Huawei H12-821 Exam Questions
Questions for the H12-821 were updated on : Feb 18 ,2026
Page 1 out of 15. Viewing questions 1-15 out of 219
Question 1
On the OSPF network shown in the figure, R1, R2, and R3 run OSPF, and R1 advertises four VPN
routes to OSPF. A filter-policy needs to achieve the following goal: R1's and R3's routing tables
contain the routes to 192.168.3.0/24, but R2's routing table does not. Which of the following filter-
policies cannot meet this requirement?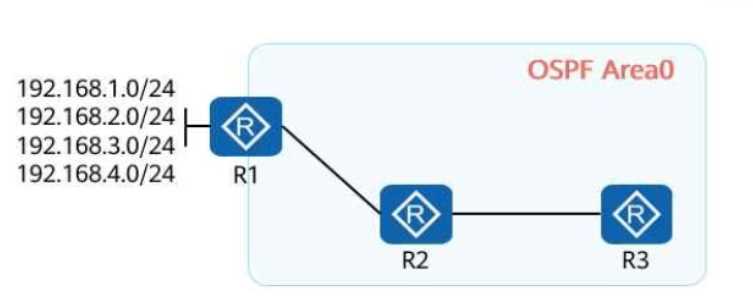
- A. A filter-policy on R2 for filtering received routes
- B. A filter-policy on R2 for filtering the routes to be advertised
- C. A filter-policy on R1 for filtering the routes to be imported
- D. A filter-policy on R1 for filtering the imported routes to be advertised
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Goal Analysis:
Requirement:
The route to 192.168.3.0/24 must exist in R1's and R3's routing tables.
The route must not exist in R2's routing table.
This requires filtering to ensure the route is either:
Blocked on R2's routing table (via filtering on R2), or
Blocked before it is advertised to R2.
Analysis of Each Option:
Option A (Filter-policy on R2 for filtering received routes):
Applying a filter-policy on R2 to filter received routes will block the route from entering R2's routing
table but still allow it to propagate to R3.
This meets the requirement.
Option B (Filter-policy on R2 for filtering the routes to be advertised):
Blocking the advertisement of routes from R2 to other routers does not affect the routes received by
R2 itself.
This does not meet the requirement but does not affect the propagation to R3.
This is valid if the received route is blocked.
Option C (Filter-policy on R1 for filtering the routes to be imported):
If the route is filtered on R1 during the import phase, the route will not exist in R1’s routing table and
thus cannot be advertised to either R2 or R3.
This fails to meet the requirement because the route must exist in R1's and R3's routing tables.
Option D (Filter-policy on R1 for filtering the imported routes to be advertised):
Filtering routes on R1 before advertising to R2 will prevent R2 from receiving the route but allow R1
to advertise the route to R3.
This meets the requirement.
Correct Option:
C (Filter-policy on R1 for filtering the routes to be imported): This will prevent the route from existing
in both R1 and R3, violating the stated requirement.
Reference:
HCIA-Datacom Study Guide, Chapter: OSPF Route Filtering
Huawei OSPF Configuration and Filtering Methods
Question 2
On the OSPF network shown in the figure, an adjacency has been established between R1 and R2. An
engineer configures the commands in the figure on R2. In this case, which of the following routing
entries may exist in the routing table of R2?
- A. 10.1.4.0/24
- B. 10.1.3.0/24
- C. 10.1.2.0/24
- D. 10.1.1.0/24
Answer:
ABC
Explanation:
Configuration Analysis:
On R2, the following configuration has been applied:
acl 200
rule deny source 10.1.0.0 0.0.3.0
rule permit
#
ospf 1
filter-policy 2000 import
This configuration uses ACL 200 to filter routes during import into the OSPF routing table on R2.
Rule deny source 10.1.0.0 0.0.3.0: Blocks routes in the range 10.1.0.0/24 to 10.1.3.0/24 (inclusive).
Rule permit: Allows all other routes to be imported.
Impact of ACL 200 on Route Import:
10.1.0.0/24 to 10.1.3.0/24: These subnets are explicitly denied by ACL 200 and will not appear in R2's
routing table.
