HP HPE7-J02 Exam Questions
Questions for the HPE7-J02 were updated on : Feb 18 ,2026
Page 1 out of 4. Viewing questions 1-15 out of 50
Question 1
The storage solution based on the exhibit is deployed at a customer site.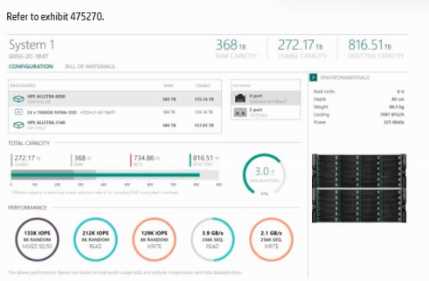
How can the sequential read performance values be enhanced for this configuration?
- A. By adding another expansion shelf
- B. By increasing the amount of 10/25 Gb NICs
- C. By replacing 10/25 Gb with a 32 Gb FC HBA
- D. By adding SCM to the solution
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Detailed Explanatio n:
Rationale for Correct Answe r:
The exhibit shows a system delivering ~2.3 GB/s sequential read. For large-block sequential
workloads, aggregate host link bandwidth (number × speed of front-end ports) is the primary limiter.
Increasing the count of 10/25 Gb iSCSI NICs adds parallel lanes, raising sustained read GB/s to the
hosts. This is a recommended first step in HPE sizing before changing protocols.
Analysis of Incorrect Options (Distractors):
A: Adding an expansion shelf increases capacity, not front-end bandwidth.
C: Moving to 32 Gb FC can help, but simply adding more existing 10/25 Gb ports achieves the same
goal without a protocol/adapter change and is the straightforward, supported scale-out path.
D: SCM (Storage Class Memory) targets latency/IOPS; it doesn’t materially lift sequential GB/s if the
link budget is the bottleneck.
Key Concept: Scale front-end connectivity to increase sequential throughput; capacity or media class
changes won’t fix a link-limited system.
Reference: HPE Alletra 6000/MP Sizing and Host Connectivity Guidelines (throughput scaling via
additional host ports).
Question 2
The storage solution based on the exhibit is deployed at a customer site.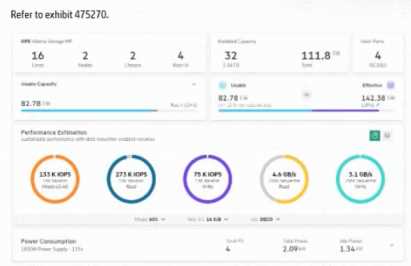
How can the sequential read performance be enhanced with this setup?
- A. By increasing the amount of 10Gb NICs
- B. By adding a third node to the solution
- C. By upgrading the nodes to 32-core IOMs
- D. By adding more NVMe media to the solution
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Detailed Explanatio n:
Rationale for Correct Answe r:
The exhibit shows an Alletra MP configuration delivering ~4.6 GB/s (256 KB sequential read) with
four 10 Gb host ports. That throughput is close to the aggregate front-end bandwidth ceiling of 4×10
GbE (≈5 GB/s raw, less with protocol overhead). For large-block sequential workloads, the front-end
link budget is often the bottleneck; adding additional 10 GbE ports (or moving to higher-speed links)
increases available host bandwidth and raises sustained sequential read throughput. This aligns with
HPE sizing guidance: scale host connectivity to meet sequential throughput targets before adding
media.
Analysis of Incorrect Options (Distractors):
B: Adding a third node isn’t applicable to a 2-node HA block pair and would not address a front-end
bandwidth limit.
C: More controller cores don’t raise link-level throughput if host I/O is already constrained by port
bandwidth.
D: Adding NVMe media primarily boosts IOPS/parallelism; sequential read is bounded here by front-
end ports.
Key Concept: Sequential throughput is front-end bandwidth bound; scale host ports to increase GB/s.
Reference: HPE Alletra MP Performance and Sizing best practices (host connectivity scaling for
throughput).
Question 3
Refer to the exhibit.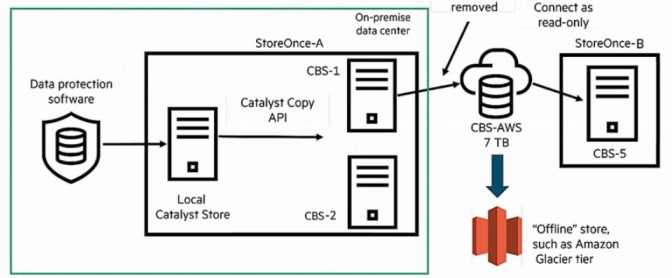
A junior engineer is expanding a StoreOnce deployment for a law firm with a hybrid environment.
