HP HPE7-A07 Exam Questions
Questions for the HPE7-A07 were updated on : Feb 18 ,2026
Page 1 out of 5. Viewing questions 1-15 out of 70
Question 1
What is me recommended configuration to ensure link aggregation is consistent in a campus
topology using VSX with two aggregation switches and downlinks to access switches?
- A. Use a custom LACP hash algorithm for improved load Balancing.
- B. Keep the MTU values at the default setting for GRE and VXLAN communications
- C. Use the command "vsx-sync mclag-interfaces" under the VSX context.
- D. Use the command "vsx-sync active-gateways" under the VSX context.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
When configuring Virtual Switching Extension (VSX) in a campus topology for link aggregation across
two aggregation switches, it is important to synchronize Multi-Chassis Link Aggregation Group (MC-
LAG) interfaces. The command "vsx-sync mclag-interfaces" ensures that the state and configuration
of MC-LAG interfaces are synchronized between the two VSX-linked switches, providing consistent
link aggregation and preventing any loops or mismatched configurations that might occur if the
interfaces were not in sync.
Question 2
Your customer added third-party USB dongles to the USB ports of their AOS 10 access points. The
customer uses AP-615 and AP-635 Each AP is connected with a Cat 6A cable to a CX 6300F Class 4
PoE switch All APs are in the same group in HPE Aruba Networking Central and share the same
configuration However, many of the dongles do not come up.
Which option will solve this issue?
- A. Replace the Class a PoE switches with Class 6 PoE switches.
- B. Create two separate service profiles in the loT tab of the Central configuration settings.
- C. Perform a "poe disable" followed by a "poe enable" for the switch ports which connect to the APs so that the APs reboot.
- D. Move the AP-635 access points to a different group in Central to configure the dongles separately from the AP-615.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
USB dongles often require additional power, which may exceed the power delivery capabilities of
Class 4 PoE switches. Aruba AP-615 and AP-635 are designed to work with USB dongles that require
additional power for proper operation. Since the Cat 6A cable can support higher power levels,
replacing the Class 4 PoE switches with Class 6 PoE switches, which can deliver higher power, should
resolve the issue with the dongles not powering up.
Question 3
Exhibit.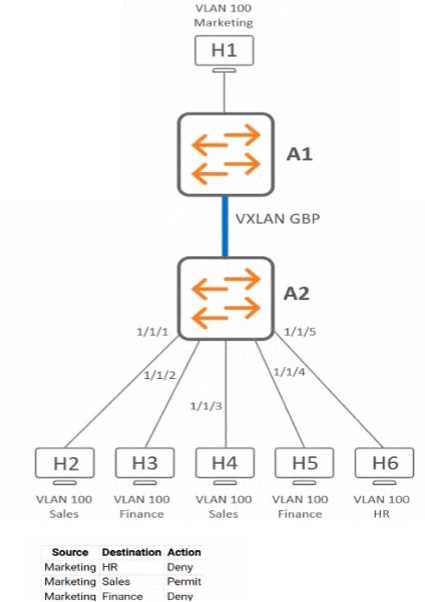
What is me expected behavior for ARP traffic sent from H1?
- A. A2 will drop the ARP traffic.
- B. A2 will send the ARP traffic out of ports 1/1/1-1/1/4.
- C. A2 will flood the ARP traffic out of all interfaces.
- D. A2 will send the ARP traffic out of ports 1/1/1 and 1/1/3.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
In a VXLAN environment, unknown unicast traffic, such as ARP requests from H1, which does not
have a specific destination MAC address learned by the switch A2, will be flooded out of all
interfaces. This flooding behavior is necessary because A2 needs to ensure that the ARP request
reaches its intended destination, which might be on any of the interfaces. It's a part of the standard
behavior of switches to handle ARP traffic when the destination hardware address is unknown.
Question 4
A customer has interfering devices that are seen over the air. They contact you and ask you to
configure RAPIDS to help identify interfering and rogue APs. HPE Aruba Networking Central identifies
a rogue AP and displays the connected switch port.
How can HPE Aruba Networking Central identify which switch port the AP is connected to?