10.1.4.0/24 and beyond: These subnets are permitted by the rule permit statement and will be
imported into R2's routing table.
Routing Table Entries on R2:
Option A (10.1.4.0/24): Exists in R2's routing table because it is permitted.
Option B (10.1.3.0/24): Does not exist because it is denied by ACL 200.
Option C (10.1.2.0/24): Does not exist because it is denied by ACL 200.
Option D (10.1.1.0/24): Does not exist because it is denied by ACL 200.
Correct Options:
A (10.1.4.0/24)
Reference:
HCIA-Datacom Study Guide, Chapter: OSPF Route Filtering
Huawei ACL Configuration for Route Policies
Question 3
On a broadcast IS-IS network shown in the following figure, a DIS needs to be elected to create and
update pseudonodes. Which of the following routers is elected as the DIS?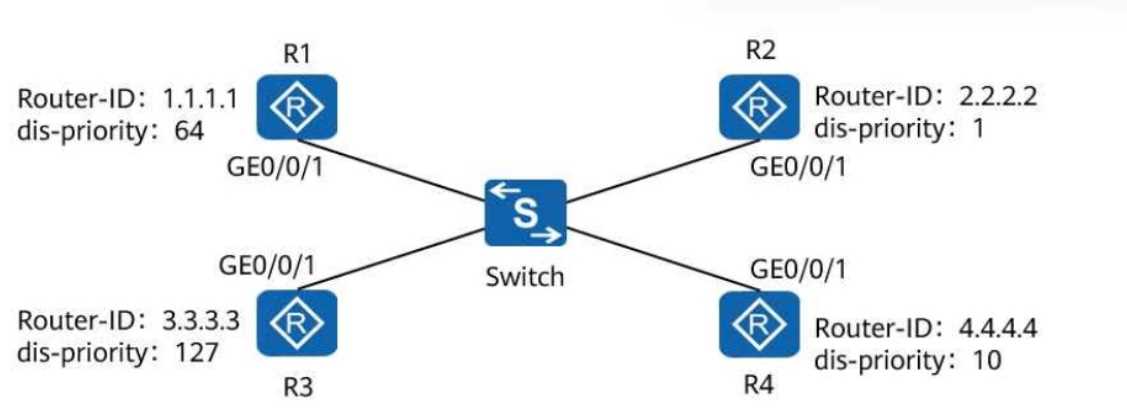
- A. R1
- B. R3
- C. R4
- D. R2
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Understanding DIS Election in IS-IS:
On an IS-IS broadcast network, a Designated Intermediate System (DIS) is elected to create and
update pseudonodes for efficient communication.
The election is based on the following criteria:
DIS Priority: The router with the highest priority is elected as the DIS.
Router ID (tie-breaker): If priorities are equal, the router with the highest Router ID is elected.
Analyzing the DIS Priorities and Router IDs:
R1: Priority = 64, Router ID = 1.1.1.1
R2: Priority = 1, Router ID = 2.2.2.2
R3: Priority = 127, Router ID = 3.3.3.3
R4: Priority = 10, Router ID = 4.4.4.4
Among the routers, R3 has the highest DIS priority (127), making it the DIS.
Correct Option:
Option B (R3): Correct, as R3 has the highest priority.
Option A (R1): Incorrect, as its priority is lower (64).
Option C (R4): Incorrect, as its priority is lower (10).
Option D (R2): Incorrect, as its priority is the lowest (1).
Reference:
HCIA-Datacom Study Guide, Chapter: IS-IS DIS Election
Huawei IS-IS Configuration and DIS Role Details
Question 4
On the campus OSPF network shown in the following figure, the interfaces connecting the five
routers are GE interfaces, and their costs are not changed. The import-route command is run on R1.
