HP HPE7-A03 Exam Questions
Questions for the HPE7-A03 were updated on : Feb 18 ,2026
Page 1 out of 5. Viewing questions 1-15 out of 73
Question 1
A customer wants to have the ability to show network usage. Which product would allow them to
have this visibility?
- A. UXI
- B. HPE Aruba Networking Central
- C. ArubaOS 8.x
- D. HPE Aruba Networking ClearPass
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract:
Aruba Central:
Aruba Central is the cloud-native management and monitoring platform within the Aruba ESP
architecture. It provides:
Network usage visibility: dashboards and reports on client, application, and device traffic across
wired, wireless, and WAN.
Application visibility and deep packet inspection (DPI): showing how much bandwidth is consumed
by each app or category.
Historical and real-time analytics: enabling IT to monitor utilization trends and demonstrate network
usage to stakeholders.
Why not the other options?
UXI (User Experience Insight): Provides end-user experience monitoring by using sensor devices to
simulate client behavior (e.g., connectivity tests, SaaS performance), but it does not give full network
usage visibility in terms of traffic volume or bandwidth utilization.
ArubaOS 8.x: This is the operating system for Aruba mobility controllers and APs, enabling advanced
WLAN features, but not a dedicated platform for traffic visibility dashboards or long-term usage
reporting.
ClearPass: Provides policy-based access control and security (authentication, authorization,
accounting, device profiling), but it is not designed to show network traffic usage or utilization
statistics.
Aruba Design Guidance Alignment:
According to Aruba’s Campus Access Design Guides and Aruba Central documentation, the correct
tool for showing and reporting network usage visibility is Aruba Central, which integrates AI Insights,
traffic monitoring, and reporting capabilities as part of the ESP cloud platform.
Final Justification:
Option B is correct because only HPE Aruba Networking Central provides the ability to monitor and
display network usage visibility in a centralized, graphical, and reportable way.
Reference Extracts (Aruba Official Study & Design Guides):
Aruba ESP Campus Design Guide: Aruba Central as the management and visibility layer.
Aruba Central Technical Overview: built-in dashboards for bandwidth utilization, client traffic, and
application visibility.
Aruba Central AI Insights: usage trends and capacity monitoring.
Question 2
A global cruise line company needs to refresh its current fleet. They will refresh the 'insides' of the
ship to be cost-effective and increase their sustainability. They will replace the complete WLAN/LAN
hardware of the ship. In this refresh, the company will not refresh its current security requirements.
The CIO also wants to limit the number of unused ports in the switches. Future expansion will always
mean a refresh of hardware. They start with the smallest ship with a maximum of 800 guests.
Each ship has a LAN infrastructure consisting of two core switches, up to 10 redundant distribution
switches, and up to 500 access switches (400 cabins, 100 technical rooms). The core switches are
located in the MDF of the ship and the distribution switches are located in the IDFs of the ship. Each
cabin and technical room gets one single access switch.
The cabling structure of the ship will not be refreshed. Each IDF is connected to the MDF by SMF, of
which two pairs are available for the interconnect between the core and distribution. The length of
SM fiber between MDF and IDF is less than 300 meters (980 ft) and the type used is OS1. Each cabin
is connected by a single OM2 pair to the IDF, the maximum length is 60 meters (200 ft). Each
technical room is connected by a single OM2 pair to the IDF, with lengths between 100 and 150
meters (320 and 500 ft).
For each cabin/technical room the customer is looking to replace their current fan-less 2530/2540
without changing the requirements, except they need to upgrade the uplink to distribution switch to
10 GbE to handle the increased network traffic, and the technical rooms need redundant power.
The WLAN infrastructure will be 1:1 refreshed without new cabling or new AP locations. Their WLAN
infrastructure is based on the 200/300 series indoor and outdoor APs running InstantOS (less than
300 APs), the customer has no change in WLAN requirements.
The cruise line company will replace its current Internet connection before the LAN/WLAN refresh.
The new Internet connection will provide a 99.8% uptime, which is needed to ensure the paid guest
Wi-Fi is always operational. With this new Internet connection, the CIO of the cruise line wants to
base the design on the ESP architecture from Aruba because the Internet connection is guaranteed.
Based on best practices, what should you recommend as the correct optic type for the connection
between the IDF and the cabins?
