Fortinet NSE8-812 Exam Questions
Questions for the NSE8-812 were updated on : Feb 12 ,2026
Page 1 out of 7. Viewing questions 1-15 out of 105
Question 1
Refer to the exhibits.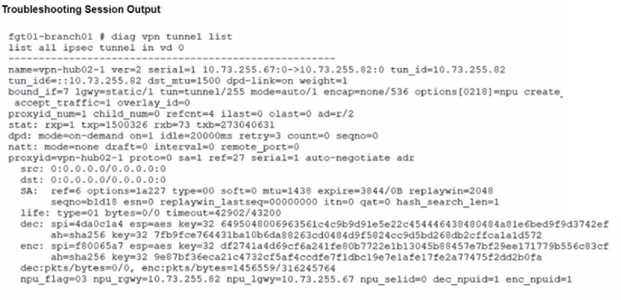
A customer is trying to restore a VPN connection configured on a FortiGate. Exhibits show output
during a troubleshooting session when the VPN was working and the current baseline VPN
configuration.
Which configuration parameters will restore VPN connectivity based on the diagnostic output?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- A. Option A
- B. Option B
- C. Option C
- D. Option D
Answer:
C
Question 2
Refer to the exhibit.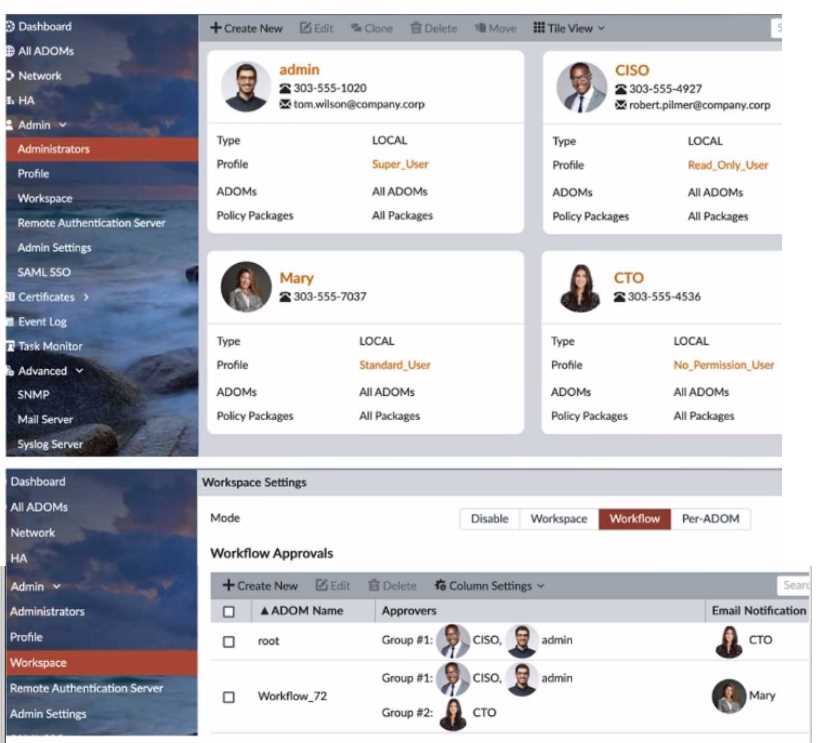
The Company Corp administrator has enabled Workflow mode in FortiManager and has assigned
approval roles to the current administrators. However, workflow approval does not function as
expected. The CTO is currently unable to approve submitted changes.
Given the exhibit, which two possible solutions will resolve the workflow approval problems with the
Workflow_72 ADOM? (Choose two.)
- A. The CTO must have a defined email address for their admin user account.
- B. The CTO and CISO need to swap Approval Groups so that the highest authority is in Group #1.
- C. The CTO must have Standard access level or higher for FortiManager.
- D. The CISO must have a higher access level than "Read_Only_User" in FortiManager.
- E. The CTO needs to be added to "Email Notification" in the Workflow_72 ADOM.
