Fortinet NSE4-FGT-7-2 Exam Questions
Questions for the NSE4-FGT-7-2 were updated on : Jan 26 ,2026
Page 1 out of 13. Viewing questions 1-15 out of 183
Question 1
What is the primary FortiGate election process when the HA override setting is disabled?
- A. Connected monitored ports > Priority > HA uptime > FortiGate serial number
- B. Connected monitored ports > Priority > System uptime > FortiGate serial number
- C. Connected monitored ports > HA uptime > Priority > FortiGate serial number
- D. Connected monitored ports > System uptime > Priority > FortiGate serial number
Answer:
C
Question 2
What are two features of the NGFW policy-based mode? (Choose two.)
- A. NGFW policy-based mode does not require the use of central source NAT policy.
- B. NGFW policy-based mode can only be applied globally and not on individual VDOMs_
- C. NGFW policy-based mode policies support only flow inspection.
- D. NGFW policy-based mode supports creating applications and web filtering categories directly in a firewall policy
Answer:
CD
Explanation:
C. NGFW policy-based mode policies support only flow inspection. This is correct.
This is a feature of
the NGFW policy-based mode, according to the Fortinet documentation "Profile-based NGFW vs
policy-based NGFW"1
. The documentation states that “In policy-based NGFW mode, you can only
select flow inspection. Proxy inspection is not supported.”
D. NGFW policy-based mode supports creating applications and web filtering categories directly in a
firewall policy. This is correct.
This is a feature of the NGFW policy-based mode, according to the
Fortinet documentation "Profile-based NGFW vs policy-based NGFW"1
. The documentation states
that “In policy-based NGFW mode, you allow applications and URL categories to be used directly in
security policies, without requiring web filter or application control profiles.”
Question 3
How can you disable RPF checking?
- A. Disable strict-src-check under system settings.
- B. Disable src-check on the interface level settings
- C. Unset fail-alert-interfaces on the interface level settings.
- D. Disable fail-detect on the interface level settings.
Answer:
B
Question 4
Which three pieces of information does FortiGate use to identify the hostname of the SSL server
when SSL certificate inspection is enabled? (Choose three.)
- A. The server name indication (SNI) extension in the client hello message
- B. The subject alternative name (SAN) field in the server certificate
- C. The host field in the HTTP header
- D. The serial number in the server certificate
- E. The subject field in the server certificate
Answer:
ABE
Explanation:
A) The server name indication (SNI) extension in the client hello message. This is correct. This is a
piece of information that FortiGate uses to identify the hostname of the SSL server when SSL
certificate inspection is enabled. The SNI extension is a feature of the TLS protocol that allows a client
to indicate the hostname of the server it wants to connect to during the TLS handshake.
This helps
the server to present the appropriate certificate for the requested hostname, especially when the
server hosts multiple domains on the same IP address1
.
FortiGate can use the SNI extension in the
client hello message to identify the hostname of the SSL server and verify it against the server
certificate2
.
B) The subject alternative name (SAN) field in the server certificate. This is correct. This is a piece of
information that FortiGate uses to identify the hostname of the SSL server when SSL certificate
inspection is enabled. The SAN field is an extension of the X.509 certificate standard that allows a
certificate to specify multiple hostnames or IP addresses that are valid for the certificate.
This helps
the certificate to support multiple domains or subdomains on the same server, or multiple servers
with different IP addresses3
.
FortiGate can use the SAN field in the server certificate to identify the
hostname of the SSL server and verify it against the client request2
.
E) The subject field in the server certificate. This is correct. This is a piece of information that
FortiGate uses to identify the hostname of the SSL server when SSL certificate inspection is enabled.
The subject field is a part of the X.509 certificate standard that contains information about the
identity of the entity that owns the certificate, such as common name, organization, country, and so
on.
The common name usually specifies the hostname or domain name of the server that owns the
certificate4
.
FortiGate can use the subject field in the server certificate to identify the hostname of
the SSL server and verify it against the client request2
.
Question 5
Refer to the exhibits.