After the network converges, the route to the server at 192.168.1.0/24 is queried on R2. Which of
the following is the cost of this route?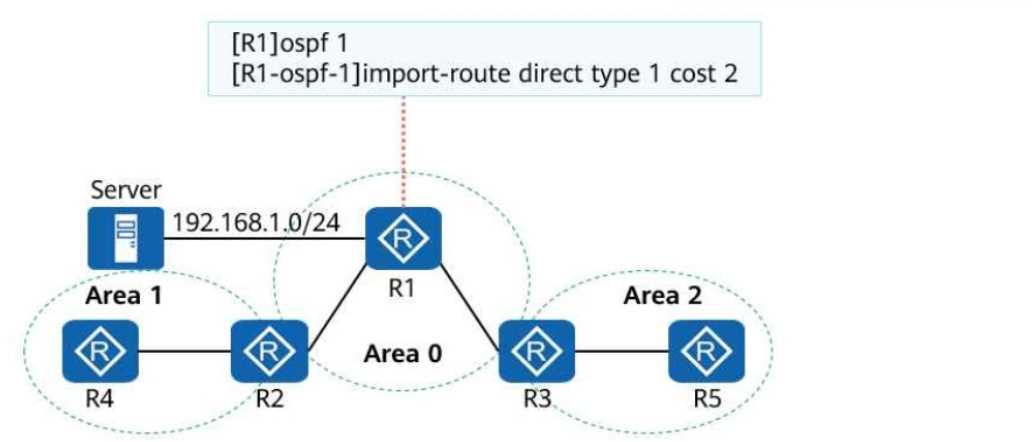
- A. 2
- B. 4
- C. 3
- D. 1
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Understanding the Network Setup:
The OSPF network consists of three areas (Area 1, Area 0, and Area 2).
The server's subnet 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected to R1 and imported into OSPF using the
command:
import-route direct type 1 cost 2
The type 1 specifies the route as an OSPF Type 1 external route, meaning both the external cost and
the internal OSPF cost will be included when calculating the total cost.
The external cost specified for the imported route is 2.
Cost Calculation to R2:
The interfaces between the routers are GE interfaces, and the default cost for GE interfaces is 1.
The path from R2 to the server goes through the following hops:
R2 → R1: Cost = 1 (intra-area link).
R1 → Server: External cost = 2 (specified in the import-route command).
Total cost to R2:
Intra-area cost (1) + External cost (2) = 3
Verification of Each Option:
Option A (2): Incorrect. This only accounts for the external cost, ignoring the internal OSPF cost.
Option B (4): Incorrect. This overestimates the cost by adding an extra hop.
Option C (3): Correct. The total cost is 3 (1 for the intra-area link + 2 for the external cost).
Option D (1): Incorrect. This ignores the external cost of the imported route.
Reference:
HCIA-Datacom Study Guide, Chapter: OSPF Route Types and Cost Calculation
Huawei OSPF Cost Configuration Details
Question 5
A wide area network (WAN) is a remote network that connects local area networks (LANs) or
metropolitan area networks (MANs) in different areas for communication purposes. It is typically
used to interconnect campus networks or data center networks.
- A. TRUE
- B. FALSE
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Step-by-Step
WAN Definition:
A WAN is a large-scale network spanning a wide geographical area, connecting smaller networks
such as LANs and MANs.
Use Cases:
WANs are commonly used for interconnecting campus networks, branch offices, and data centers
over long distances.
Correct Statement:
The statement accurately describes the purpose and scope of WANs.
Reference:
HCIA-Datacom Study Guide, Chapter: WAN Fundamentals
Huawei Networking Basics
Question 6
On a WLAN, the HSB service sets up an HSB channel between two devices that back up each other,
maintains the channel status, and backs up dat
a. Which of the following can HSB back up in real time?
- A. CAPWAP tunnel information
- B. DHCP address information
- C. AP entries
- D. User data information
Answer:
A, C, D
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Step-by-Step
HSB (Hot Standby Backup) Service:
HSB is used on WLAN controllers to back up critical information in real time to a backup device,
ensuring service continuity in case of failures.
Backed-Up Information:
CAPWAP Tunnel Information (A): Essential for maintaining connections between APs and controllers.
AP Entries (C): Information about connected APs is backed up.
User Data Information (D): Includes client authentication and session details.
Incorrect Option:
DHCP Address Information (B): Not part of HSB's responsibilities, as DHCP is handled separately.
