HP HPE6-A84 Exam Questions
Questions for the HPE6-A84 were updated on : Feb 18 ,2026
Page 1 out of 4. Viewing questions 1-15 out of 60
Question 1
Refer to the scenario.
# Introduction to the customer
You are helping a company add Aruba ClearPass to their network, which uses Aruba network
infrastructure devices.
The company currently has a Windows domain and Windows C
- A. EAP and AD/LDAP Server
- B. LDAP and Aruba infrastructure
- C. Radsec and Aruba infrastructure
- D. EAP and Radsec
Answer:
A
Question 2
Refer to the scenario.
An organization wants the AOS-CX switch to trigger an alert if its RADIUS server (cp.acnsxtest.local)
rejects an unusual number of client authentication requests per hour. After some discussions with
other Aruba admins, you are still not sure how many rejections are usual or unusual. You expect that
the value could be different on each switch.
You are helping the developer understand how to develop an NAE script for this use case.
You are helping a customer define an NAE script for AOS-CX switches. The script will monitor
statistics from a RADIUS server defined on the switch. You want to future proof the script by enabling
admins to select a different hostname or IP address for the monitored RADIUS server when they
create an agent from the script.
What should you recommend?
- A. Use this variable, %{radius-ipV when defining the monitor URI in the NAE agent script.
- B. Define a parameter for the RADIUS server; reference that parameter instead of the server name/ip when defining the monitor URI.
- C. Use a callback action to collect the name of any RADIUS servers defined on the switch at the time the agent is created.
- D. Make the script editable so that admins can edit it on demand when they are creating scripts.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
This is because a parameter is a variable that can be defined and modified by the user or the script,
and can be used to customize the behavior and output of the NAE script. A parameter can be
referred to by using the syntax self ^ramsfname], where ramsfname is the name of the parameter.
By defining a parameter for the RADIUS server, you can make the NAE script more flexible and
adaptable to different scenarios and switches. The parameter can be set to a default value, such as
cp.acnsxtest.local, but it can also be changed by the user or the script based on the network
conditions and requirements. For example, the user can select a different hostname or IP address for
the monitored RADIUS server when they create an agent from the script, or the script can
automatically detect and update the parameter based on the switch configuration. This way, the NAE
script can monitor statistics from any RADIUS server defined on the switch without hard-coding the
server name or IP address in the monitor URI.
A. Use this variable, %{radius-ipV when defining the monitor URI in the NAE agent script. This is not a
valid recommendation because %{radius-ipV is not a valid variable in NAE scripts. Variables in NAE
scripts are prefixed with self ^ramsfname], not with %. Moreover, radius-ipV is not a predefined
variable that contains the RADIUS server name or IP address, but rather a generic term that could
refer to any IP version.
C. Use a callback action to collect the name of any RADIUS servers defined on the switch at the time
the agent is created. This is not a bad recommendation, but it is not as good as defining a parameter.
A callback action is a feature that allows an NAE script to execute a command on the switch and
collect its output for further processing or display. A callback action can be used to collect the name
of any RADIUS servers defined on the switch by executing a command such as show radius-server or
show running-config radius-server and parsing its output. However, a callback action might not be as
fast or reliable as using a parameter, as it depends on the availability and responsiveness of the
switch and its CLI.
D. Make the script editable so that admins can edit it on demand when they are creating scripts. This
is not a good recommendation because making the script editable exposes it to potential errors or
modifications that could affect its functionality or performance. Making the script editable also
requires more effort and expertise from the admins, who might not be familiar with NAE scripting
syntax or logic. Moreover, making the script editable does not future proof it, as it does not allow for
dynamic changes or updates based on network conditions or requirements.
10of30
Question 3
Refer to the scenario.
A customer has an AOS10 architecture that is managed by Aruba Central. Aruba infrastructure
devices authenticate clients to an Aruba ClearPass cluster.