- A. 10G SFP+ LC LRM 220 m MMF Transceiver
- B. 10G SFP+ LC SR 300 m MMF Transceiver
- C. 10GBASE-T SFP+ RJ-45 30 m Cat6A Transceiver
- D. 10G LC BiDi 40 km 1330/1270 XCVR
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract:
Cabling Type in Use:
Each cabin and technical room is connected to the IDF with a single OM2 multimode fiber pair. The
maximum length to cabins is 60 meters, and to technical rooms 100–150 meters.
Best Practice for 10 GbE over OM2:
According to Aruba’s Campus Access Design Guides and HPE Aruba CX switch transceiver support
matrices:
OM2 multimode fiber supports 10GBASE-SR optics up to 82 meters.
Since the maximum run is 60 meters, 10GBASE-SR is fully supported with headroom.
10GBASE-LRM can reach 220 m on MMF, but is not required here because the fiber length is much
shorter. SR optics are simpler, lower cost, and recommended in best practices when distances are
within OM2 limits.
10GBASE-T RJ-45 (Cat6A) is not applicable, as the cabling is fiber, not copper.
BiDi 40 km optics are for long-haul single-mode fiber links, not short multimode fiber runs.
Aruba Validated Design Reference:
Aruba’s Validated Solution Guides for Campus Access state that for short multimode connections
(OM2/OM3/OM4), the recommended transceiver type is 10GBASE-SR (SFP+ LC) as it provides the
most cost-effective and reliable option within the supported reach.
Requirement Mapping:
Uplinks to access switches in cabins/technical rooms must be 10 GbE capable.
The OM2 cabling length (60–150 m) is within the supported distance for 10GBASE-SR.
Therefore, the correct and most efficient optic choice is 10G SFP+ LC SR 300 m MMF Transceiver.
Final Justification:
Option B is correct because 10GBASE-SR over OM2 supports the required distances, aligns with
Aruba design best practices, and avoids unnecessary cost/complexity of LRM or BiDi optics.
Reference Extracts (Aruba Official Study & Design Guides):
Aruba Campus Access Design Guide: recommended transceiver selection for MMF cabling.
Aruba CX Transceiver Guide: 10GBASE-SR supports OM2 up to 82 m, OM3 up to 300 m, OM4 up to
400 m.
Aruba Validated Solution Guide: Always select SR optics for OM2 ≤ 82 m runs as the cost-effective
standard.
Question 3
A global cruise line company needs to refresh its current fleet. They will refresh the 'insides' of the
ship to be cost-effective and increase their sustainability. They will replace the complete WLAN/LAN
hardware of the ship. In this refresh, the company will not refresh its current security requirements.
The CIO also wants to limit the number of unused ports in the switches. Future expansion will always
mean a refresh of hardware. They start with the smallest ship with a maximum of 800 guests.
Each ship has a LAN infrastructure consisting of two core switches, up to 10 redundant distribution
switches, and up to 500 access switches (400 cabins, 100 technical rooms). The core switches are
located in the MDF of the ship and the distribution switches are located in the IDFs of the ship. Each
cabin and technical room gets one single access switch.
The cabling structure of the ship will not be refreshed. Each IDF is connected to the MDF by single-
mode fiber (SMF), of which two pairs are available for the interconnect between the core and
distribution. The length of SM fiber between MDF and IDF is less than 300 meters (980 ft), type used
is OS1. Each cabin is connected by a single OM2 pair to the IDF, maximum length 60 m (200 ft). Each
technical room is connected by a single OM2 pair to the IDF, with lengths 100–150 m (320–500 ft).
For each cabin/technical room the customer is looking to replace their current fan-less 2530/2540
without changing the requirements, except they need to upgrade the uplink to distribution switch to
10 GbE to handle the increased network traffic, and the technical rooms need redundant power.
The WLAN infrastructure will be 1:1 refreshed without new cabling or new AP locations. Their WLAN
infrastructure is based on the 200/300 series indoor and outdoor APs running InstantOS (less than
300 APs), the customer has no change in WLAN requirements.
The cruise line company will replace its current Internet connection before the LAN/WLAN refresh.
The new Internet connection will provide a 99.8% uptime, which is needed to ensure the paid guest
Wi-Fi is always operational. With this new Internet connection, the CIO of the cruise line wants to
base the design on the ESP architecture from Aruba because the Internet connection is guaranteed.