- A. device profiting on the switch
- B. from the AP MAC address table
- C. from the switch LLDP neighbors table
- D. from the switch MAC address table
Answer:
D
Explanation:
HPE Aruba Networking Central can identify which switch port a rogue AP is connected to by using the
switch's MAC address table. The MAC address table contains the associations between MAC
addresses and the switch ports to which devices (including APs) are connected. When Aruba Central
detects a rogue AP, it can look up the MAC address of the rogue AP in the switch's MAC address table
to find the specific switch port it is connected to. This enables network administrators to quickly
locate and address the rogue AP issue.
Question 5
A customer’s infrastructure is set up to use Doth primary and secondary gateway clusters on the SSID
profile What is a valid reason for the AP to failover to the secondary gateway cluster?
- A. The primary gateway cluster is up. out the AP is unable to reach the primary gateway cluster.
- B. The secondary gateway cluster is up. hut the AP is unable to reach the secondary gateway cluster
- C. The secondary gateway cluster is heterogeneous.
- D. The secondary gateway cluster is homogeneous.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
In Aruba's infrastructure, the Access Points (APs) are configured with primary and secondary gateway
clusters to ensure connectivity and resiliency. The APs will failover to the secondary gateway cluster
if they are unable to reach the primary gateway cluster, even if the primary cluster is operational.
This mechanism ensures that the APs maintain connectivity to the network infrastructure for
continuous service delivery.
Question 6
A customer is deploying a new warehouse with AP-634 APs in the united States with mobile devices
that can operate in the 6GHz spectrum All testing and RF analyses were performed during the POC
using AP-635 APs In a different location During the deployment, they noticed fewer 6GHz channels
were broadcasting in the air.
Why would the AP-634 deployment have a lesser amount of broadcasting channels?
- A. The AP-634 APs do not have an advanced subscription.
- B. The AP-634 APs cannot broadcast an 6Gnz channels due to regulatory restrictions.
- C. The AP-635 APs received different allowable 6GHz channels from the AFC service versus the AP- 634 APs due to the POC running in a different location.
- D. The AP-634 AP’s persona was configured in the Central group as Standard Power.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
In the United States, the operation in the 6GHz band for Wi-Fi devices such as the AP-634 and AP-635
is regulated by the Automated Frequency Coordination (AFC) system, which determines the channels