In Aruba Central, you are examining network traffic flows on a wireless IoT device that is categorized
as “Raspberry Pi” clients. You see SSH traffic. You then check several more wireless IoT clients and
see that they are sending SSH also.
You want a fast way to find a list of all the IoT clients that have used SSH.
What step can you take?
- A. Create and apply a Central client profile tag that selects the SSH application and the clients' category.
- B. Run a search for SSH traffic and loT client IDs in Aruba ClearPass Policy Manager's (CPPM's) accounting information.
- C. Use Central's Live Events monitoring tool to detect which clients meet the desired criteria.
- D. Use Central's Gateway IDS/IPS Security Dashboard to search for SSH events and sources.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
This is because the Live Events monitoring tool is a feature that allows you to view and filter real-
time events and alerts from your network devices and clients on Aruba Central. You can use the Live
Events monitoring tool to detect which IoT clients have used SSH by applying the following filters:
Category: IoT
Application: SSH
The Live Events monitoring tool will then display a list of all the IoT clients that have used SSH, along
with other information such as their IP address, MAC address, hostname, SSID, AP name, etc. You can
also export the list as a CSV file for further analysis or reporting.
A. Create and apply a Central client profile tag that selects the SSH application and the clients’
category. This is not the fastest way to find a list of all the IoT clients that have used SSH because
creating and applying a client profile tag is a process that involves several steps and might take some
time to take effect. A client profile tag is a feature that allows you to group and classify clients based
on various criteria, such as device type, OS, category, application, etc. To create and apply a client
profile tag that selects the SSH application and the clients’ category, you need to do the following:
Navigate to Clients > Client Profile Tags on Aruba Central.
Click Add Tag and enter a name and description for the tag.
Click Add Rule and select Application as the attribute and SSH as the value.
Click Add Rule again and select Category as the attribute and IoT as the value.
Click Save to create the tag.
Navigate to Clients > Client List on Aruba Central.
Select the clients that you want to apply the tag to and click Assign Tag.
Select the tag that you created and click Apply.
After applying the tag, you can then filter the client list by the tag name and see a list of all the IoT
clients that have used SSH. However, this method might not be as fast or accurate as using the Live
Events monitoring tool, as it depends on how often the client profile tags are updated and
synchronized with Aruba Central.
B. Run a search for SSH traffic and loT client IDs in Aruba ClearPass Policy Manager’s (CPPM’s)
accounting information. This is not the fastest way to find a list of all the IoT clients that have used
SSH because running a search in CPPM’s accounting information is a process that involves accessing
another system and querying a large amount of data. Accounting information is a feature that allows
CPPM to collect and store data about network sessions, such as start time, end time, duration, bytes
sent/received, etc. To run a search for SSH traffic and IoT client IDs in CPPM’s accounting
information, you need to do the following:
Log in to CPPM and navigate to Monitoring > Live Monitoring > Accounting.
Click on Advanced Search and enter SSH as the value for Service Name.
Click on Add Filter and enter IoT as the value for Endpoint Category.
Click on Search to run the query.
The query will then return a list of all the network sessions that involved SSH traffic and IoT clients.
However, this method might not be as fast or convenient as using the Live Events monitoring tool, as
it requires logging in to another system and searching through a large amount of data that might not
be relevant or current.
D. Use Central’s Gateway IDS/IPS Security Dashboard to search for SSH events and sources. This is
not a valid way to find a list of all the IoT clients that have used SSH because the Gateway IDS/IPS
Security Dashboard is a feature that only applies to wired network devices connected to Aruba
gateways, not wireless devices connected to Aruba APs. The Gateway IDS/IPS Security Dashboard is a
feature that allows you to monitor and manage security events and alerts from your wired network
devices on Aruba Central. You can use the Gateway IDS/IPS Security Dashboard to search for security
events related to SSH, such as brute force attacks or unauthorized access attempts, but not for
normal SSH traffic from wireless IoT devices. Therefore, this method will not help you find a list of all
the IoT clients that have used SSH.
Question 4
Refer to the scenario.