The customer already has Veeam backing up to StoreOnce 3660 Gen 4 at both primary and
secondary sites. They want to add Cloud Bank Storage (CBS) to archive into AWS Glacier tier for
compliance. The junior engineer has added Cloud Bank licenses for the 80TB onsite capacity at the
primary office.
Question : What does the junior engineer need to add to enable this scenario?
- A. Federated Management
- B. Cloud Bank Storage for AWS Glacier
- C. Catalyst License for StoreOnce-B
- D. Detach License on StoreOnce-A
Answer:
D
Question 4
Your new customer asks about HPE storage networking capabilities for multisite implementations.
Which statement about HPE’s FCIP capabilities is correct?
- A. FCIP trunking provides both additional bandwidth and availability.
- B. FCIP does not require multiple fabrics to ensure availability.
- C. Dedicated network links are required for data migration over FCIP.
- D. FCIP can be encrypted with no impact on performance.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Detailed Explanatio n:
Rationale for Correct Answe r:
In Brocade (HPE B-Series) SAN switches, FCIP trunking allows multiple IP circuits to be aggregated.
This increases bandwidth and provides resiliency (if one link fails, traffic continues over remaining
paths). It is the correct statement regarding HPE’s FCIP feature set.
Distractors:
B: High availability still requires redundant fabrics; FCIP trunking alone doesn’t replace fabric design
best practices.
C: FCIP can run over shared IP WANs; no need for dedicated links.
D: Encryption adds overhead; performance impact exists (although minimal with hardware offload).
Key Concept: FCIP trunking = bandwidth + availability for multisite SAN.
Reference: HPE B-Series SAN Networking FCIP Trunking Best Practices.
Question 5
A customer experienced a replication network outage during setup of Alletra 6000 arrays. They want
to allow HPE support remote root access to troubleshoot once the outage is resolved.
How can this be enabled?
- A. Enable HPE support access in the InfoSight portal.
- B. Access array with SSH login to retrieve ciphertext blob for hpesupport user.
- C. Confirm remote access request in the Data Ops Manager.
- D. Allow access in the local GUI by enabling secure tunnel.
Answer:
A
Question 6
You are sizing an HPE Alletra Storage MP B10000 array (graphic provided).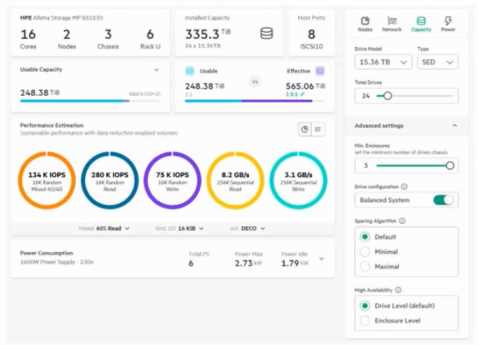
What happens when the High Availability (HA) option is switched from Drive Level to Enclosure
Level?
- A. The Enclosure Level option is not possible with the current number of disk enclosures
- B. The Enclosure Level option is only available with a switched configuration
- C. The estimated performance decreases due to lower IOPS and GB/s values
- D. The Usable Capacity for the array decreases when selecting Enclosure Level HA
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Detailed Explanatio n:
Rationale for Correct Answe r:
Changing HA from Drive Level to Enclosure Level means the system must reserve additional capacity
to tolerate the loss of an entire disk enclosure. This decreases usable capacity, as more parity/spare
space is required. Performance remains similar, but capacity overhead increases.
Distractors:
A: Multiple enclosures exist in the config; option is valid.
B: Switched vs direct-connect is unrelated to HA settings.
C: Performance estimates are not directly reduced by HA level change; capacity is.
Key Concept: Enclosure HA = more reserve overhead → less usable capacity.
Reference: HPE Alletra MP Sizing Tool User Guide.
Question 7
Your customer has 2 Alletra 6000 arrays configured for asynchronous replication. The facilities team
is planning grid maintenance in the datacenter hosting the source array. They want to proactively
move all host I/O to the target array.
Which action needs to be done on the Alletra group level to move the host I/O to the other
datacenter?
- A. Failover
- B. Promote
- C. Demote
- D. Handover
Answer:
A
Question 8
A mid-sized enterprise needs a file storage solution that offers scalable storage and integrated data
protection, backup, and disaster recovery.
Which solution best meets the company’s needs?