A week after the presentation of your design to the CIO of the cruise line company, the CIO calls you
to discuss increasing the security of the wired network infrastructure. Since one of their competitors
had one of their cruise ships cyber hacked, the CSO of the cruise line has mandated increased
security on the wired network. They have heard about dynamic segmentation and central and
decentral overlay networks. For their POS (Point of Sale) systems, they need a low-latency network
connection between the POS system and the PCS server in the data center on the ship. Also, the CSO
wants to enhance the WLAN security as well by tunneling all user traffic.
What solution fits the customer’s requirements?
- A. Standardize on 6300 switches for the edge, 3320 for the RR, 8320 for the stub/border, 9240 for the WLAN Gateway, and utilize HPE Aruba Networking Central NetConductor.
- B. Standardize on 6300 switches for the edge, 8320 for the RR, 8360 for the stub/border, 9240 for the WLAN Gateway, and utilize HPE Aruba Networking Central NetConductor.
- C. Standardize on 6300 switches for the edge, 8325 for the RR, 8360 for the stub/border, 9240 for the WLAN Gateway, and utilize HPE Aruba Networking Central NetConductor.
- D. Standardize on 6300 switches for the edge, 8320 for the RR, 8360 for the stub/border, and utilize HPE Aruba Networking Central NetConductor.
- E. Standardize on 6200 switches for the edge, 8325 for the RR, 8360 for the stub/border, and utilize HPE Aruba Networking Central NetConductor.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract:
Aruba’s ESP Campus Access Design and NetConductor Architecture guides outline the validated roles
of devices in dynamic segmentation deployments.
Access Layer (Edge): Aruba CX 6300
The CX 6300 provides 10 Gb uplinks to distribution, advanced features like VXLAN and EVPN, and
support for role-based access control at the edge. It is the recommended choice for modern edge
deployments in an ESP fabric.
Route Reflector (RR): Aruba CX 8325
The CX 8325 is optimized for routing and control-plane operations. As a route reflector, it scales
overlay BGP sessions and distributes policies/roles through the fabric. It is explicitly referenced as the
ideal RR platform in Aruba ESP campus validated designs.
Stub/Border: Aruba CX 8360
The CX 8360 family provides advanced aggregation and fabric services. It supports VXLAN, EVPN, and
border routing functions, making it the right choice for stub/border persona in ESP designs.
WLAN Gateway: Aruba 9240
The Aruba 9200/9240 series gateways provide role-based policy enforcement for tunneled WLAN
traffic. They terminate GRE/IPsec tunnels from APs, enforce user policies, and forward into the fabric.
This is critical to meet the requirement of tunneling all WLAN user traffic for enhanced security.
Dynamic Segmentation with NetConductor
Aruba Central NetConductor enables centralized definition and orchestration of user roles and
segmentation policies. Roles are automatically enforced across the fabric using VXLAN with Group-
Based Policy (GBP). This supports both centralized tunneling (for WLAN traffic) and distributed
segmentation (for wired POS traffic requiring low latency).
Requirement Mapping:
Low-latency POS traffic → Distributed role enforcement within the fabric via 8360/8325.
Secure WLAN traffic → User traffic tunneled to the 9240 gateway for role-based enforcement.
10 Gb uplinks and redundancy → Provided by 6300 edge switches with dual power options in
technical rooms.
ESP architecture → NetConductor automates overlay, segmentation, and role orchestration.
Other options are eliminated because:
A uses 3320 for RR, which lacks overlay fabric scalability.
B uses 8320 for RR (possible, but Aruba recommends 8325 for RR roles in NetConductor designs).
D omits the WLAN Gateway, which is required to tunnel WLAN traffic.
E uses 6200 at the edge, which does not provide the required 10 Gb uplink capability.
Therefore, Option C is the only design that fully satisfies the cruise line’s requirements while aligning
with Aruba’s ESP Campus validated architectures.
Reference Extracts (Aruba Official Study & Design Guides):
Aruba ESP Campus Design Guide: device personas (edge, RR, stub/border, gateway) and
NetConductor integration.
Aruba NetConductor Technical Overview: VXLAN-GBP, dynamic segmentation, and centralized role
enforcement.
Aruba Dynamic Segmentation Solution Overview: tunneling of WLAN traffic, role-based security
across wired and wireless.