Answer:
A, C
Question 3
Refer to the exhibit of a FortiNAC configuration.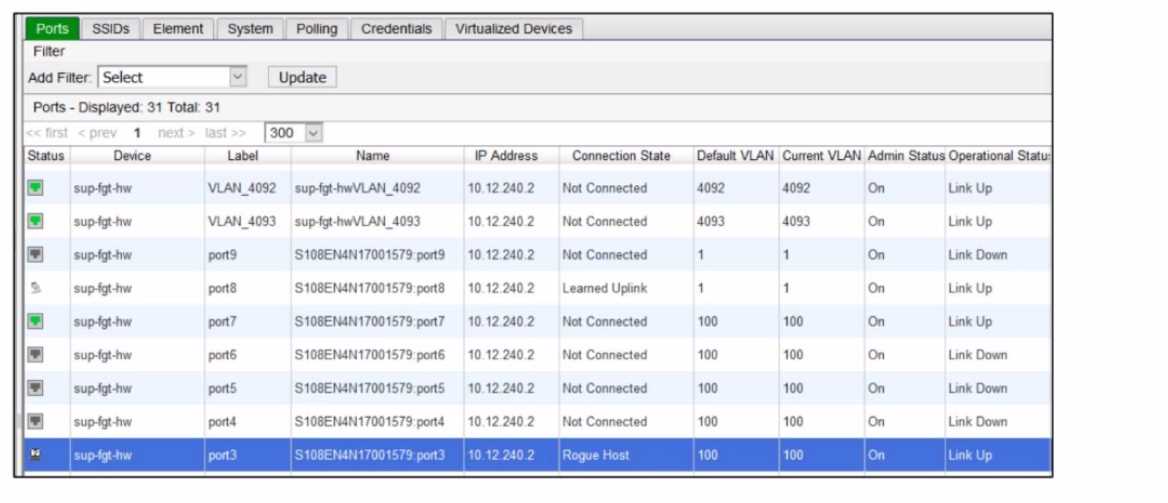
In this scenario, which two statements are correct? (Choose two.)
- A. A device that is modeled in FortiNAC is connected on VLAN 4093.
- B. An unknown host is connected to port3.
- C. The IP address of the FortiSwitch is 10.12.240.2.
- D. Port8 is connected to a FortiGate in FortiLink mode.
Answer:
C, D
Explanation:
C . The IP address of the FortiSwitch is 10.12.240.2:
This statement is correct based on the exhibit and your clarification. The exhibit lists the "IP Address"
as 10.12.240.2 across multiple entries, including ports and VLANs associated with the device "sup-
fgt-hw" (FortiSwitch). Your reasoning indicates that this IP is the management address of the
FortiSwitch, as it is consistently shown as the IP for the device containing the ports. In Fortinet’s
architecture, as described in the NSE 8 study guide, the management IP of a FortiSwitch is typically
configured and visible in such configurations, especially when integrated with FortiGate and
FortiNAC. The "Device" column labeling "sup-fgt-hw" further supports that this is the FortiSwitch,
and the IP 10.12.240.2 is its management address. This aligns with FortiSwitch management and
integration details in the NSE 8 study guide.
D . An unknown host is connected to port3:
This statement is correct as the exhibit highlights port3 under the "Name" column for the device
"sup-fgt-hw" with a "Rogue Host" status in the "Connection" column, an IP address of 10.12.240.2, a
Default VLAN of 100, and an Operational Status of "Link Up." In FortiNAC, a "Rogue Host" indicates
an unknown or unauthorized device connected to the network, which FortiNAC identifies for further
action or isolation. This is consistent with FortiNAC’s capabilities for detecting and classifying
unknown devices, as detailed in the NSE 8 study guide under network access control and rogue
device detection.
Why A and B are incorrect:
A . A device that is modeled in FortiNAC is connected on VLAN_4093: This is incorrect based on your
clarification that there is no device connected on that port—it is simply the default VLAN (4093) for
that entry. The exhibit shows VLAN_4093 with a "Not Connected" status and "Link Up" operational
status, but no active device connection is indicated. The NSE 8 study guide emphasizes that FortiNAC
requires an active connection and device profiling for a device to be considered "connected," which
is not evident here for VLAN_4093.