An organization wants the AOS-CX switch to trigger an alert if its RADIUS server (cp.acnsxtest.local)
rejects an unusual number of client authentication requests per hour. After some discussions with
other Aruba admins, you are still not sure how many rejections are usual or unusual. You expect that
the value could be different on each switch.
You are helping the developer understand how to develop an NAE script for this use case.
The developer explains that they plan to define the rule with logic like this:
monitor > value
However, the developer asks you what value to include.
What should you recommend?
- A. Checking one of the access switches' RADIUS statistics and adding 10 to the number listed for rejects
- B. Defining a baseline and referring to it for the value
- C. Using 10 (per hour) as a good starting point for the value
- D. Defining a parameter and referring to it (self ^ramsfname]) for the value
Answer:
D
Explanation:
This is because a parameter is a variable that can be defined and modified by the user or the script,
and can be used to customize the behavior and output of the NAE script. A parameter can be
referred to by using the syntax self ^ramsfname], where ramsfname is the name of the parameter.
By defining a parameter for the value, the developer can make the NAE script more flexible and
adaptable to different scenarios and switches. The parameter can be set to a default value, such as
10, but it can also be changed by the user or the script based on the network conditions and
requirements. For example, the parameter can be adjusted dynamically based on the average or
standard deviation of the number of rejects per hour, or based on the feedback from the user or
other admins. This way, the NAE script can trigger an alert only when the number of rejects is truly
unusual and not just arbitrary.
A. Checking one of the access switches’ RADIUS statistics and adding 10 to the number listed for
rejects. This is not a good recommendation because it does not account for the variability and
diversity of the network environment and switches. The number of rejects listed for one switch might
not be representative or relevant for another switch, as different switches might have different traffic
patterns, client types, RADIUS configurations, etc. Moreover, adding 10 to the number of rejects is an
arbitrary and fixed value that might not reflect the actual threshold for triggering an alert.
B. Defining a baseline and referring to it for the value. This is not a bad recommendation, but it is not
as good as defining a parameter. A baseline is a reference point that represents the normal or
expected state of a network metric or performance indicator. A baseline can be used to compare and
contrast the current network situation and detect any anomalies or deviations. However, a baseline
might not be easy or accurate to define, as it might require historical data, statistical analysis, or
expert judgment. Moreover, a baseline might not be stable or constant, as it might change over time
due to network growth, evolution, or optimization.
C. Using 10 (per hour) as a good starting point for the value. This is not a good recommendation
because it is an arbitrary and fixed value that might not reflect the actual threshold for triggering an
alert. Using 10 (per hour) as the value might result in false positives or false negatives, depending on
the network conditions and switches. For example, if the normal number of rejects per hour is 5,
then using 10 as the value might trigger an alert too frequently and unnecessarily. On the other
hand, if the normal number of rejects per hour is 15, then using 10 as the value might miss some
important alerts and risks.
Question 5
Refer to the scenario.
# Introduction to the customer
You are helping a company add Aruba ClearPass to their network, which uses Aruba network
infrastructure devices.
The company currently has a Windows domain and Windows C
- A. Deep packet inspection is enabled on the role to which the Aruba APs assign the wireless clients.
- B. Firewall application visibility is enabled on the Aruba gateways, and the gateways have been rebooted.
- C. Gateway IDS/IPS is enabled on the Aruba gateways, and the gateways have been rebooted.
- D. Deep packet inspection is enabled on the Aruba Aps, and the APs have been rebooted.
Answer:
A
Question 6
Refer to the scenario.
An organization wants the AOS-CX switch to trigger an alert if its RADIUS server (cp.acnsxtest.local)
rejects an unusual number of client authentication requests per hour. After some discussions with
other Aruba admins, you are still not sure how many rejections are usual or unusual. You expect that
the value could be different on each switch.
You are helping the developer understand how to develop an NAE script for this use case.
You are helping the developer find the right URI for the monitor.