Exhibit A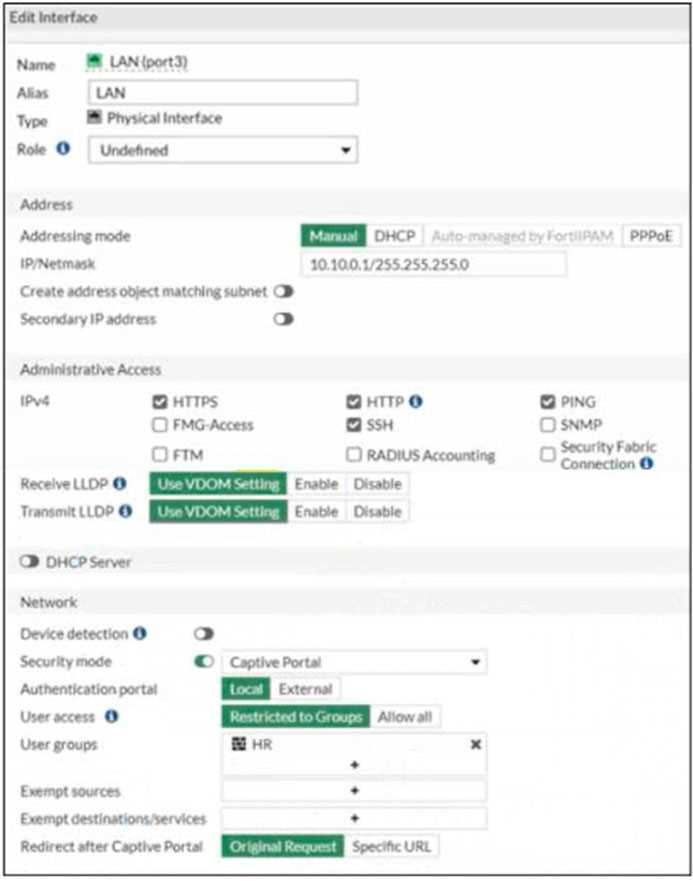
Exhibit B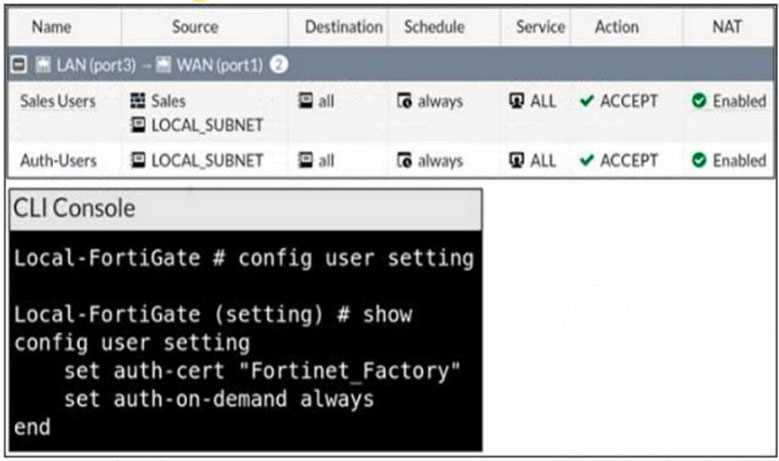
The exhibit contains a network interface configuration, firewall policies, and a CLI console
configuration.
How will FortiGate handle user authentication for traffic that arrives on the LAN interface?
- A. If there is a fall-through policy in place, users will not be prompted for authentication.
- B. Authentication is enforced at a policy level; all users will be prompted for authentication.
- C. All users will be prompted for authentication, users from the Sales group can authenticate successfully with the correct credentials.
- D. All users will be prompted for authentication, users from the HR group can authenticate successfully with the correct credentials.
