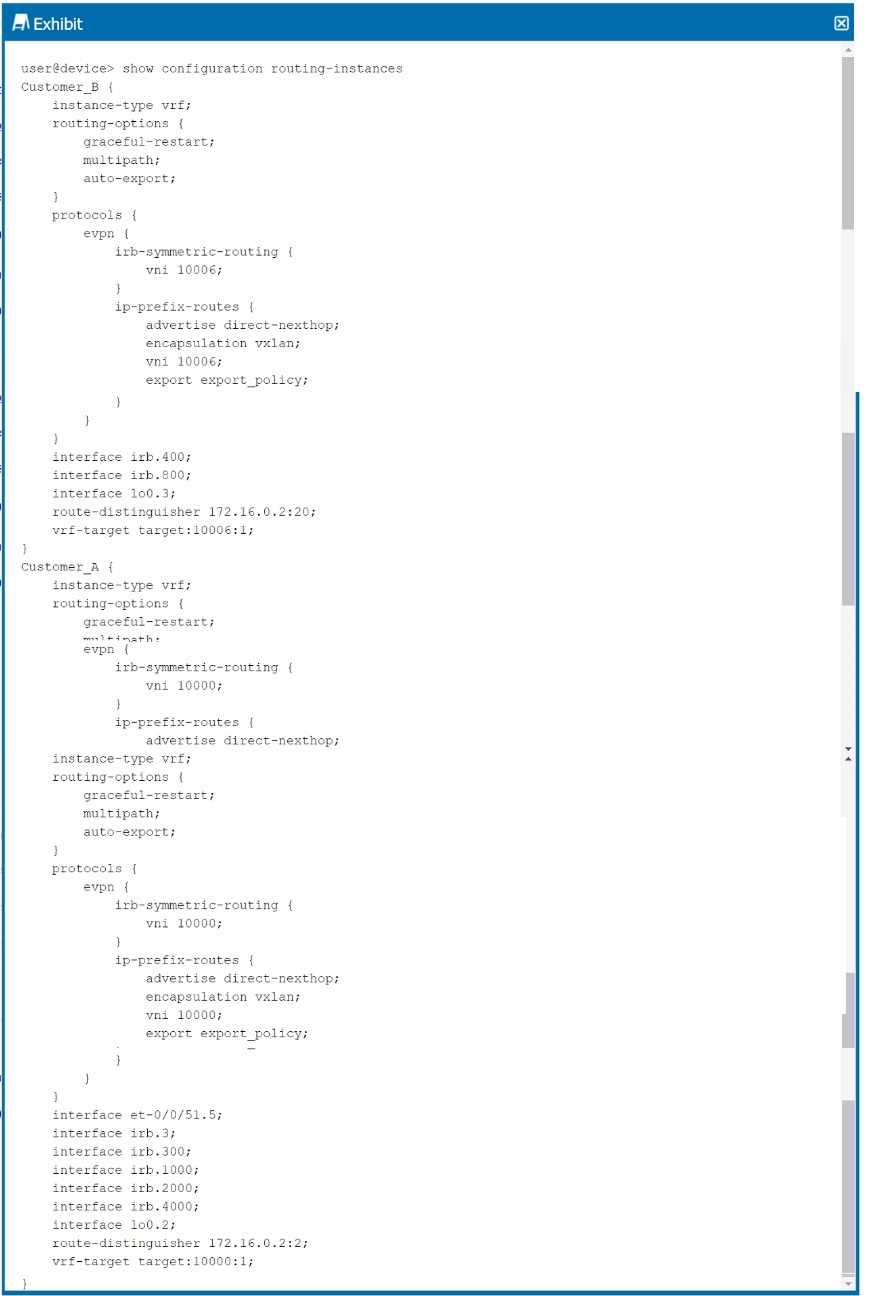
Referring to the configuration shown in the exhibit, assume that there is no external router present,
and that the configuration is fabric-only.
Which two statements are true about the example configuration? (Choose two.)
- A. VNI 10006 is assigned to vlan 800 (irb.800).
- B. Devices in irb.400 (vlan 400) are not able to communicate directly with devices in routing instance Customer A.
- C. Devices in routing instance Customer A are able to communicate with devices in routing instance Customer B
- D. Devices in irb.400 (vlan 400) and irb.800 (vlan 800) are able to communicate over the fabric.
Answer:
BD
Explanation:
Understanding the Configuration:
The exhibit shows configurations for two VRFs (Customer_A and Customer_B) with specific VLANs
and VNIs assigned. Each VRF has interfaces (IRBs) associated with particular VLANs.
Communication Between VLANs and Routing Instances:
Option B: VLAN 400 (irb.400) is part of Customer_B, and there is no direct connection or routing
between Customer_A and Customer_B in the configuration provided. Therefore, devices in irb.400
cannot communicate directly with devices in the Customer_A routing instance.
Option D: Since irb.400 (VLAN 400) and irb.800 (VLAN 800) are part of the same routing instance
(Customer_B), they can communicate over the fabric using VXLAN encapsulation.
Conclusion:
Option B: Correct—There is no direct communication between devices in irb.400 (Customer_B) and
routing instance Customer_A.
Option D: Correct—Devices in VLAN 400 and VLAN 800 can communicate within the Customer_B
routing instance over the fabric.
Question 15
You are asked to configure telemetry on the OFX Series devices in your data center fabric. You want
to use sensors that have a vendor-neutral data model Which type of sensor should you use in this
scenario?
- A. JTI OpenConfig sensors
- B. JTI native sensors
- C. Python sensors
- D. analog sensors
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Telemetry in Data Centers:
Telemetry allows for real-time monitoring of network devices by collecting and exporting data such
as interface statistics, routing table updates, and other key metrics.
Vendor-Neutral Data Models:
Option A: JTI (Junos Telemetry Interface) OpenConfig sensors use a vendor-neutral data model,
which is important for ensuring compatibility across different network devices and systems.
OpenConfig is an industry-standard model, which facilitates integration with various telemetry
collection systems.
Conclusion:
Option A: Correct—OpenConfig sensors provide a vendor-neutral solution for telemetry, ensuring
broad compatibility and flexibility in data center environments.