- A. Qumulo
- B. Scality
- C. HPE GreenLake for File Storage
- D. Cohesity
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Detailed Explanatio n:
Rationale for Correct Answe r:
HPE GreenLake for File Storage (powered by VAST Data) delivers scale-out NAS capabilities with
native data protection, snapshots, and disaster recovery integration. It is designed for enterprises
that need both scalability and integrated protection in a single consumption or CapEx model.
Distractors:
A (Qumulo): Excellent scale-out file, but lacks deep HPE ecosystem integration.
B (Scality): Primarily focused on object storage, not file workloads.
D (Cohesity): Strong in backup and secondary storage, but not primary enterprise file services.
Key Concept: HPE GreenLake for File Storage = enterprise-grade file storage + integrated protection.
Reference: HPE GreenLake for File Storage Overview.
Question 9
Your customer is a hospital that recently experienced an outage that impacted patient care. They are
evaluating HPE SimpliVity.
Which statement about HPE SimpliVity RapidDR is correct?
- A. HPE RapidDR ensures an RTO of 0 in a stretched cluster topology.
- B. HPE RapidDR requires domain administrator credentials to re-IP virtual machines in the failover site.
- C. HPE RapidDR auto-commit and auto-rollback policies are completed without user interaction.
- D. HPE RapidDR requires an authorized person to execute a pre-configured recovery plan during failover.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Detailed Explanatio n:
Rationale for Correct Answe r:
HPE SimpliVity RapidDR simplifies and automates DR failover processes, but execution requires an
authorized operator to trigger a pre-configured recovery plan. This balances automation with
compliance and security requirements (important for healthcare). It does not guarantee zero RTO,
but it does minimize RTO through automation.
Distractors:
A: RTO of 0 is not possible; RapidDR reduces but does not eliminate recovery time.
B: Domain admin credentials for re-IP are not required; automation handles reconfiguration.
C: Auto-commit/rollback require administrator validation; no “silent” automation is allowed for
compliance.
Key Concept: RapidDR = automation of failover/failback but requires authorized trigger.
Reference: HPE SimpliVity RapidDR Technical Overview.
Question 10
You are working with a customer to upgrade their current VMware infrastructure. The hardware is
outdated, and the customer has no information about performance requirements for the new
servers and storage array. You are using HPE CloudPhysics to run an assessment.
Which Card Deck will give you insights on the under- and overprovisioning of the current
environment?
- A. Storage Space Management
- B. Reclaimable VMware vDisk Space
- C. Simulator for VM Rightsizing
- D. Infrastructure Planning
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Detailed Explanatio n:
Rationale for Correct Answe r:
The Simulator for VM Rightsizing Card Deck in HPE CloudPhysics evaluates actual VM utilization
against provisioned resources. It identifies under- and overprovisioned VMs, providing insights into
reclaimable resources and accurate sizing recommendations. This directly helps plan server and
storage upgrades.
Distractors:
A: Storage Space Management focuses on datastore usage trends, not provisioning mismatches.
B: Reclaimable VMware vDisk Space identifies unused storage, not CPU/RAM sizing.
D: Infrastructure Planning helps plan new builds but doesn’t directly analyze current over/under
provisioning.
Key Concept: VM Rightsizing = CloudPhysics tool for over/under provisioning analysis.
Reference: HPE CloudPhysics Card Decks Guide.
Question 11
You are sizing an HPE Alletra 5030. Unless otherwise indicated by the HPE sizer or the customer's
requirements, HPE best practices state that you should default to which minimum FDR calculation?
- A. 23% of the largest drive size
- B. Above 12% for low-read latency
- C. Below 12% for low-read latency
- D. 23% of the smallest drive size
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Detailed Explanatio n:
Rationale for Correct Answe r:
In Alletra 5000/6000 sizing, the Failure Domain Reserve (FDR) is used to account for rebuild overhead
in case of drive failure. HPE best practices define that, unless otherwise directed by the sizing tool or
customer requirements, the minimum FDR value should be set to 23% of the largest drive size. This
ensures enough reserve capacity for fault tolerance and sustained performance during rebuilds.
Distractors:
B/C: Low-read latency is influenced by cache and workload profile, not by arbitrary FDR percentages.
D: Using the smallest drive is incorrect — rebuild impact must be sized against the largest drive.
Key Concept: FDR sizing based on 23% of largest drive = HPE best practice.
Reference: HPE Alletra 5000/6000 Sizing and Configuration Guide.
Question 12
A growing technology company is planning to upgrade its data center infrastructure. Their
considerations:
Budget: Predictable monthly payments, no upfront CapEx.