Answer:
D
Question 6
Refer to the exhibit to view the firewall policy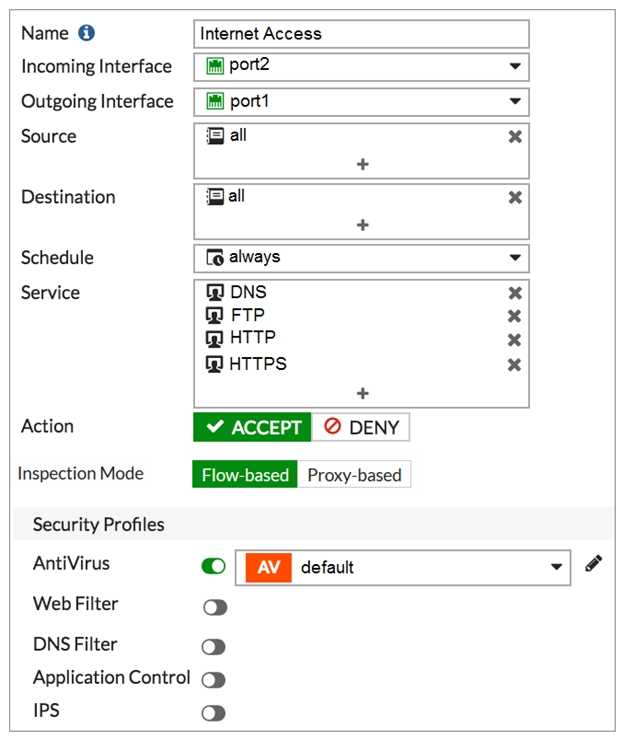
Why would the firewall policy not block a well-known virus, for
example eicar?
- A. Web filter is not enabled on the firewall policy to complement the antivirus profile.
- B. The firewall policy does not apply deep content inspection.
- C. The firewall policy is not configured in proxy-based inspection mode.
- D. The action on the firewall policy is not set to deny
Answer:
B
Question 7
What is a reason for triggering IPS fail open?
- A. The IPS socket buffer is full and the IPS engine cannot process additional packets.
- B. The IPS engine cannot decode a packet.
- C. The IPS engine is upgraded.
- D. The administrator enabled NTurbo acceleration.
Answer:
A
Question 8
Refer to the exhibit.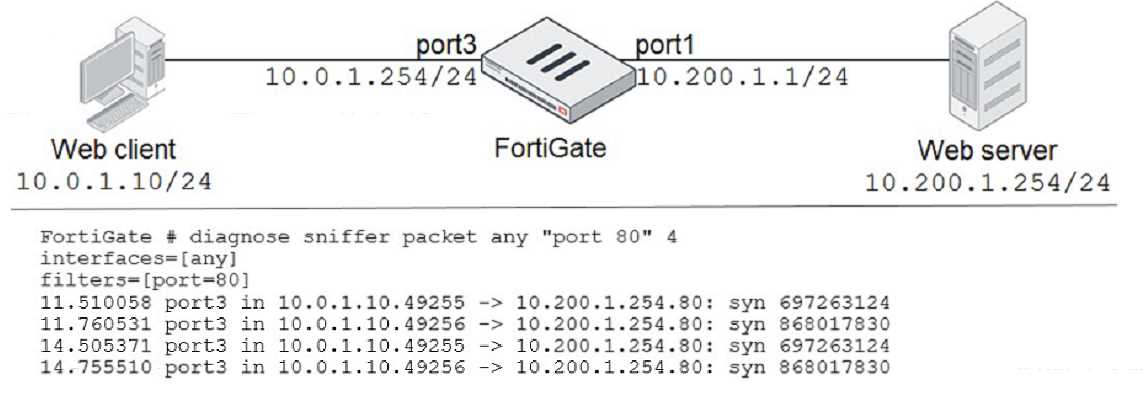
In the network shown in the exhibit, the web client cannot connect to the HTTP web server. The
administrator runs the FortiGate built-in sniffer and gets the output as shown in the exhibit.
What should the administrator do next to troubleshoot the problem?
- A. Run a sniffer on the web server.
- B. Capture the traffic using an external sniffer connected to port1.
