IBM C1000-138 Exam Questions
Questions for the C1000-138 were updated on : Mar 07 ,2026
Page 1 out of 4. Viewing questions 1-15 out of 60
Question 1
Within the client security policy, the credential extraction method is set to Form.
Which statement is a requirement in this case?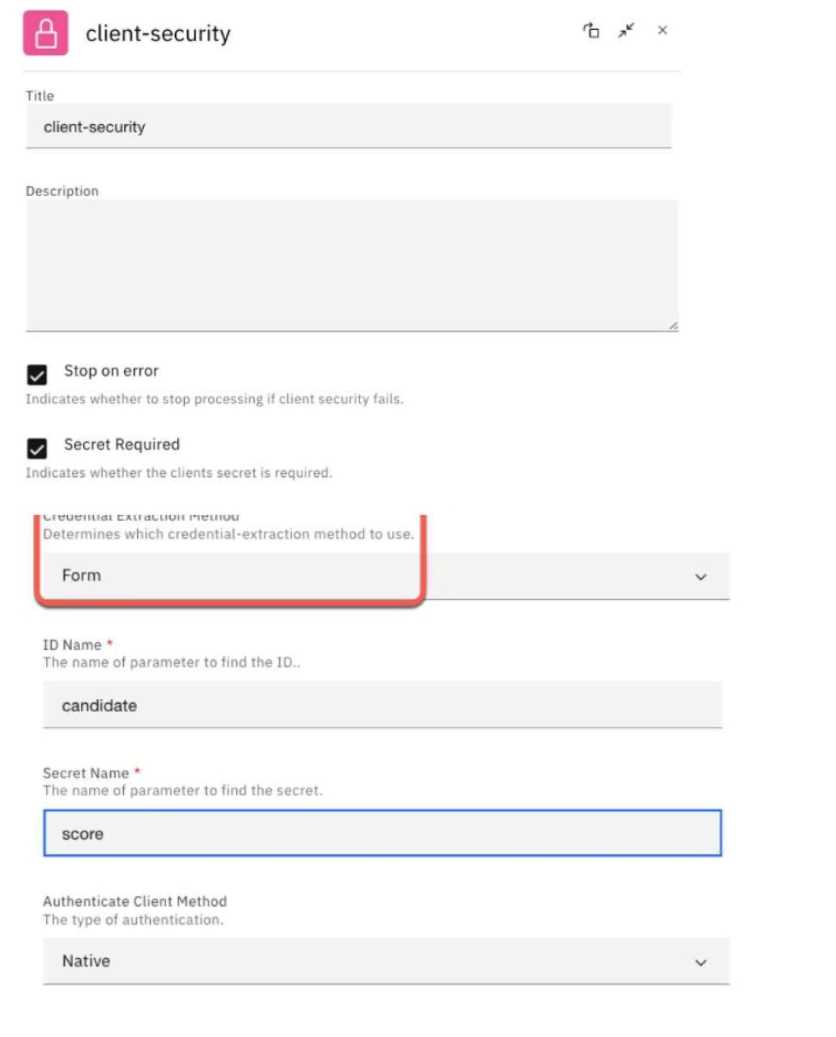
- A. "Stop on error" has to be active as well.
- B. Credentials have to be gathered via a custom form.
- C. A prefix will be added to the secret-name and id at runtime.
- D. Client id and secret must be supplied via a POST request.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
In IBM API Connect, when the credential extraction method is set to Form in the client security
policy, it means that the client credentials (such as the client ID and secret) must be supplied in a
specific format using a POST request. Specifically, the credentials are included in the body of the
request in a URL-encoded form. This is typical in OAuth 2.0 workflows where client credentials need
to be extracted from a form-based submission, often used in situations involving login or token
exchanges.
"Client id" and "secret" are provided in the request body through form fields, rather than being
passed in the URL or headers.
This method adheres to secure practices where sensitive credentials are sent via POST to avoid
exposing them in the URL.
Therefore, the correct statement is that client ID and secret must be supplied via a POST request
when using the Form credential extraction method.