B . Port8 is connected to a FortiGate in FortiLink mode: This is incorrect because the exhibit shows
port8 with a "Learned Uplink" status, which, as you noted, refers to any kind of uplink and does not
specifically indicate FortiLink mode. FortiLink mode is a specific configuration between FortiGate and
FortiSwitch requiring explicit settings, which are not mentioned or implied in the exhibit. The NSE 8
study guide clarifies that FortiLink mode involves distinct configuration details (e.g., FortiLink
interfaces), which are absent here.
Fortinet Network Security Expert 8 Study Guide Reference:
FortiNAC 7.2 Admin Guide (NSE 8): Sections on Device Visibility, VLAN Management, and Rogue
Device Detection.
FortiSwitch 7.2 Admin Guide (NSE 8): Sections on FortiLink Configuration, Network Segmentation,
and Management IP Configuration.
FortiGate 7.2 Admin Guide (NSE 8): Sections on Integration with FortiNAC and FortiSwitch for
Network Security.
Question 4
Refer to the exhibit.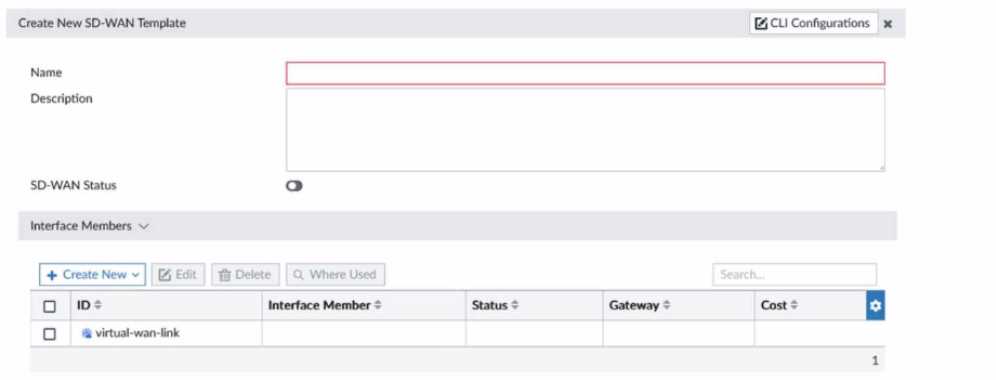
You need to create a base SD-WAN configuration that includes SD-WAN rules and Performance SLAs
for spoke sites with various connectivity types. It needs to be done in a way that can be easily applied
to new sites with a minimum amount of change. How should you create the SD-WAN zones?
- A. With members and assign overlay interfaces
- B. With members without interface assignments
- C. With no members configured
- D. With members and assign interfaces but do not specify a gateway
Answer:
A
Question 5
A Hub FortiGate is connecting multiple branch FortiGate devices separating the traffic centrally in
unique VRFs. Routing information is exchanged using BGP between the Hub and the Branch
FortiGate devices.
You want to efficiently enable route leaking of specific routes between the VRFs.
Which two steps are required to achieve this requirement? (Choose two.)
- A. Create a vdom link between VRF10 and VRF12
- B. Enable Multi-VDOM mode on the Hub FortiGate and add a VDOM to connect VRF10 and VRF12
- C. Enable BGP recursive routing on the HUB FortiGate
- D. Configure route-maps to leak the selected routes using BGP
Answer:
AD
Explanation:
https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortigate/7.0.1/administration-guide/834664/route-leaking-
between-vrfs-with-bgp
Question 6
A FortiGate deployment contains the following configuration:
What is the result of this configuration?
- A. Route-maps are not configurable in VDOM SERVICES
- B. Route-maps from the Root VDOM configuration are available in VDOM SERVICES
- C. Route-maps from VDOM SERVICES are available in all other VDOMs
- D. Route-maps for VDOM SERVICES are excluded from HA configuration synchronization
Answer:
D
Explanation:
https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortigate/7.2.4/administration-guide/105611
Question 7
You have configured a Site-to-Site IPsec VPN tunnel between a FortiGate and a third-party device but
notice that one of the error counters on the tunnel interface keeps increasing.
Which two configuration options can resolve this problem? (Choose two.)
- A. Enable Forward Error Correction (FEC) on the VPN interface for egress traffic.
- B. Adjust the MTU of the physical interface to which the IPsec tunnel is bound.
- C. Enable DF-bit honoring in the global settings.
- D. Adjust the MTU of the IPsec interface.
