Fortinet FCSS EFW AD 7 6 Exam Questions
Questions for the FCSS EFW AD 7 6 were updated on : Feb 22 ,2026
Page 1 out of 4. Viewing questions 1-15 out of 57
Question 1
Refer to the exhibit.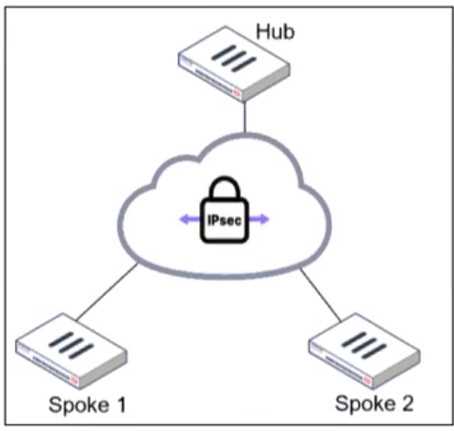
An administrator is deploying a hub and spokes network and using OSPF as dynamic protocol.
Which configuration is mandatory for neighbor adjacency?
- A. Set bfd enable in the router configuration
- B. Set network-type point-to-multipoint in the hub interface
- C. Set rfc1583-compatible enable in the router configuration
- D. Set virtual-link enable in the hub interface
Answer:
B
Explanation:
In a hub-and-spoke topology using OSPF over IPsec VPNs, the point-to-multipoint network type is
necessary to establish neighbor adjacencies between the hub and spokes. This network type ensures
that OSPF operates correctly without requiring a designated router (DR) and allows dynamic routing
updates across the IPsec tunnels.
Question 2
Refer to the exhibit, which shows the VDOM section of a FortiGate device.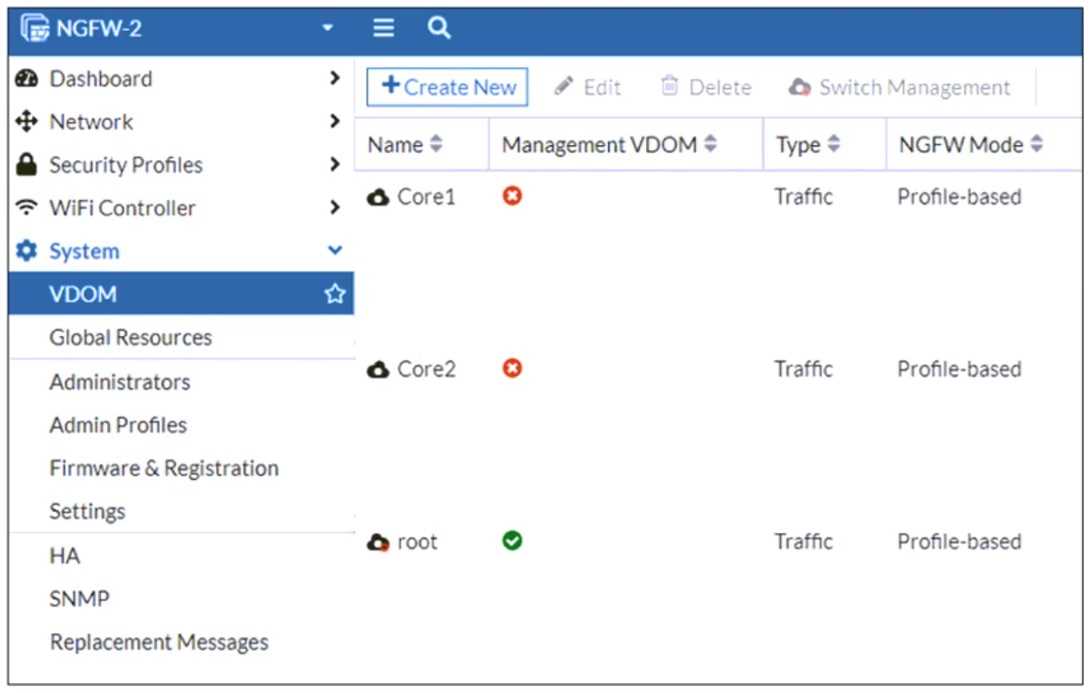
An administrator discovers that webfilter stopped working in Core1 and Core2 after a maintenance
window.
Which two reasons could explain why webfilter stopped working? (Choose two.)
- A. The root VDOM does not have access to FortiManager in a closed network.
- B. The root VDOM does not have a VDOM link to connect with the Corel and Core2 VDOMs.
- C. The Core1 and Core2 VDOMs must also be enabled as Management VDOMs to receive FortiGuard updates
- D. The root VDOM does not have access to any valid public FDN.
Answer:
B, D
Explanation:
Since Core1 and Core2 are not designated as management VDOMs, they rely on the root VDOM for
connectivity to external resources such as FortiGuard updates. If the root VDOM lacks a VDOM link to
these VDOMs or cannot reach FortiGuard services, security features like web filtering will stop
working.