Refer to the exhibit.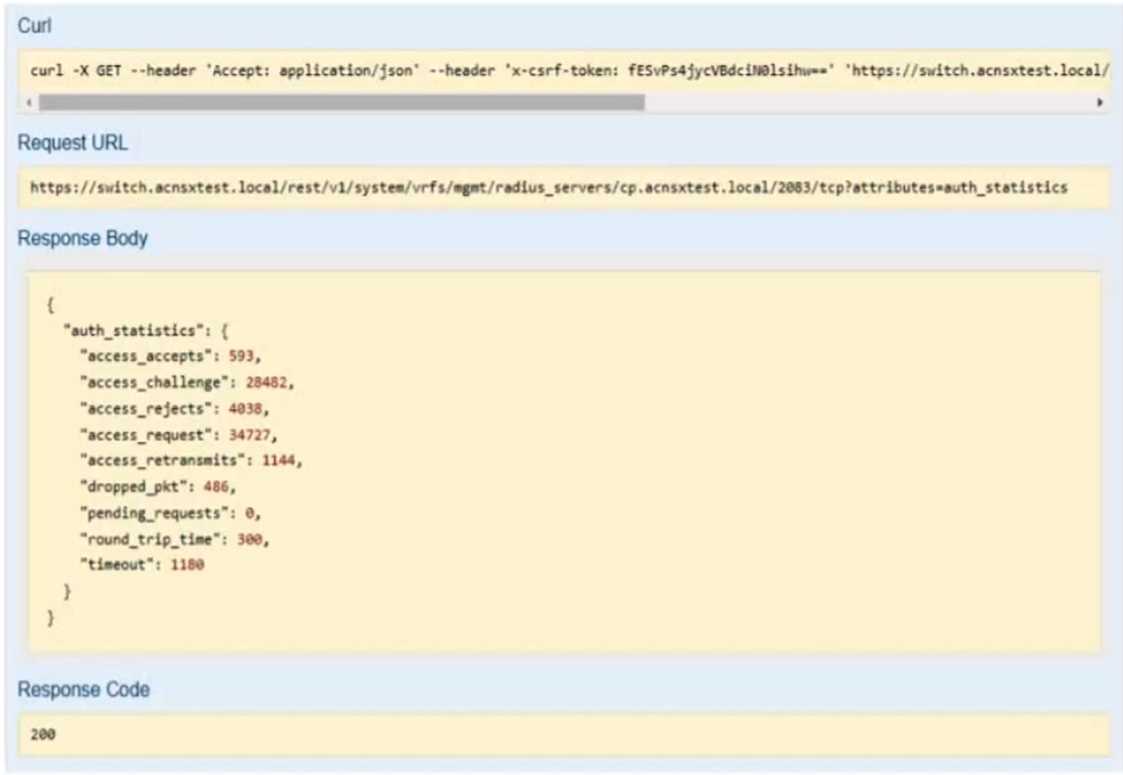
You have used the REST API reference interface to submit a test call. The results are shown in the
exhibit.
Which URI should you give to the developer?
- A. /rest/v1/system/vrfs/mgmt/radius/servers/cp.acnsxtest.local/2083/tcp?attributes=authstatistics B. /rest/v1/system/vrfs/mgmt/radius/servers/cp.acnsxtest.local/2083/tcp?attributes=authstatistics?att ributes=access_rejects
- C. /rest/v1/system/vrfs/mgmt/radius/_servers/cp.acnsxtest.local/2083/tcp D. /rest/v1/system/vrfs/mgmt/radius/servers/cp.acnsxtest.local/2083/tcp?attributes=authstatistics.acc ess_rejects
Answer:
D
Explanation:
This is because this URI specifies the exact attribute that contains the number of access rejects from
the RADIUS server, which is the information that the NAE script needs to monitor and trigger an
alert.
A. /rest/v1/system/vrfs/mgmt/radius/servers/cp.acnsxtest.local/2083/tcp?attributes=authstatistics.
This is not the correct URI because it returns the entire authstatistics object, which contains more
information than the access rejects, such as access accepts, challenges, timeouts, etc. This might
make the NAE script more complex and inefficient to parse and process the data.