Reference:
HCIA-Datacom Study Guide, Chapter: WLAN Redundancy with HSB
Huawei HSB Configuration Guide
Question 7
On an enterprise WLAN where Portal authentication is deployed, an AC functions as an access device
and communicates with a Portal server using the Portal protocol. Which of the following statements
are true about the Portal protocol?
- A. The HTTP or HTTPS protocol can be used as the Portal access or authentication protocol.
- B. By default, the access device processes Portal protocol packets through port 2000.
- C. By default, the device uses the destination port number 50100 to proactively send packets to the Portal server.
- D. Portal protocol packets are transmitted over TCP.
Answer:
A, D
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Step-by-Step
Portal Authentication:
Portal authentication uses a web-based mechanism where clients are redirected to a login page.
Communication between the access device and Portal server uses HTTP or HTTPS protocols.
Correct Statements:
Option A: HTTP or HTTPS is used for Portal authentication.
Option D: Portal protocol packets are transmitted over TCP for reliable communication.
Incorrect Statements:
Option B: Port 2000 is not the default for processing Portal packets.
Option C: The default destination port for communication with the Portal server is not 50100.
Reference:
HCIA-Datacom Study Guide, Chapter: WLAN Portal Authentication
Huawei WLAN Authentication Protocols
Question 8
iMaster NCE-Campus can be used as an authentication server on a WLAN to authenticate STAs.
- A. TRUE
- B. FALSE
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Step-by-Step
iMaster NCE-Campus Overview:
iMaster NCE-Campus is Huawei’s network management platform for managing and controlling
campus networks.
It supports user authentication, including STA (Station) authentication, in WLAN environments.
Authentication Modes Supported:
iMaster NCE-Campus integrates with AAA (RADIUS) servers to perform authentication for wireless
clients.
Correct Statement:
The platform can function as an authentication server for WLAN STAs.
Reference:
HCIA-Datacom Study Guide, Chapter: WLAN Management with iMaster NCE-Campus
Huawei iMaster NCE-Campus Product Overview
Question 9
After the administrator of an enterprise deploys a DHCP server, employees complain that their
clients cannot obtain IP addresses from the DHCP server. Which of the following may cause this
problem?
- A. Multiple DHCP servers are configured.
- B. STP is enabled on the DHCP server.
- C. The DHCP function is disabled by default, and the administrator forgets to enable the DHCP function.
- D. DHCP clients and the DHCP server are on different network segments, and no DHCP relay agent is configured on the network.
Answer:
C, D
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Step-by-Step
DHCP Configuration Issues:
Option C: The DHCP function is disabled by default on Huawei devices. If the administrator forgets to
enable it, clients cannot receive IP addresses.
Option D: DHCP uses broadcast messages, which do not traverse routers. If the clients and DHCP
server are on different subnets, a DHCP relay agent must be configured.
Other Options:
Option A: Multiple DHCP servers can coexist as long as their IP address pools do not overlap. This is
unlikely to cause the problem.
Option B: STP does not affect DHCP operations unless it delays port activation, which is uncommon in
this scenario.
Reference:
HCIA-Datacom Study Guide, Chapter: DHCP Configuration and Troubleshooting
Huawei DHCP Relay Agent Configuration
Question 10
When deploying a VRRP network, an enterprise administrator sets the virtual IP address to
192.168.1.254 and VRID to 1. Which of the following is the virtual MAC address after the network
becomes stable?
- A. 0000-5e01-0101
- B. 0000-5e01-0254
- C. 0000-5e00-0101
- D. 0000-5e00-0254
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Step-by-Step
VRRP Virtual MAC Address Format:
The VRRP virtual MAC address is generated using the format:
0000-5e00-01XX, where XX represents the VRID in hexadecimal.
Calculation:
VRID = 1 → Hexadecimal = 01.
Virtual MAC = 0000-5e00-0101.
Correct Option:
C (0000-5e00-0101).
Reference:
HCIA-Datacom Study Guide, Chapter: VRRP MAC Address Format
Huawei VRRP Configuration Guidelines
Let me continue with the next set of questions!
Question 11
Which of the following is used as the destination port for single-hop BFD?