Answer:
C, D
Question 8
Refer to the exhibits.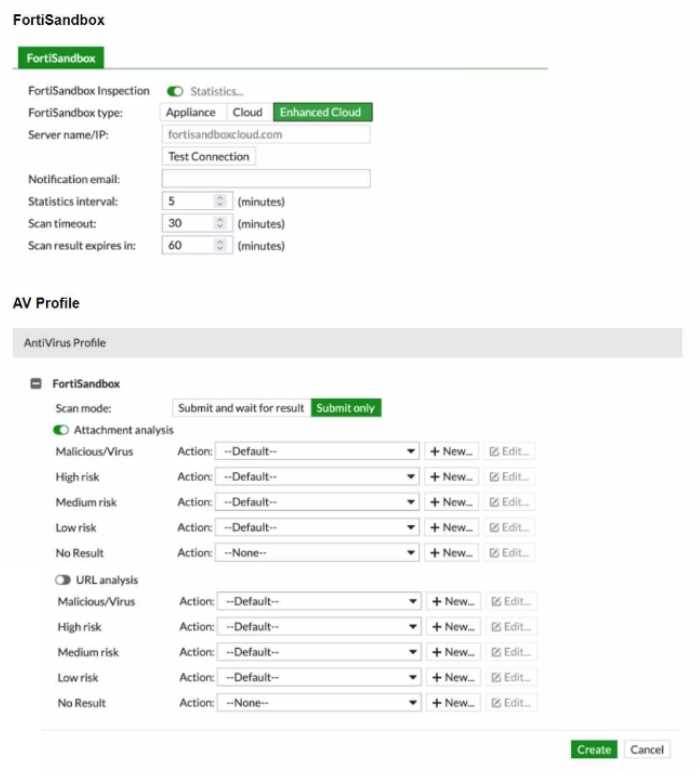
You must integrate a FortiMail and FortiSandbox Enhanced Cloud solution for a customer who is
concerned about the e-mails being delayed for too long.
According to the configuration shown in the exhibits, which would be an expected behavior?
- A. FortiMail will relay valid e-mails to the mail server as soon as it is done with other local inspections.
- B. If an attachment is sent to the FortiSandbox while the job queue is full, the e-mail might be delayed for up to 30 minutes, then e-mail will be relayed to the mail server.
- C. FortiMail will not wait for results but only for attachments that have been already submitted to the FortiSandbox in the last 60 minutes.
- D. FortiMail will ignore the timeout value if content disarm and reconstruction (CDR) is enabled.
Answer:
A
Question 9
A FortiGate must be configured to accept VoIP traffic which will include session initiation protocol
(SIP) traffic. Which statement about the VoIP configuration options is correct?
- A. Restricting SIP requests is only possible when using the SIP Session Helper.
- B. Rate tracking of SIP requests is only possible when the application layer gateway (ALG) is set to Flow mode.
- C. FortiOS cannot accept SIP traffic if both the SIP Session Helper and the application layer gateway (ALG) are disabled.
- D. By default, VoIP traffic will be processed using the SIP Session Helper.
Answer:
C
Question 10
Refer to the exhibit.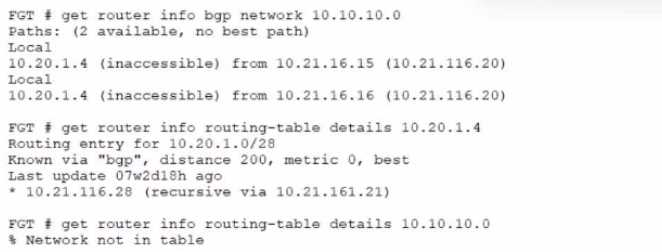
A customer reports that they are not able to reach subnet 10.10.10.0/24 from their FortiGate device.
Based on the exhibit, what should you do to correct the situation?