B.
/rest/v1/system/vrfs/mgmt/radius/servers/cp.acnsxtest.local/2083/tcp?attributes=authstatistics?att
ributes=access_rejects. This is not a valid URI because it has two question marks, which is a syntax
error. The question mark is used to indicate the start of the query string, which can have one or more
parameters separated by ampersands. The correct way to specify multiple attributes is to use a
comma-separated list after the question mark, such as ?attributes=attr1,attr2,attr3.
C. /rest/v1/system/vrfs/mgmt/radius/_servers/cp.acnsxtest.local/2083/tcp. This is not a valid URI
because it has an extra underscore before servers, which is a typo. The correct resource name is
servers, not _servers. Moreover, this URI does not specify any attributes, which means it will return
the default attributes of the RADIUS server object, such as name, port, protocol, etc., but not the
authstatistics or access_rejects.
7of30
Question 7
Several AOS-CX switches are responding to SNMPv2 GET requests for the public community. The
customer only permits SNMPv3. You have asked a network admin to fix this problem. The admin
says, “I tried to remove the community, but the CLI output an error.”
What should you recommend to remediate the vulnerability and meet the customer’s requirements?
- A. Enabling control plane policing to automatically drop SNMP GET requests
- B. Setting the snmp-server settings to “snmpv3-only”
- C. Adding an SNMP community with a long random name
- D. Enabling SNMPv3, which implicitly disables SNMPv1/v2
Answer:
B
Explanation:
This is because SNMPv3 is a secure version of SNMP that provides authentication, encryption, and
access control for network management. SNMPv3-only is a configuration option on AOS-CX switches
that disables SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c, which are insecure versions of SNMP that use plain text
community strings for authentication. By setting the snmp-server settings to “snmpv3-only”, the
switch will only respond to SNMPv3 requests and reject any SNMPv1 or SNMPv2c requests, thus
remedying the vulnerability and meeting the customer’s requirements.
A. Enabling control plane policing to automatically drop SNMP GET requests. This is not a valid
recommendation because control plane policing is a feature that protects the switch from denial-of-
service (DoS) attacks by limiting the rate of traffic sent to the CPU. Control plane policing does not
disable SNMPv1 or SNMPv2c, but rather applies a rate limit to all SNMP requests, regardless of the
version. Moreover, control plane policing might also drop legitimate SNMP requests if they exceed
the rate limit, which could affect the network management.
C. Adding an SNMP community with a long random name. This is not a valid recommendation
because an SNMP community is a shared secret that acts as a password for accessing network
devices using SNMPv1 or SNMPv2c. Adding an SNMP community with a long random name does not
disable SNMPv1 or SNMPv2c, but rather creates another community string that can be used for
authentication. Moreover, adding an SNMP community with a long random name does not improve
the security of SNMPv1 or SNMPv2c, as the community string is still transmitted in plain text and can
be intercepted by an attacker.
D. Enabling SNMPv3, which implicitly disables SNMPv1/v2. This is not a valid recommendation
because enabling SNMPv3 does not implicitly disable SNMPv1 or SNMPv2c on AOS-CX switches.
Enabling SNMPv3 only adds support for the secure version of SNMP, but does not remove support for
the insecure versions. Therefore, enabling SNMPv3 alone does not remedy the vulnerability or meet
the customer’s requirements.
Question 8
Refer to the scenario.
# Introduction to the customer
You are helping a company add Aruba ClearPass to their network, which uses Aruba network
infrastructure devices.
The company currently has a Windows domain and Windows C
- A. Setting up traffic classes and role mapping rules within Central's global settings
- B. Creating server-based role assignment rules on APs that apply roles to clients based on traffic destinations
- C. Creating server-based role assignment rules on gateways that apply roles to clients based on traffic destinations
- D. Creating a tag on Central to select the proper destination connection and integrating CPPM with Device Insight
Answer:
C
Question 9
Refer to the scenario.