that can be used based on the location. Since the Proof of Concept (POC) was conducted in a
different location using AP-635 APs, the allowable channels identified by the AFC service for that
location would be different than the channels allowed for the actual deployment location of the AP-
634 APs. This would result in a different set of broadcasting channels being available for use in the
new warehouse deployment.
Question 7
Exhibit.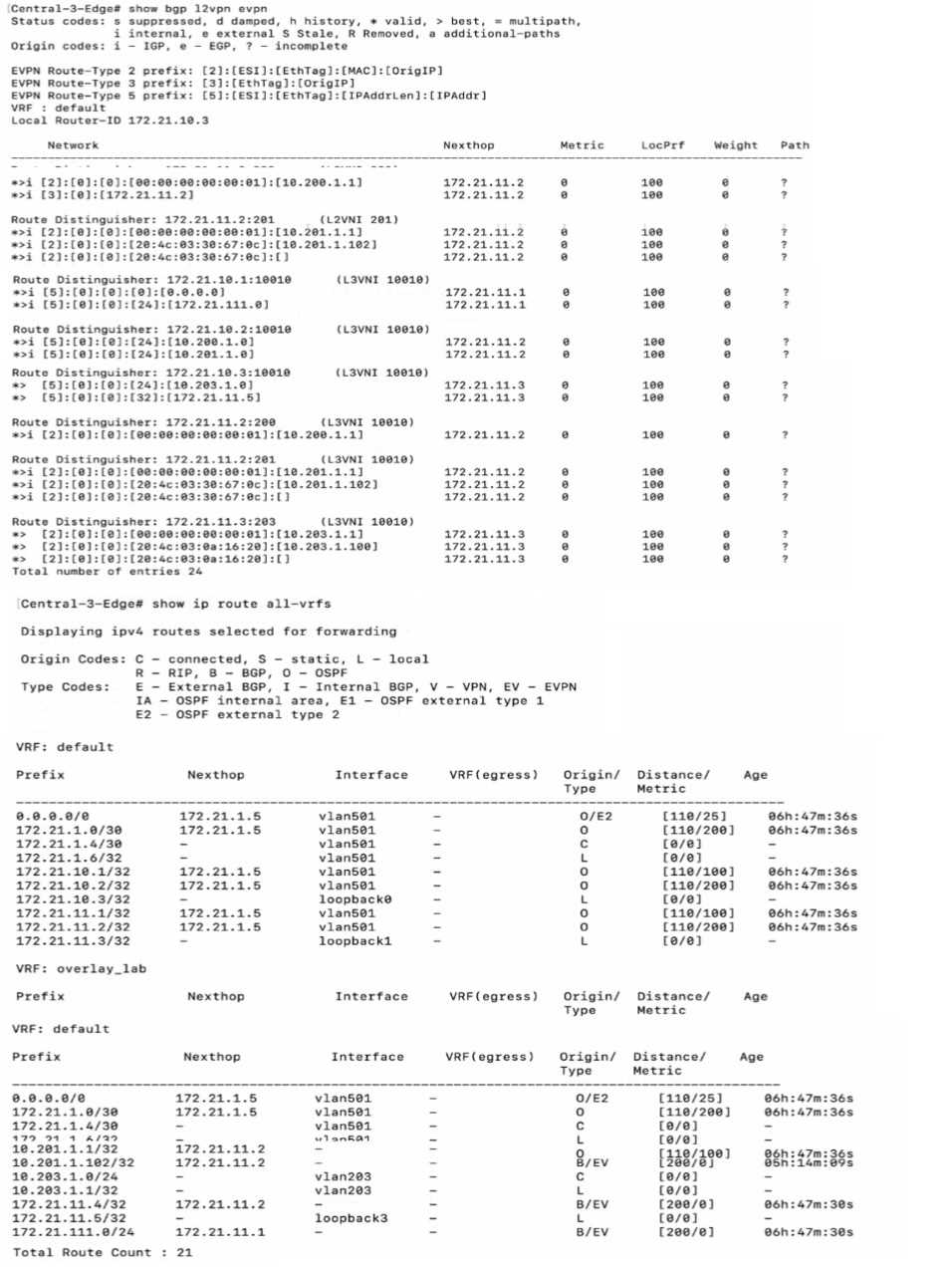
Which statement is true given the following CLI output from a CX 6300?
- A. There are no active fabric clients on the CX switch with RD 172.16.10.1
- B. A wired client with IP address 10.203 1.100 is on a remote CX 6300 in the fabric with loopback IP address 172.21.11.2.
- C. A wired client with IP address 10 203 1 100 has a host route that is not being properly advertised
- D. The overlay loopbacK addresses are advertised in the faerie with 2d-bit subnet masks
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The CLI output provided shows routing information from a CX 6300 switch. The output under "VRF:
default" shows various IP routes, including a route for 10.203.1.100/32 with a next hop of
172.21.11.2. This indicates that the route to the client with IP address 10.203.1.100 is known in the
network and is reachable via another device in the fabric, which has the loopback IP address
172.21.11.2. Since the route is present in the routing table, it means that the client is known and
active within the fabric network.
Question 8
Based on best practices if an SSID is configured Tor a primary and secondary gateway cluster with
cluster preemption enabled, which will decide if the APs move to the secondary gateway cluster if all
of the nodes in the primary gateway cluster are down?
- A. tunnel orchestrator for LAN tunnel service in HPE Aruba Networking Central
- B. every AP individually
- C. cluster leader in the primary gateway cluster
- D. cluster leader in the secondary gateway cluster
Answer:
B
Explanation:
In an Aruba network, if an SSID is configured for a primary and secondary gateway cluster with
cluster preemption enabled, each AP individually will decide to move to the secondary gateway
cluster if all of the nodes in the primary gateway cluster are down. This decentralized decision-
making process enhances network resilience and ensures uninterrupted service for clients connected
to the APs.
Question 9
A client connecting to a tunneled open network is receiving the wrong VLAN Your customer has a
gateway and has sent over a packet capture from a switch port mirror taken from the upstream
switch with a packet capture from the IPsec tunnel and the GRE tunnel to help Identify the VLAN
being sent from the controller to the AP.
Where will you see the VLAN assignment?