- A. Enable iBGP multipath
- B. Enable recursive resolution for BGP routes
- C. Enable next-hop-self feature
- D. Enable additional-path feature
Answer:
C
Question 11
Refer to the exhibits, which show a network topology and VPN configuration.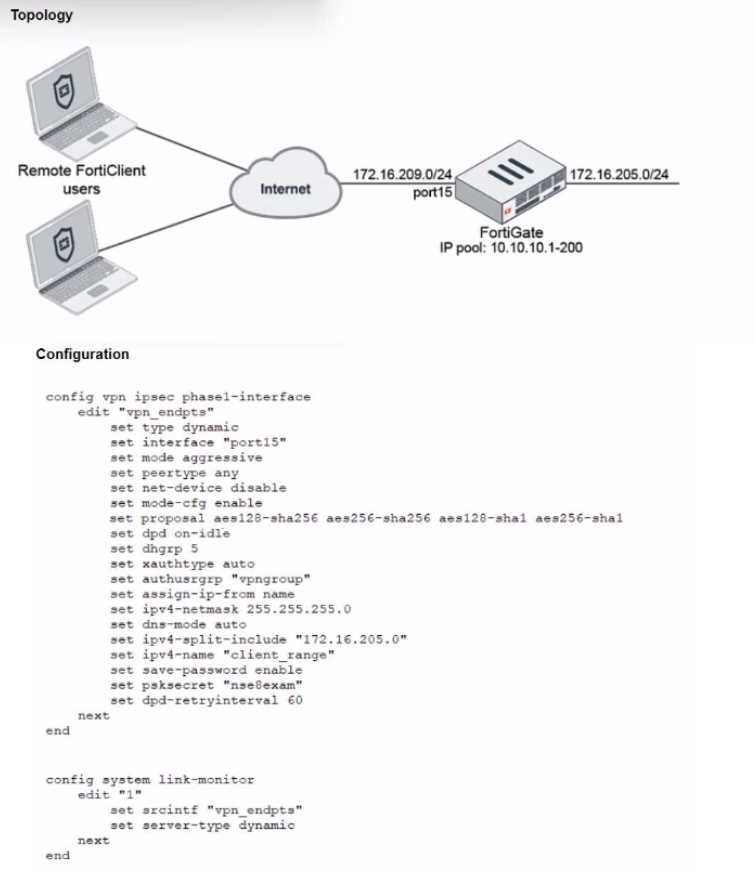
A network administrator has been tasked with modifying the existing dial-up IPsec VPN infrastructure
to detect the path quality to the remote endpoints.
After applying the configuration shown in the configuration exhibit, the VPN clients can still connect
and access the protected 172.16.205.0/24 network, but no SLA information shows up for the client
tunnels when issuing the diagnose sys link-monitor tunnel all command on the FortiGate CLI.
What is wrong with the configuration?
- A. SLA link monitoring does not work with the net-device setting.
- B. The admin needs to disable the mode-cfg setting.
- C. IPsec Phase1 Interface has to be configured in IPsec main mode.
- D. It is necessary to use the IKEv2 protocol in this situation.
Answer:
A
Question 12
Which two types of interface have built-in active bypass in FortiDDoS devices? (Choose two.)
- A. SFP
- B. LC
- C. QSFP+
- D. Copper
- E. SFP+
Answer:
BD
Explanation:
https://help.fortinet.com/fddos/4-3-0/FortiDDoS/Built_in_bypass.htm
Question 13
Refer to the exhibits.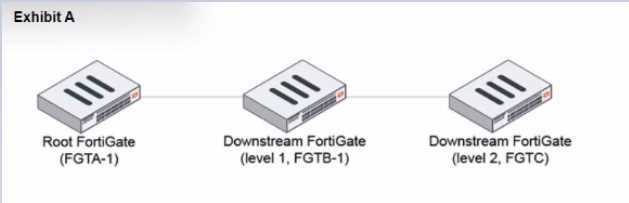
During the implementation of a Fortinet Security Fabric configuration, CLI commands were issued in
the order shown in the exhibit. On the next day, the local admin for FGTC issues the following
command: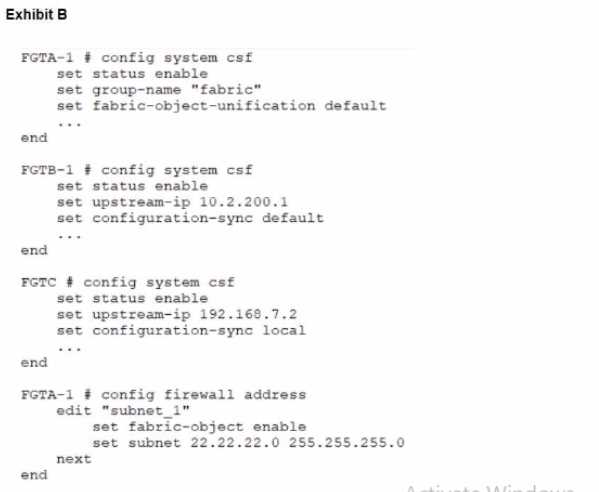
FGTC # config system csf
set configuration-sync default
end
In this scenario, which outcome is true regarding the "subnet_1" firewall address object on FGTC?