Reference:
IBM API Connect Documentation
IBM API Connect v10.0.3 - Now Available
Question 2
DRAG DROP
Select all that apply
In what order do the following steps need to be performed, to enable CORS and restrict the pages
from where the API can be called in an OpenAPI 3.0 definition?
Answer:
None
Explanation:
To enable CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing) and restrict the pages from where the API can be
called in an OpenAPI 3.0 definition in IBM API Connect, the following steps should be performed in
the correct order:
Open the required API for editing: Start by opening the API definition that you want to modify to
enable CORS.
Select the Gateway tab and expand the settings section: Navigate to the Gateway tab and expand the
settings section to access the relevant configurations.
Add policy: In the API assembly, add a new policy. This will allow you to add specific configurations
for CORS.
Select and enable CORS: From the available policies, select the CORS policy and enable it. This step
ensures that CORS headers are added to the API responses.
Add allowed origins: Finally, specify the allowed origins that are permitted to make requests to the
API. This restricts access to certain domains or pages based on your configuration.
In summary, the correct order is:
Open the required API for editing.
Select the Gateway tab and expand the settings section.
Add policy.
Select and enable CORS.
Add allowed origins.
Question 3
DRAG DROP
Select all that apply
What is the correct order of these activities to create and then subscribe an application to a Product?
Answer:
None
Explanation:
To create and then subscribe an application to a product in IBM API Connect, the correct order of
activities would be as follows:
Log in to API Manager UI: The first step is to log into the API Manager user interface, where the APIs
and products are managed.
Go to Manage Catalogs and then the Catalog to work with: After logging in, navigate to the specific
Catalog where you want to manage the products and subscriptions.
Click on the Applications tab: Once in the Catalog, you need to navigate to the Applications tab,
which allows you to manage applications.
Add an Application: In the Applications tab, you can add a new application that will be subscribed to
an API product.
Fill the form and create it: After selecting to add an application, you must complete the required
form and create the application.
On the Applications tab, navigate to Create a subscription: With the application created, navigate to
the area where you can create a subscription for this application.
Select the Product/Plan combination for the API and create it: Finally, select the appropriate product
and plan combination to which the application will subscribe and complete the subscription process.
In summary, the correct order is:
Log in to API Manager UI.
Go to Manage Catalogs and then the Catalog to work with.
Click on the Applications tab.
Add an Application.
Fill the form and create it.
On the Applications tab, navigate to Create a subscription.
Select the Product/Plan combination for the API and create it.
Question 4
DRAG DROP
Select all that apply
A Catalog holds some published API Products before enabling Spaces.
What are the steps that need to be done for spaces to work?
Answer:
None
Explanation:
In IBM API Connect, when enabling Spaces in a Catalog that already holds published API Products,
there are specific steps that need to be followed to ensure proper transition and functionality.
Here are the necessary steps:
Retire published Products: First, you need to retire the existing published products. This is necessary
because spaces require a different organization of products, and retiring the current products
prevents conflicts.
Remove all published Products: Once the products are retired, they need to be removed from the
Catalog before you enable spaces. This ensures that no previously published products interfere with
the spaces configuration.
Enable Spaces: After retiring and removing the published products, you can proceed to enable
Spaces within the Catalog. Spaces allow for more granular organization within a Catalog.
Republish Products: Once Spaces are enabled, you can republish the API products within the correct
spaces. This step ensures that the products are organized within the spaces structure in the Catalog.
Recreate application subscriptions: After republishing the products, you will need to recreate any
application subscriptions to ensure that applications are correctly subscribed to the republished
products within their respective spaces.
Thus, the correct steps for enabling spaces in a Catalog that holds published API products are:
Retire published Products.
Remove all published Products.
Enable Spaces.
Republish Products.
Recreate application subscriptions.
These steps ensure that the Catalog and its associated products are restructured correctly after
enabling Spaces.
Question 5
DRAG DROP
Select all that apply
Given an API that executes on an API Gateway service with pre-request, post-request, and error
global policies, what is the order that the different assemblies will be executed if the process fails
while executing the post-request?