Flexibility: Long-term use, no forced returns.
Ownership: Prefer eventual ownership, spread payments.
Control: Full customization and upgrades.
Which procurement option best meets their needs?
- A. Consumption based
- B. Operating lease
- C. Capital purchase
- D. Capital lease
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Detailed Explanatio n:
Rationale for Correct Answe r:
A Capital Lease (also known as a finance lease) spreads costs over time like OpEx, while giving the
customer the ability to own the equipment at the end of the lease term. This matches the desire for
predictable payments, eventual ownership, and full control.
Distractors:
A (Consumption model): GreenLake provides OpEx flexibility but does not lead to ownership.
B (Operating lease): Pure rental; equipment must be returned, no ownership.
C (Capital purchase): Requires large upfront payment, which the customer wants to avoid.
Key Concept: Capital Lease = predictable payments + ownership path.
Reference: HPE Financial Services Procurement Options.
Question 13
A local startup company has grown rapidly and now needs block storage for enterprise workloads.
They are virtualized with VMware and have a small IT staff. They are evaluating an HPE Alletra MP
and a Pure FlashArray //X90R4.
Environment:
VMware 8.0
Cisco switches
Dell servers
HPE servers
What statement about HPE should you point out as a differentiator?
- A. HPE provides full-stack visibility up to the app layer with prescriptive, actionable recommendations.
- B. HPE has live workload migration via the ActiveWorkload feature, based on a stretch cluster.
- C. HPE has the ability to disable garbage collection and overhead to meet workload requirements.
- D. HPE can natively tier data on a software-only deployment.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Detailed Explanatio n:
Rationale for Correct Answe r:
HPE Alletra with InfoSight provides end-to-end visibility from infrastructure through to virtual
machines and applications. It offers prescriptive, AI-driven recommendations to simplify
management — a key differentiator for startups with small IT staff. Pure arrays do not offer the same
level of integrated, cross-stack predictive analytics.
Distractors:
B: “ActiveWorkload” is not an HPE feature — HPE uses Peer Persistence for stretch clusters.
C: Garbage collection is managed automatically in HPE arrays; disabling it is not supported.
D: Data tiering is not natively provided as “software-only” — HPE uses GreenLake and Alletra
services.
Key Concept: InfoSight = predictive analytics and app-to-infra visibility differentiator.
Reference: HPE InfoSight for Alletra Datasheet.
Question 14
Your customer has expressed an interest in an HPE CloudPhysics assessment of their environment.
They would like to know what to expect from this process.
Which of the following statements is true of a CloudPhysics assessment?
- A. Some assessment results are visible in only 2 hours.
- B. An auto-generated token from HPE is required to view the results.
- C. Your customer can only access a partial view of the results.
- D. The assessment period lasts for 5 business days.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Detailed Explanatio n:
Rationale for Correct Answe r:
HPE CloudPhysics begins collecting performance and capacity data immediately after deployment of
the Observer VM/collector. Some initial assessment results (e.g., environment inventory, early
utilization stats) can be visible within 2 hours, while deeper trending insights require longer data
collection (days/weeks).
Distractors:
B: Tokens are not required for customers to view results; reports are available via the portal.
C: Customers get a full dashboard view of results, not partial.
D: Assessments can run for longer periods (days–weeks), not fixed at 5 days.
Key Concept: CloudPhysics delivers initial insights within hours.
Reference: HPE CloudPhysics Technical Overview.
Question 15
Your customer has just gone through a merger and is consolidating datacenters. They are currently
using a mix of manufacturers. They are evaluating whether to consolidate on HPE as their new
standard. You are helping them size their new virtualized environment.
What additional information do you need to decide on an assessment tool?
- A. If they are using AWS or Azure public cloud storage
- B. If they are virtualized on VMware or Hyper-V
- C. If any equipment has expired support contracts
- D. If they are only purchasing in a CapEx model
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Detailed Explanatio n:
Rationale for Correct Answe r:
The choice of assessment tool (e.g., HPE CloudPhysics for VMware vs. CloudPhysics.vhdx collector for
Hyper-V) depends primarily on the virtualization platform in use. VMware and Hyper-V require
different collectors, and this is the deciding factor for tool selection.
Distractors:
A: Public cloud use matters for hybrid sizing but not for tool selection.
C: Expired contracts are unrelated to tool choice.
D: Procurement model (CapEx vs. GreenLake) is separate from sizing assessment.
Key Concept: Assessment tool choice = based on hypervisor platform (VMware vs Hyper-V).
Reference: HPE CloudPhysics Assessment Guide.