Aruba CX Switch Series Data Sheets: CX 6300 (edge with 10 Gb uplinks), CX 8325 (RR), CX 8360
(border/stub), Aruba 9240 (WLAN gateway).
Question 4
HOTSPOT
Based on this campus design, which layer is the most appropriate to be designed as a Border
Persona, considering an EVPN VXLAN Fabric?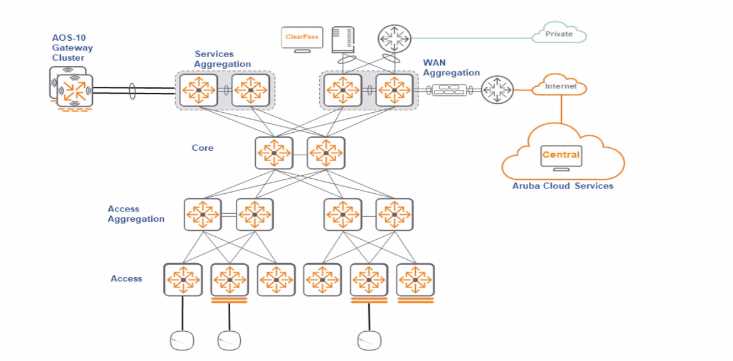
Answer:
None
Explanation:
Based on the campus design provided and considering an EVPN VXLAN Fabric, the most appropriate
layer to be designed as a Border Persona would be the "Services Aggregation" layer. In an EVPN
VXLAN architecture, the Border or Border Leaf nodes provide connectivity to external networks, such
as WAN, internet, or private connections. They are responsible for routing traffic into and out of the
VXLAN fabric and typically also handle services like firewalling, load balancing, and other network
services.
Question 5
Which alternative source is best suited for site surveys or simul-ations if no floor plans are available?
- A. blank sheet of paper
- B. Google Maps
- C. simple wall drawings
- D. tire escape plan
Answer:
D
Explanation:
When floor plans are not available for site surveys or simulations, the best alternative source to use
is the fire escape plan (Option D). Fire escape plans are typically available in most buildings and
provide a simplified layout of the premises, including walls, doors, and sometimes the location of
permanent fixtures. While not as detailed as architectural floor plans, fire escape plans can offer
enough information for initial site survey estimations and RF planning. They allow network designers
to understand the basic layout and potential RF obstacles or coverage areas, making them a practical
tool for preliminary wireless network planning and simulations in the absence of more detailed floor
plans.
Question 6
You are designing a solution with Aruba OS10-based access points and redundant gateways and
these are the requirements:
• W1-F16E based access points
• support for tunneled traffic
• application visibility
• rogue APs
• live upgrades
• Air Slice
• Cloud Guest Authentication
• Ai insights
Which licenses are needed? (Select two.)
- A. AP Foundation
- B. WIAN Gateway
- C. AP Advanced
- D. Gateway Foundation
Answer:
AC
Explanation:
For a solution design incorporating Aruba OS10-based access points with the specified requirements,
including Wi-Fi 6E support, tunneled traffic, application visibility, rogue AP detection, live upgrades,
Air Slice, Cloud Guest Authentication, and AI insights, the necessary licenses are AP Foundation
(Option A) and AP Advanced (Option C). The AP Foundation license provides basic connectivity and
network access control features essential for establishing a Wi-Fi network. The AP Advanced license
adds advanced capabilities such as application visibility and control, enhanced security features like
rogue AP detection, and performance optimization features like Air Slice. These licenses together
ensure the access points can deliver the full range of required functionalities, from reliable basic
connectivity to sophisticated network management and security, making them suitable for a
comprehensive and high-performing wireless network solution.
Question 7
which documentation resources con be used for finding validated information on Aruba products
that assist the architect in building the solution design? (Select three.)
- A. product reviews (CNET, Network World)
- B. configuration guides
- C. datasheets
- D. Gartner annual reports
- E. competitive documentation
- F. validated Solution Guide
Answer:
BCF
Explanation:
When seeking validated information on Aruba products to assist in building a solution design, the
most reliable resources include configuration guides (Option B), datasheets (Option C), and validated
Solution Guides (Option F). Configuration guides provide detailed instructions and best practices for
setting up and optimizing Aruba products, ensuring their proper integration into the network
infrastructure. Datasheets offer concise overviews of product specifications, features, and
capabilities, allowing architects to assess product suitability for specific requirements. Validated
Solution Guides compile comprehensive information on deploying Aruba solutions in various
scenarios, ensuring that the solution design is based on proven methodologies and recommended
practices, thereby enhancing the reliability and performance of the network solution.