Answer:
None
Explanation:
In IBM API Connect, the sequence of execution for global policies and API assembly is crucial,
especially in cases where the process fails. If the process fails while executing the post-request, the
execution order is as follows:
Pre-request global policy: This is the first to execute before the API request is processed.
API assembly: After the pre-request global policy, the API assembly (which contains the core business
logic of the API) is executed.
Post-request global policy: This is executed after the API assembly has been processed, but if the
process fails here, the post-request global policy may not complete.
Error global policy: When the failure occurs, the error global policy is triggered to handle any errors
that occur during the execution of the API, specifically after the failure in the post-request.
Thus, if a failure occurs in the post-request global policy, the subsequent step would involve invoking
the Error global policy to handle the failure. The execution order is as follows:
Pre-request global policy
API assembly
Post-request global policy (failure occurs here)
Error global policy
This is the correct flow based on API execution steps in the presence of global policies.
Question 6
Which two statements about the following code snippet are true?
- A. The value to the param1 variable will be provided by the application calling an API with the policy.
- B. It updates the pre-defined 'set-variable' policy.
- C. The action type can be 'append'.
- D. The policy sets a variable called param1.
- E. The value to the param1 variable will be provided by the API developer.
Answer:
AD
Explanation:
The given code snippet represents a configuration for the "set-variable" policy in IBM API Connect.
This policy is used to define and set variables dynamically within the API assembly flow.
Statement D is true because the code explicitly sets a variable named param1 using the "set-
variable" policy.
Statement A is also true as the value assigned to param1 is derived from
${local.parameter.credential}, which indicates that the value is dynamically provided by the
application calling the API. The placeholder ${local.parameter.credential} implies that the credential
parameter is provided by the calling application.
Reference:
IBM API Connect Assembly Policies Documentation
Question 7
The DevOps team would like to incorporate API unit testing into the build and deploy step.
What could the API Connect Test application create to allow unit testing of their APIs?
- A. API Hooks
- B. API JUnit snippets
- C. Mock tests
- D. DataPower loopbacks
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The API Connect Test application can create mock tests to allow unit testing of APIs. Mock tests
simulate the behavior of real APIs, allowing developers to test their code in isolation without relying
on external dependencies. This can help to improve the quality and reliability of APIs.
Reference:
IBM API Connect: API Connect Test Application
IBM API Connect: Unit Testing APIs
Question 8
What is the effect of enabled Spaces for the management of Consumer (applications, subscriptions,
etc.)?
- A. There is no visible change.
- B. Only analytics is specific per Space.
- C. Subscription approvals and analytics are specific per Space.
- D. Consumers, applications, subscriptions approvals, and analytics are now specific per Space.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
When Spaces are enabled in API Connect, Consumers, applications, subscriptions approvals, and
analytics are now specific per Space. This means that each Space becomes an isolated environment
for managing and controlling API usage within that specific context.
Reference:
IBM API Connect: Managing Spaces
IBM API Connect: Understanding Spaces
Question 9
For the policy JSON to XML to work, what needs to be followed for the Datapower API Gateway?
- A. Nothing needs to be done the policy can directly follow the invoke policy.
- B. Input for the policy needs to be parsed data.
- C. The service to perform the transformation needs to be configured.
- D. The policy needs to be configured with the corresponding schemas to perform the transformation.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
For the JSON to XML policy to work on the DataPower API Gateway, you need to configure the policy
with the corresponding schemas to perform the transformation. The schemas define the structure
and data types of the JSON and XML formats, allowing the policy to accurately convert between the
two.
Reference:
IBM API Connect: DataPower API Gateway Policies
IBM API Connect: JSON to XML Policy
Question 10
Which statement is correct about superseding one Product with another?
- A. The Product to be superseded must be in the Staged, Retired, or Deprecated state.
- B. The Product that was superseded is in the Retired state.
- C. Existing customers of the Product that was superseded are automatically migrated to the superseding product.