# Introduction to the customer
You are helping a company add Aruba ClearPass to their network, which uses Aruba network
infrastructure devices.
The company currently has a Windows domain and Windows C
- A. Configure OCSP override and set the OCSP URL to localhost/onboard/mdps ocspphp/2
- B. Enable certificate comparison.
- C. Enable authorization.
- D. Configure OCSP override and leave the OCSP URL blank.
Answer:
A
Question 10
Refer to the scenario.
A customer has an AOS10 architecture that is managed by Aruba Central. Aruba infrastructure
devices authenticate clients to an Aruba ClearPass cluster.
In Aruba Central, you are examining network traffic flows on a wireless IoT device that is categorized
as “Raspberry Pi” clients. You see SSH traffic. You then check several more wireless IoT clients and
see that they are sending SSH also.
You want an easy way to communicate the information that an IoT client has used SSH to Aruba
ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM).
What step should you take?
- A. On CPPM create an Endpoint Context Server that points to the Central API.
- B. On CPPM enable Device Insight integration.
- C. On Central configure APs and gateways to use CPPM as the RADIUS accounting server.
- D. On Central set up CPPM as a Webhook application.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
This is because an Endpoint Context Server (ECS) is a feature that allows ClearPass to receive
contextual information from external sources, such as Aruba Central, and use it for policy
enforcement and reporting. An ECS can be configured to point to the Aruba Central API and fetch
data such as device type, category, OS, applications, traffic flows, etc.
An ECS can be used to communicate the information that an IoT client has used SSH to Aruba
ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM). The ECS can query the Aruba Central API and retrieve the network
traffic flows of the wireless IoT devices that are categorized as “Raspberry Pi” clients. The ECS can
then filter the traffic flows by the SSH protocol and send the relevant information to CPPM. CPPM
can then use this information for policy decisions, such as allowing or denying SSH access, or
triggering alerts or actions.
B. On CPPM enable Device Insight integration. This is not a valid step because Device Insight is a
feature that allows ClearPass to discover, profile, and fingerprint devices on the network using deep
packet inspection (DPI) and machine learning (ML). Device Insight does not communicate with Aruba
Central or receive information from it. Moreover, Device Insight might not be able to detect SSH
traffic on encrypted wireless IoT devices without decrypting it first.
C. On Central configure APs and gateways to use CPPM as the RADIUS accounting server. This is not a
valid step because RADIUS accounting is a feature that allows network devices to send periodic
updates about the status and activity of authenticated users or devices to a RADIUS server, such as
CPPM. RADIUS accounting does not communicate with Aruba Central or receive information from it.
Moreover, RADIUS accounting might not be able to capture SSH traffic on wireless IoT devices
without inspecting it first.
D. On Central set up CPPM as a Webhook application. This is not a valid step because Webhook is a
feature that allows Aruba Central to send notifications or events to external applications or services
using HTTP requests. Webhook does not communicate with CPPM or send information to it.
Moreover, Webhook might not be able to send SSH traffic information on wireless IoT devices
without filtering it first.
Question 11
Refer to the scenario.
# Introduction to the customer
You are helping a company add Aruba ClearPass to their network, which uses Aruba network
infrastructure devices.
The company currently has a Windows domain and Windows C
- A. Change the EST authentication method to use an external validator.
- B. Change the EST Digest Algorithm to SHA-512.
- C. Recreate the CA as a registration authority under Azure AD.
- D. Specify an OCSP responder, setting the hostname to localhost.
Answer:
A
Question 12
The customer needs a way for users to enroll new wired clients in Intune. The clients should have
limited access that only lets them enroll and receive certificates. You plan to set up these rights in an
AOS-CX role named “provision.”
The customer’s security team dictates that you must limit these clients’ Internet access to only the
necessary sites. Your switch software supports IPv4 and IPv6 addresses for the rules applied in the
“provision” role.
What should you recommend?