- C. Execute another sniffer in the FortiGate, this time with the filter host 10.0.1.10ג€
- D. Execute a debug flow.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
This solution will help the administrator troubleshoot the problem by tracing the packet flow through
the FortiGate device and displaying the details of each step.
A debug flow can show the source and
destination interfaces, the firewall policy, the routing table, the NAT translation, the security profiles,
and the session information of the packet1
. A debug flow can also show any errors or anomalies that
occur during the packet processing.
To execute a debug flow, the administrator can use the diagnose
debug flow command in the CLI
Question 9
What are two scanning techniques supported by FortiGate? (Choose two.)
- A. Machine learning scan
- B. Antivirus scan
- C. Ransomware scan
- D. Trojan scan
Answer:
AB
Explanation:
FortiGate Security 7.2 Study Guide (p.341):
"Like viruses, which use many methods to avoid detection, FortiGate uses many techniques to detect
viruses. These detection techniques include:
• Antivirus scan
• Grayware scan
• Machine learning (AI) scan
If all antivirus features are enabled, FortiGate applies the following scanning order: antivirus scan,
followed by grayware scan, followed by AI scan."
Question 10
Refer to the exhibit.
The exhibit shows a diagram of a FortiGate device connected to the network and the firewall policy
and IP pool configuration on the FortiGate device.
Two PCS, PCI and PC2, are connected behind FortiGate and can access the internet successfully.
However, when the administrator adds a third PC to the network (PC3), the PC cannot connect to the
Intarnet_
Based on the information shown in the exhibit, which three configuration changes should the
administrator make to fix the connectivity issue for PC3? (Choose three.)
- A. In the IP pool configuration, set type to overload.
- B. Configure 192.2. O. 12/24 as the secondary IP address on port1
- C. Configure another firewall policy that matches only the address of PC3 as source, and then place the policy on top of the list.
- D. In the IP pool configuration, set endip to 192.2. O .12
- E. In the firewall policy configuration, disable ippool.
Answer:
ADE
Question 11
Refer to the exhibit showing a debug flow output.
What two conclusions can you make from the debug flow output? (Choose two.)
- A. The debug flow is for ICMP traffic.
- B. The default route is required to receive a reply.
- C. Anew traffic session was created.
- D. A firewall policy allowed the connection.
Answer:
AC
Explanation:
The debug flow output shows the result of a diagnose command that captures the traffic flow
between the source and destination IP addresses1
.
The debug flow output reveals the following
information about the traffic flow1
:
The protocol is 1, which means that the traffic uses ICMP protocol2
.
ICMP is a protocol that is used to
send error messages and test connectivity between devices2
.
The session state is 0, which means that a new traffic session was created3
.
A session is a data
structure that stores information about a connection between two devices3
.
The policy ID is 1, which means that the traffic matched the firewall policy with ID 14
.
A firewall
policy is a rule that defines how FortiGate processes traffic based on the source, destination, service,
and action parameters4
.
The action is 0, which means that the traffic was allowed by the firewall policy. An action is a
parameter that specifies what FortiGate does with the traffic that matches a firewall policy.
Therefore, two conclusions that can be made from the debug flow output are:
The debug flow is for ICMP traffic.
A new traffic session was created.
Question 12
An administrator configures outgoing interface any in a firewall policy.
What is the result of the policy list view?
- A. Search option is disabled.
- B. Policy lookup is disabled.
- C. By Sequence view is disabled.
- D. Interface Pair view is disabled.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
"If you use multiple source or destination interfaces, or the any interface in a firewall policy, you
cannot separate policies into sections by interface pairs—some would be triplets or more. So
instead, policies are then always displayed in a single list (By Sequence)."
Question 13
What are two functions of the ZTNA rule? (Choose two.)
- A. It redirects the client request to the access proxy.
- B. It applies security profiles to protect traffic.
- C. It defines the access proxy.
- D. It enforces access control.
Answer:
BD
Explanation:
A ZTNA rule is a policy that enforces access control and applies security profiles to protect traffic
between the client and the access proxy1
.
A ZTNA rule defines the following parameters1
:
Incoming interface: The interface that receives the client request.