- D. If the access to the superseding Product is more restrictive than the Product to be superseded, the supersede operation fails.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
When one Product is superseded by another in IBM API Connect, it is essential that the new
(superseding) Product does not have more restrictive access controls than the original Product. If the
superseding Product has more restrictive access policies, the supersede operation will fail because it
could potentially disrupt access for existing customers or violate their expectations and agreements.
Reference:
IBM API Connect Product Superseding Documentation
Question 11
Which set of APIs should be used to register users in the Developer Portal, create applications, and
subscribe to APIs?
- A. Management APIs
- B. Consumer APIs
- C. Subscription APIs
- D. Portal Admin APIs
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The Consumer APIs should be used to register users in the Developer Portal, create applications, and
subscribe to APIs. These APIs provide the necessary endpoints and functionality for Consumers to
interact with the Developer Portal and manage their API usage.
Reference:
IBM API Connect: Consumer APIs
IBM API Connect: Using the Consumer APIs
Question 12
An app developer has registered an app and has received a Client ID and secret.
Where can the developer request an additional Client ID and secret?
- A. Use the Portal admin Ul to enable the multiple Client ID option.
- B. An additional Client ID and secret can be added on the Subscriptions tab.
- C. Use the app alias link on the existing app page.
- D. Only one Client ID and secret is allowed per app.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
In IBM API Connect, an app is typically associated with a single Client ID and secret to maintain a
unique identity and secure access to APIs. Each app is expected to use this unique Client ID and
secret for authentication and authorization purposes. Therefore, only one Client ID and secret pair is
allowed per app, and additional Client IDs and secrets cannot be requested or generated for the
same app.
Question 13
A developer has asked to modify the default global behavior of ratelimit enforcement to allow
execution of the API even if the ratelimit is exceeded.
When creating the global policy yaml file which is true?
- A. Add to the info section "full-custom: true".
- B. At the beginning of the YAML add global-reflow-policy: 1.0.0.
- C. At the beginning of the YAML add policy: 1.0.0.
- D. Ensure the version at the beginning of the YAML is the same as the version in the info section.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
When creating a global policy YAML file to modify the default behavior of rate limit enforcement in
IBM API Connect v10.0.3, it is crucial to ensure that the version specified at the beginning of the
YAML file matches the version in the info section. This alignment is necessary for the system to
recognize and apply the correct policy settings across all configurations.
Other options are incorrect:
Option A is not a valid configuration setting for global policies.
Option B and C do not represent the correct approach to configuring global policy YAML files.
Reference:
IBM API Connect v10.0.3 Documentation:
Creating and Modifying Global Policies
Question 14
A developer would like to clean up old Products on the development environment.
Which CLI command parameters can be used to find all Products?
- A. catalog:get-products
- B. products : list-all —scope catalog
- C. products:list —realm [providerOrg]
- D. products:list --showall
Answer:
C
Explanation:
To find all Products in a specific Provider organization using the API Connect CLI, you can use the
following command:
products:list --realm [providerOrg]
This command will list all Products that belong to the specified Provider organization. You can then
use additional filtering options to find Products based on specific criteria, such as their creation date
or status.
Reference:
IBM API Connect: API Connect CLI Reference
IBM API Connect: Managing Products with the CLI
Question 15
Which of these actions is allowed?
- A. Linking the same API and version inside different Products
- B. Linking the same Product and version inside different APIs
- C. Reusing the same Plan inside different APIs
- D. Linking the same Product and version several times on the same Space
Answer:
A
Explanation:
In IBM API Connect v10.0.3, it is possible to link the same API and version inside different Products.
This flexibility allows an API to be offered under multiple Products, each potentially having different
plans, pricing, or rate limits, depending on the business needs.
Other options are incorrect:
Option B: Linking the same Product and version inside different APIs does not apply.
Option C: Plans are linked to Products, not directly to APIs.
Option D: Linking the same Product and version multiple times in the same space is not allowed.
Reference:
IBM API Connect v10.0.3 Documentation:
Managing APIs and Products