- A. The GRE tunnel will include the VLAN lag assignment
- B. VLAN tag assignment win not he captured in any of the packet captures
- C. IPsec tunnel will include the VLAN tag assignment
- D. VLAN tag assignment win be included in the port mirror
Answer:
D
Explanation:
In a packet capture from an upstream switch port mirror, you would see the VLAN assignment. The
port mirror captures the traffic as it is on the network, including any VLAN tags. GRE or IPsec tunnels
encapsulate the original packet, including VLAN tags, but the VLAN information is not visible within
the encapsulation headers.
Question 10
You created a new SSID with the security settings shown in the exhibit.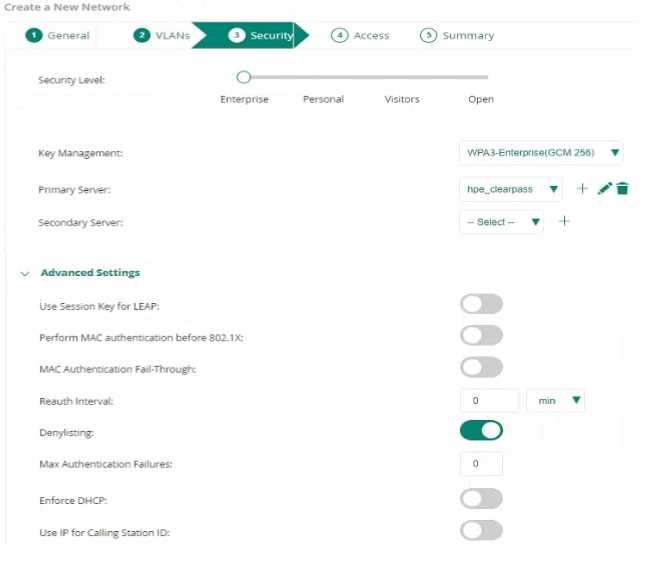
Some, but not all users complain that client devices are unable to connect to this SS1D. What is the
reason for this?
- A. The WPA3 Enterprise GCM-2S6 mode does not support transition mode.
- B. WPA3 Enterprise is not backward compatible with WPA2 Enterprise.
- C. MAC authentication after a failed 802. ix authentication is not possible as the option "MAC Authentication Fall-Through" is disabled.
- D. The primary servers shared key differs from the shared key configured for this server on HPE Aruba Networking Central.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
If some users are unable to connect to an SSID configured with WPA3-Enterprise GCM-256, and the
"MAC Authentication Fall-Through" is disabled, it means that devices which fail 802.1X
authentication will not attempt MAC authentication. If these client devices are configured to use
MAC authentication as a backup method, they will fail to connect, explaining the issue faced by some
users.
Question 11
A deployment using AP-635S is connected to a stack of CX 6300s as shown.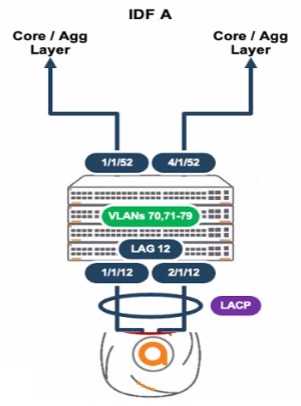
The output of the snow LACP interfaces shews the following: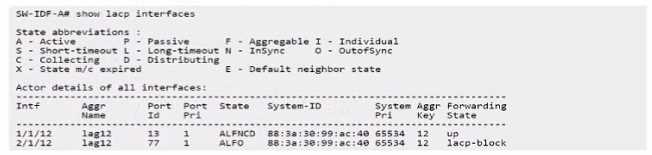
What is causing this issue?
- A. e0 is connected to a smart rate interface, and e1 is connected to a non-smart rate interface.
- B. Spanning tree and loop protect are enabled on both AP uplink ports.
- C. Each AP interface is connected to a routed-only interlace on different networks
- D. The AP is configured with LACP active
Answer:
D
Explanation:
In an Aruba deployment, if an AP's interfaces show different LACP states, it often indicates a
configuration mismatch. If one interface is up and the other is blocked as shown in the output, it's
likely due to both interfaces on the AP being set to LACP active mode, which is a correct setting for
establishing an LACP channel with Aruba switches like the CX 6300 series.
Question 12
A customer wan a gateway connected to a device on gigabitethernet 0/0/3 configures an Asset ID TLV
on the device for inventory management.
Exhibit.
The customer mentions me Asset ID is not shown What is causing the issue?
- A. LLDP TX is not enabled.
- B. LLPD-MED needs to be enabled.