Question 8
Which licenses are needed in order to use the UXl Client on Zebra (Devices? (Select two.)
- A. UXI Cloud Subscription
- B. UXl Agent Subscription
- C. UXl LTE Subscription
- D. Wireless Insights
Answer:
AB
Explanation:
To utilize the UXI Client on Zebra Devices, the necessary licenses include the UXI Cloud Subscription
(Option A) and the UXI Agent Subscription (Option B). The UXI Cloud Subscription provides access to
the UXI platform's cloud-based analytics and insights, facilitating the monitoring and management of
network performance and user experience. The UXI Agent Subscription is required for each Zebra
device, enabling it to run the UXI Client software that collects and sends network performance data
to the UXI cloud platform. Together, these licenses empower organizations to enhance network
visibility and improve the user experience on Zebra devices within their networks.
Question 9
What is the difference between 0M4 and 0M5 cabling? (Select two)
- A. 0M4 supports distances up to 100 m. while 0M5 supports distances up to 150 m using 100 GBps transceivers.
- B. 0M5 supports Multiplexing operating in the 850 to 950 nm range, while 0M4 does not
- C. 0M5 is approved as wide Band Multimode Fiber (WBMMF). while 0M4 Is not.
- D. 0M5 supports speeds up to 100 Gbps. while OM4 does not.
Answer:
AC
Explanation:
The primary differences between OM4 and OM5 cabling include their support for transmission
distances and the type of multimode fiber. OM4 fiber supports distances up to 100 meters when
using 100 Gbps transceivers (Option A), which is suitable for most data center and enterprise
networking applications. OM5, also known as Wide Band Multimode Fiber (WBMMF) (Option C),
extends this capability by supporting higher wavelengths in the 850 to 950 nm range, allowing for
more efficient multiplexing and potentially longer distances or higher bandwidths under certain
conditions. This makes OM5 a more versatile and future-proof option for organizations looking to
deploy advanced technologies like shortwave division multiplexing.
Question 10
'Don't Buy at Us' is a US-based retail company that is expanding Into Europe. They are expanding into
EMEA with a regional headquarters called HQ2 inside The Netherlands.
Their US-based headquarters HQ1 was refreshed last year based on the Aruba ESP architecture. You
have treated the design for HQ? based on the same design as HQ1. a two-tier architecture. The high
level is shown below.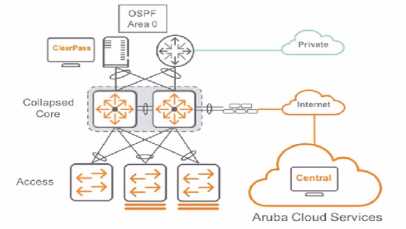
Switch BOM for this project based on Two Tier:
Collapsed Core: 2 x Aruba 8360-16Y2C in VSX (ISL 2» ICOG0E DAC)
Access Slack: 10 x Slack of Aruba 6200F 48G Class4 PoE 4SFP- 740W each stack has A members. VSF
with 10GbE VSF links) 12 x 10GbE uplink pet stack)
During the presentation of your design to the CTO of "Don't Buy at Us" you were informed about the
changes they want you to incorporate into the updated design
1. HQ2 will include the EMEA regional distribution center (EMEA-OISTR) next to the HQ2.
2. Only two pairs of 0S1 are available between HQ2 and EMEA-DlSTR.
3. The uplinks from all access stacks need to increase to 2 x 25GbE. the fiber in HQ2 and EMEA-DI5TRI
is certified for 25GbE.
4. EMEA-DlSTR needs at least 7 x stack of Aruba 48 ports switches (each stack has 4 members).
Which answer based on best practice is presenting the correct Switch BOM tor the updated design?