Source: The address and user group of the client.
ZTNA tag: The tag that identifies the domain that the client belongs to.
ZTNA server: The server that hosts the access proxy.
Destination: The address of the application that the client wants to access.
Action: The action to take for the traffic that matches the rule. It can be accept, deny, or redirect.
Security profiles: The security features to apply to the traffic, such as antivirus, web filter, application
control, and so on.
A ZTNA rule does not redirect the client request to the access proxy.
That is the function of a policy
route that matches the ZTNA tag and sends the traffic to the ZTNA server2
.
A ZTNA rule does not define the access proxy.
That is done by creating a ZTNA server object that
specifies the IP address, port, and certificate of the access proxy3
.
FortiGate Infrastructure 7.2 Study Guide (p.177): "A ZTNA rule is a proxy policy used to enforce
access control. You can define ZTNA tags or tag groups to enforce zero-trust role-based access. To
create a rule, type a rule name, and add IP addresses and ZTNA tags or tag groups that are allowed or
blocked access. You also select the ZTNA server as the destination. You can also apply security
profiles to protect this traffic."
Question 14
Refer to the exhibit, which contains a static route configuration.
An administrator created a static route for Amazon Web Services.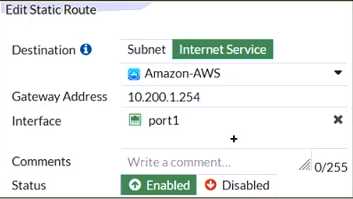
Which CLI command must the administrator use to view the route?
- A. get router info routing-table database
- B. diagnose firewall route list
- C. get internet-service route list
- D. get router info routing-table all
Answer:
B
Explanation:
ISDB static route will not create entry directly in routing-table. Reference:
https://community.fortinet.com/t5/FortiGate/Technical-Tip-Creating-a-static-route-for-Predefined-
Internet/ta-p/198756
and here
https://community.fortinet.com/t5/FortiGate/Technical-Tip-Verify-the-matching-policy-
route/ta-p/190640
FortiGate Infrastructure 7.2 Study Guide (p.16 and p.59): "Even though they are configured as static
routes, ISDB routes are actually policy routes and take precedence over any other routes in the
routing table. As such, ISDB routes are added to the policy routing table." "FortiOS maintains a policy
route table that you can view by running the diagnose firewall proute list command."
Question 15
An organization requires remote users to send external application data running on their PCs and
access FTP resources through an SSL/TLS connection.
Which FortiGate configuration can achieve this goal?
- A. SSL VPN bookmark
- B. SSL VPN tunnel
- C. Zero trust network access
- D. SSL VPN quick connection
Answer:
B
Explanation:
FortiGate Infrastructure 7.2 Study Guide (p.198): "Tunnel mode requires FortiClient to connect to
FortiGate. FortiClient adds a virtual network adapter identified as fortissl to the user’s PC. This virtual
adapter dynamically receives an IP address from FortiGate each time FortiGate establishes a new
VPN connection. Inside the tunnel, all traffic is SSL/TLS encapsulated. The main advantage of tunnel
mode over web mode is that after the VPN is established, any IP network application running on the
client can send traffic through the tunnel."
An SSL VPN tunnel allows remote users to establish a secure and encrypted Virtual Private Network
(VPN) connection to the private network using the SSL/TLS protocol1
.
An SSL VPN tunnel can provide
access to network resources such as FTP servers, as well as external applications running on the
user’s PC1
.
An SSL VPN bookmark is a web link that provides access to network resources through the SSL VPN
web portal1
. It does not support external applications running on the user’s PC.
Zero trust network access (ZTNA) is a security model that provides role-based application access to
remote users without exposing the private network to the internet2
. It does not use SSL/TLS
protocol, but rather a proprietary ZTNA protocol.
SSL VPN quick connection is a feature that allows users to connect to an SSL VPN tunnel without
installing FortiClient or any other software on their PC3
. It requires a web browser that supports Java
or ActiveX. It does not support external applications running on the user’s PC.