- C. MTU size is too small.
- D. Unknown TLVs cannot be displayed.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The issue is that unknown TLVs (Type Length Values) cannot be displayed. LLDP (Link Layer Discovery
Protocol) is used to share device information with network neighbors, but if a TLV is not recognized
by the LLDP implementation on the gateway, it won't be displayed or processed. Hence, the Asset ID
TLV set on the device for inventory management is not showing up because it is unrecognized or
unsupported by the gateway's LLDP.
Question 13
Exhibit.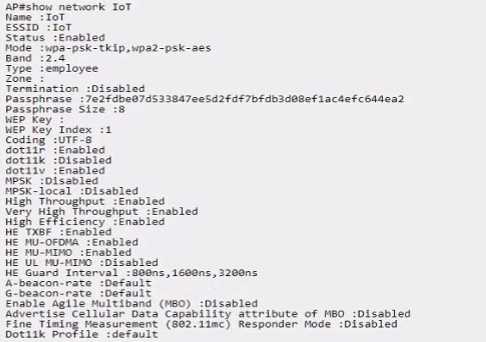
Which statement is true?
- A. The SSID supports RC4 encryption.
- B. The SSID supports 802.11nac clients.
- C. The SSID supports implicit beamforming.
- D. The SSID supports sending neighbor reports.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The SSID supports 802.11ac clients, which is indicated by the "High Throughput" and "Very High
Throughput" options being enabled. These are terms associated with the 802.11ac wireless standard,
indicating that the SSID can serve clients that support this technology.
Question 14
A customer would like to allow their IT Helpdesk to configure loT devices to connect lo a single SSID
using a unique PSK that other devices cannot use. Which solution would you recommend?
- A. MPSK AES with MAC Auth
- B. MPSK Local
- C. MPSK AES with Cloud Auth
- D. MPSK AES with ClearPass
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Multi-Pre-Shared Key (MPSK) with ClearPass is the recommended solution for a scenario where the
IT Helpdesk needs to configure IoT devices to connect to a single SSID using unique PSKs. MPSK
allows for the use of different PSKs on the same SSID, and ClearPass enables the management of
these unique keys efficiently.
Question 15
A Windows device attempts to connect to an 802.1X network but it is not receiving the correct role.
TEAP has been configured as the only authentication method in ClearPass. The wireless configuration
is correct.
Exhibit.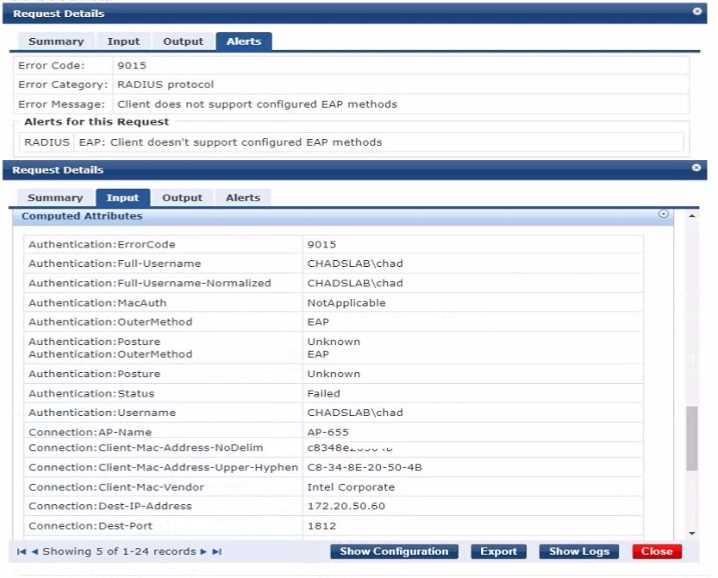
What is me most likely cause?
- A. The Windows device needs 10 De configured tor TEAP.
- B. ClearPass requires a second authentication method.
- C. 802.1X is not compatible with TEAP in windows device
- D. Only machine authentication should be configured on the Windows device
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The issue likely stems from the Windows device not being configured to use TEAP (Tunneled
Extensible Authentication Protocol) as specified in the ClearPass configuration. TEAP is an EAP
method that encapsulates an inner EAP method for secure authentication. The Windows device must
have TEAP enabled and correctly configured in its network settings to authenticate successfully on
the network using ClearPass.