A)
B)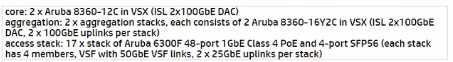
C)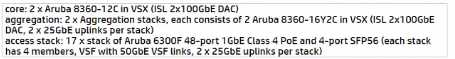
D)
- A. Option A
- B. Option B
- C. Option C
- D. Option D
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Based on the requirements provided by "Don't Buy at Us," the updated design needs to
accommodate 25GbE uplinks and a minimum of 7 stacks of 48-port Aruba switches for the EMEA-
DISTR. Option C is the most suitable based on best practices, as it proposes:
A core configuration consisting of two Aruba 8360-12C in VSX for the collapsed core with ISL of
2x100GbE DAC, which will provide robust core networking with high-speed interconnects, suitable
for the demands of a regional distribution center and headquarters.
Aggregation with two stacks, each with 2 Aruba 8360-12C in VSX (ISL 2x100GbE DAC),
accommodating the uplink capacity requirements.
Access stacks with a total of 17 stacks of Aruba 6300F 48-port 1GbE Class 4 PoE with 4-port SFP56
(each stack has 4 members, VSF with 50GbE VSF links, 2 x 25GbE uplinks per stack), which exceeds
the minimum requirement of 7 stacks and provides the necessary uplink bandwidth.
This configuration supports the 25GbE uplink speeds, satisfies the required number of switch stacks
for the EMEA distribution center, and is compatible with the existing 25GbE-certified fiber
infrastructure at HQ2 and EMEA-DISTR.
Question 11
'Don't Buy at Us' is a US-based retail company that is expanding Into Europe. They are expanding into
EMEA with a regional headquarters called HQ2 inside The Netherlands.
Their US-based headquarters HQ1 was refreshed last year based on the Aruba ESP architecture. You
have treated the design for HQ? based on the same design as HQ1. a two-tier architecture. The high
level is shown below.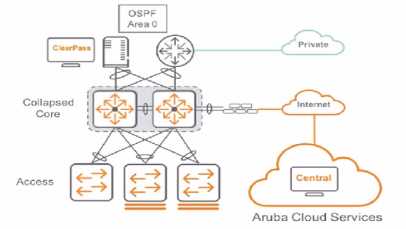
Switch BOM for this project based on Two Tier:
Collapsed Core: 2 x Aruba 8360-16Y2C in VSX (ISL 2» ICOG0E DAC)
Access Slack: 10 x Slack of Aruba 6200F 48G Class4 PoE 4SFP- 740W each stack has A members. VSF
with 10GbE VSF links) 12 x 10GbE uplink pet stack)
During the presentation of your design to the CTO of 'Don't Buy at Us' you were informed about the
updated fiber infrastructure that Don't Buy at Us' has installed in HQ2.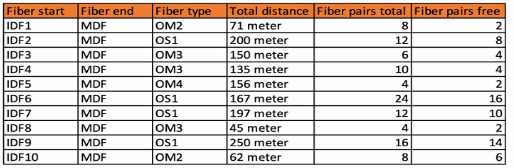
The core stack is Installed in the MDF and per IOF there is one access stack installed. Based on best
practice, what is the most cost-effective update to the switch BOM?
A)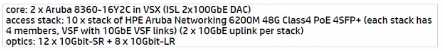
B)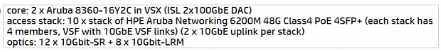
C)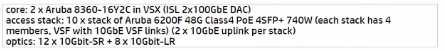
D)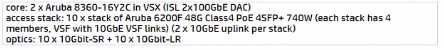
- A. Option A
- B. Option B
- C. Option C
- D. Option D
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Option B is the most cost-effective solution, as it does not include long-range optics, which are
unnecessary given the distances and fiber types specified. The 10GbE-SR optics are suitable for short-
range connections up to 300 meters over OM3 fiber and would cover the needs of the longest fiber
run mentioned, which is 250 meters. The 10GbE-LRM optics, while capable of reaching up to 220
meters over OM2 fiber, would not be necessary as the longest OM2 run is 71 meters, which is within
the range of standard 10GbE-SR optics. Thus, Option B provides the required connectivity without
incurring additional costs for long-range optics that are not needed given the fiber infrastructure of
HQ2.
Question 12
Which is true when it comes to Aruba Central licensing for gateways? (Select two.)
- A. Aruba Gateway normal licensing is subdivided into three categories: Foundation. Advanced, and Foundation Base.
- B. SD-WAN Gateway functionality requires security licensing.
- C. Aruba SD-8ranch Gateway licenses allow normal WLAN Gateway features within a campus.