- A. UDP port 3784
- B. UDP port 4784
- C. TCP port 3784
- D. TCP port 4784
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Step-by-Step
Single-Hop BFD:
Single-hop BFD is used for detecting link failures in directly connected devices.
It uses UDP port 3784 for communication.
Multi-Hop BFD:
For multi-hop scenarios, BFD uses UDP port 4784 to ensure end-to-end connectivity.
Incorrect Options:
TCP ports 3784 and 4784 (C and D): BFD does not use TCP.
Reference:
HCIA-Datacom Study Guide, Chapter: BFD Ports and Functions
Huawei BFD Configuration Details
Question 12
During routine maintenance, an enterprise administrator runs a command to check VRRP group
information. Which of the following statements is false about the command output?
yaml
CopyEdit
<HUAWEI> display vrrp verbose
Vlanif100 | Virtual Router 1 State: Master
Virtual IP: 10.1.1.100
Master IP: 10.1.1.2
PriorityRun: 120 PriorityConfig: 120
DR: None BDR: None MTU: 0
Preempt: YES Delay Time: 20s
Remain: --
Track: YES Priority Reduced: 20
Auth Type: MD5
BFD-session State: UP
- A. Preemption is enabled for the VRRP group.
- B. This VRRP group is an mVRRP group.
- C. Authentication is enabled for the VRRP group.
- D. The ID of the VRRP group is 1.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Step-by-Step
Analysis of VRRP Configuration:
Option A (Preemption): Correct. The output explicitly states that preemption is enabled.
Option C (Authentication): Correct. Authentication is enabled using MD5.
Option D (Group ID): Correct. The VRRP group ID is explicitly stated as 1.
False Statement:
Option B (mVRRP Group): The output does not indicate this is an mVRRP (Multicast VRRP) group. This
feature must be explicitly configured and is not enabled by default.
Reference:
HCIA-Datacom Study Guide, Chapter: VRRP Configuration Details
Huawei VRRP Command Reference
Question 13
BFD provides fast fault detection independent of media and routing protocols. To use this mechanism
to detect link connectivity, devices at both ends must support this feature.
- A. TRUE
- B. FALSE
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Step-by-Step
Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD):
BFD is a lightweight protocol that provides rapid fault detection on links independent of the
underlying routing protocol or media.
Requirements for BFD:
Both devices at the endpoints of the link must support and configure BFD for it to operate.
If one device does not support BFD, the feature cannot be used for link detection.
Reference:
HCIA-Datacom Study Guide, Chapter: BFD Overview
Huawei BFD Configuration Guidelines
Question 14
When a packet passes through a firewall, the firewall creates a session connection for the packet to
guide subsequent forwarding of the packet. However, the firewall does not create session entries for
all packets. For which of the following packets does the firewall not create session entries when the
packet reaches the firewall?
- A. ICMP ping packet
- B. GRE packet
- C. Subsequent fragment
- D. UDP packet
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Step-by-Step
Session Creation in Firewalls:
Firewalls create session entries for packets requiring stateful inspection (e.g., TCP, UDP, ICMP, and
GRE).
Subsequent fragments of large packets do not require new sessions. Instead, they are processed
based on the session created for the first fragment.
Correct Option:
C (Subsequent Fragment): Does not trigger a new session entry as it belongs to an existing session.
Reference:
HCIA-Datacom Study Guide, Chapter: Firewall Session Handling
Huawei Fragmentation Processing in Firewalls
Question 15
If the interval for two consecutive packets of a TCP session reaching the firewall is longer than the
aging time of the session, the firewall deletes the session information from the session table to
ensure network security.
- A. TRUE
- B. FALSE
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Step-by-Step
Firewall Session Table:
A session table is used to track active sessions. If a session remains idle for longer than the
configured aging time, it is removed to free resources and enhance security.
TCP Session Timeout:
If the interval between two packets exceeds the session timeout, the firewall deletes the session
information, requiring the session to be re-established.
Reference:
HCIA-Datacom Study Guide, Chapter: Firewall Session Management
Huawei Firewall TCP Session Timeout Configuration