- A. Configuring the rules for the “provision” role with IPv6 addresses, which tend to be more stable
- B. Enabling tunneling to the MCs on the “provision” role and then setting up the privileges on the MCs
- C. Configuring the “provision” role as a downloadable user role (DUR) in CPPM
- D. Assigning the “provision” role to a VLAN and then setting up the rules within a Layer 2 access control list (ACL)
Answer:
C
Explanation:
This is because a downloadable user role (DUR) is a feature that allows the switch to use a central
ClearPass server to download user-roles to the switch for authenticated users12 A DUR can contain
various attributes and rules that define the access level and privileges of the user, such as VLAN, ACL,
PoE, reauthentication period, etc3 A DUR can also be customized and updated on the ClearPass
server without requiring any changes on the switch1
A DUR can be used to create a “provision” role that allows users to enroll new wired clients in Intune.
The “provision” role can have limited access that only lets them enroll and receive certificates from
the Intune service. The “provision” role can also have rules that restrict the Internet access of the
users to only the necessary sites, such as the Intune portal and the certificate authority.
The rules can
be based on IPv4 or IPv6 addresses, depending on the network configuration and preference2
A. Configuring the rules for the “provision” role with IPv6 addresses, which tend to be more stable.
This is not a valid recommendation because it does not address how to create and apply the
“provision” role on the switch.
Moreover, IPv6 addresses do not necessarily tend to be more stable
than IPv4 addresses, as both protocols have their own advantages and disadvantages4
B. Enabling tunneling to the MCs on the “provision” role and then setting up the privileges on the
MCs. This is not a valid recommendation because it does not explain how to enable tunneling or
what MCs are.
Moreover, tunneling is a technique that encapsulates one network protocol within
another, which adds complexity and overhead to the network communication5
D. Assigning the “provision” role to a VLAN and then setting up the rules within a Layer 2 access
control list (ACL). This is not a valid recommendation because it does not explain how to assign a role
to a VLAN or how to create a Layer 2 ACL on the switch.
Moreover, a Layer 2 ACL is limited in its
filtering capabilities, as it can only match on MAC addresses or Ethernet types, which might not be
sufficient for restricting Internet access to specific sites
Question 13
Refer to the scenario.
# Introduction to the customer
You are helping a company add Aruba ClearPass to their network, which uses Aruba network
infrastructure devices.
The company currently has a Windows domain and Windows C
- A. The hostname used by ClearPass Policy ManaGer's RADIUS services
- B. The ClearPass Onboard hostname referenced in an Onboard provisioninG profile
- C. The ClearPass Onboard hostname referenced in Intune SCEP profiles
- D. The hostname used by the on-prem domain controllers
Answer:
B
Question 14
Refer to the scenario.
# Introduction to the customer
You are helping a company add Aruba ClearPass to their network, which uses Aruba network
infrastructure devices.
The company currently has a Windows domain and Windows C
- A. In rule 1 change Subject-CN to Issuer-CN.
- B. Move rules 2 and 3 to the top of the list.
- C. Change the rules evaluation mechanism to first applicable.
- D. Change the default role to 'mobile-onboarded*
Answer:
A
Question 15
Refer to the scenario.
A customer has an AOS10 architecture that is managed by Aruba Central. Aruba infrastructure
devices authenticate clients to an Aruba ClearPass cluster.
In Aruba Central, you are examining network traffic flows on a wireless IoT device that is categorized
as “Raspberry Pi” clients. You see SSH traffic. You then check several more wireless IoT clients and
see that they are sending SSH also.
You want a relatively easy way to communicate the information that an IoT client has used SSH to
Aruba CPPM.
What is one prerequisite?
- A. Enable event processing on subscribers in the ClearPass cluster.
- B. In CPPM's CA trust list, add the Aruba Infrastructure usage to the DigiCert certificate.
- C. Obtain a data collector token from Central's platform integration settings.
- D. Create an API application and token within the REST API settings.
Answer:
C