- D. Aruba WLAN Gateway licenses allow normal SD-Branch features within a campus.
Answer:
BC
Explanation:
In the context of Aruba Central licensing for gateways, it is true that SD-WAN Gateway functionality
requires a specific security licensing (Option B), which is essential for enabling advanced security
features and capabilities in an SD-WAN deployment. This includes functionalities like firewall, threat
management, and secure VPN connections. Additionally, Aruba SD-Branch Gateway licenses allow
for the use of standard WLAN Gateway features within a campus environment (Option C). This means
that with an SD-Branch Gateway license, the gateway can handle traditional WLAN management and
security tasks, in addition to its SD-WAN capabilities, providing a unified solution for both branch and
campus deployments.
Question 13
Which platform can be used to demo your solution to a customer? (Select three.)
- A. Aruba Support Portal
- B. Aruba CX Switch Simulator
- C. Aruba Innovation Zone
- D. Aruba Solution Exchange
- E. your own lab
- F. Aruba Demo Experience Platform
Answer:
BCF
Explanation:
To demonstrate a solution to a customer, three platforms that can be effectively used are the Aruba
CX Switch Simulator (Option B), Aruba Innovation Zone (Option C), and Aruba Demo Experience
Platform (Option F). The Aruba CX Switch Simulator provides a virtual environment where customers
can interact with the Aruba OS-CX interface, allowing them to explore features and configurations
without the need for physical hardware. The Aruba Innovation Zone offers a space for experiencing
the latest Aruba technologies and solutions in action, showcasing their capabilities in real-world
scenarios. The Aruba Demo Experience Platform is designed to give customers a comprehensive look
at Aruba's solutions, enabling interactive demos and simulations that highlight the benefits and
functionalities of the products. These platforms provide valuable resources for customers to
understand and evaluate Aruba solutions in a controlled and informative environment.
Question 14
The current IT staff is used to working with legacy Aruba OS-S (ProCurve> equipment. They are
worried that they cannot handle Aruba OS-CX switches due to the different command syntax. What
are two ways to make the transition easier for them? (Select two.)
- A. create aliases
- B. CL1 Reference Guide for Arouba OS-CX. Aruba OS-Switch, Comware at>d Cisco IOS
- C. Aruba CU Bank
- D. ASP
Answer:
AB
Explanation:
To ease the transition for IT staff accustomed to legacy Aruba OS-S (ProCurve) equipment when
moving to Aruba OS-CX switches, two effective approaches are creating aliases (Option A) and using
the CLI Reference Guide for Aruba OS-CX, Aruba OS-Switch, Comware, and Cisco IOS (Option B).
Aliases allow the creation of custom command shortcuts or mappings in Aruba OS-CX, which can
mimic or resemble the commands staff are familiar with from Aruba OS-S, making the command-line
interface (CLI) more intuitive for them. The CLI Reference Guide is an invaluable resource that
provides a comparative view of commands across different operating systems, including Aruba OS-CX
and Aruba OS-S, helping staff understand the equivalent commands and functionalities in the new
OS-CX environment. Both these tools can significantly reduce the learning curve and help the IT staff
become proficient with Aruba OS-CX switches more quickly.
Question 15
What are the considerations when using existing MMF and upgrading to equipment capable of 10
GbE speeds? (Select two)
- A. length of MMF fiber
- B. type of fiber connector
- C. type of MMF fiber
- D. single fiber tube into cabinet
- E. redundant fiber tube into cabinet
Answer:
AC
Explanation:
When upgrading existing Multimode Fiber (MMF) infrastructure to accommodate equipment
capable of 10 GbE speeds, two primary considerations are the length of the MMF fiber (Option A)
and the type of MMF fiber (Option C). The length of the fiber impacts the signal quality and
bandwidth capacity, with longer lengths potentially requiring signal conditioning or different types of
fiber to support higher speeds. The type of MMF fiber, such as OM1, OM2, OM3, or OM4,
significantly affects its bandwidth capabilities and distance limitations at 10 GbE speeds. OM3 and
OM4 fibers are designed to support 10 GbE transmissions over longer distances compared to OM1
and OM2, making them more suitable for upgrades to higher speeds. Understanding these factors is
crucial to ensure the existing fiber infrastructure can support the desired network performance
without extensive modifications or replacements.