- A. The object will only be automatically created on FGTC if it is modified on FGTA-1.
- B. The object needs to be recreated on FGTA-1 before it is automatically created on FGTC.
- C. The object is not automatically created.
- D. The object is automatically created.
Answer:
D
Question 14
A FortiGate is configured to perform outbound firewall authentication with Azure AD as a SAML IdP.
What are two valid interactions that occur when the client attempts to access the internet? (Choose
two.)
- A. FortiGate SP sends a SAML request to the IdP.
- B. The Microsoft SAML IdP sends the SAML response to the FortiGate SP.
- C. The client browser forwards the SAML response received from Microsoft SAML IdP to the FortiGate SP.
- D. FortiGate SP redirects the client browser to the local captive portal and then redirects to the Microsoft SAML IdP.
Answer:
A, B
Question 15
Refer to the exhibit.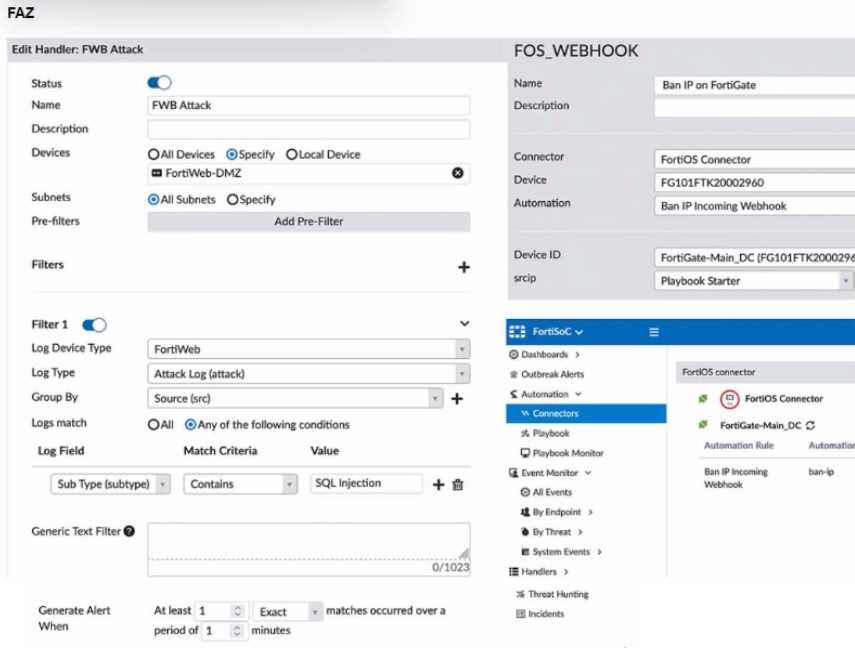
A customer is trying to setup a Playbook automation using a FortiAnalyzer, FortiWeb and FortiGate.
The intention is to have the FortiGate quarantine any source of SQL Injection detected by the
FortiWeb. They got the automation stitch to trigger on the FortiGate when simulating an attack to
their website, but the quarantine object was created with the IP 0.0.0.0. Referring to the
configuration and logs in the exhibits, which two statements are true? (Choose two.)
- A. The Group By option in the handler should be different to src, so src can be used on the Playbook configuration.
- B. FortiSOC Playbooks combining FortiWeb and FortiGate are not supported.
- C. To diagnose this issue, you need to use the command diagnose test application oftpd 22.
- D. The FortiAnalyzer ADOM Type must be Fabric.
- E. To fix the issue the parameter for script on the Playbook configuration should be epip.
Answer:
A, D