Question 3
Refer to the exhibits.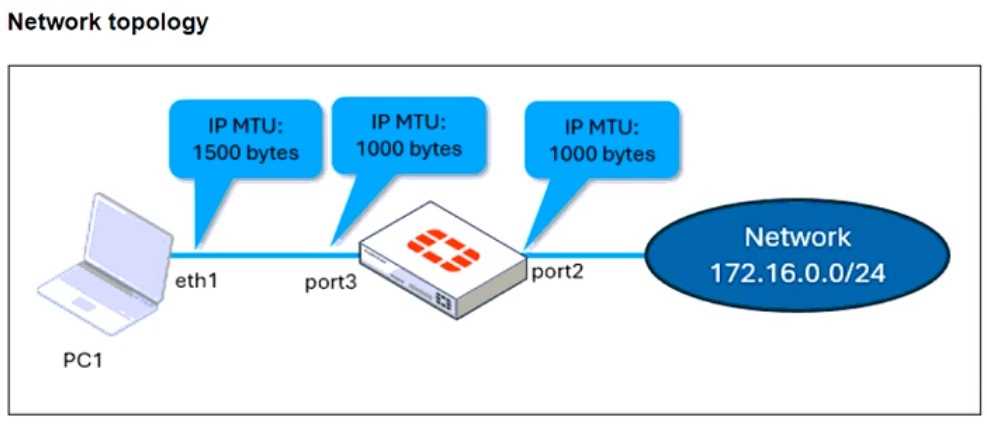
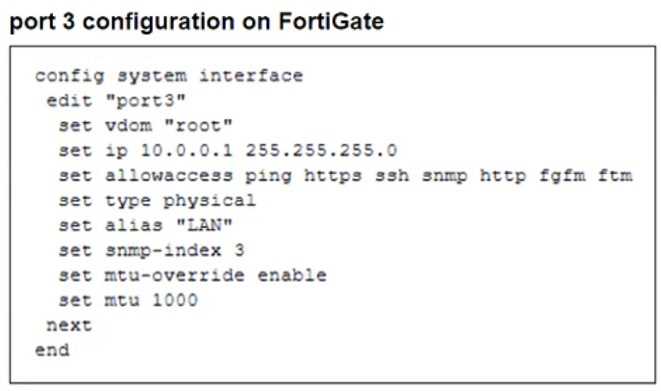
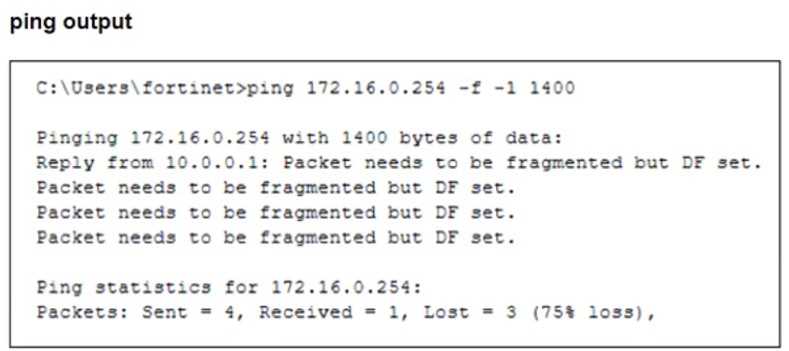
The configuration of a user's Windows PC, which has a default MTU of 1500 bytes, along with
FortiGate interfaces set to an MTU of 1000 bytes, and the results of PC1 pinging server 172.16.0.254
are shown.
Why is the user in Windows PC1 unable to ping server 172.16.0.254 and is seeing the message:
Packet needs to be fragmented but DF set?
- A. Option ip.flags.mf must be set to enable on FortiGate. The user has to adjust the ping MTU to 1000 to succeed.
- B. Fragmented packets must be encrypted. To connect any application successfully, the user must install the Fortinet_CA certificate in the Microsoft Management Console.
- C. FortiGate honors the do not fragment bit and the packets are dropped. The user has to adjust the ping MTU to 972 to succeed.
- D. The user must trigger different traffic because path MTU discovery techniques do not recognize ICMP payloads.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The issue occurs because FortiGate enforces the "do not fragment" (DF) bit in the packet, and the
packet size exceeds the MTU of the network path. When the Windows PC1 (with an MTU of 1500
bytes) attempts to send a 1400-byte packet, the FortiGate interface (with an MTU of 1000 bytes)
needs to fragment it. However, since the DF bit is set, FortiGate drops the packet instead of
fragmenting it.
To resolve this, the user should adjust the ping packet size to fit within the path MTU. In this case,
reducing the packet size to 972 bytes (1000 bytes MTU minus 28 bytes for the IP and ICMP headers)
should allow successful transmission.
Question 4
An administrator wants to scale the IBGP sessions and optimize the routing table in an IBGP network.
Which parameter should the administrator configure?
- A. network-import-check
- B. ibgp-enforce-multihop
- C. neighbor-group
- D. route-reflector-client
Answer:
D
Explanation:
In an IBGP (Internal BGP) network, all routers must be fully meshed, meaning every router must
establish a BGP session with every other router in the same autonomous system (AS). This does not
scale well in large networks due to the exponential increase in BGP sessions.
To optimize and scale IBGP, Route Reflectors (RRs) are used. A Route Reflector (RR) reduces the
number of IBGP peer connections by allowing a centralized router (RR) to redistribute IBGP routes to
other IBGP peers (called clients). This eliminates the need for a full mesh, significantly reducing BGP
session overhead.
By configuring the route-reflector-client setting on IBGP peers, an administrator can:
● Scale IBGP sessions by reducing the number of direct BGP peer connections.
● Optimize the routing table by ensuring routes are efficiently propagated within the IBGP network.
● Eliminate the need for full mesh topology, making IBGP more manageable.
Question 5
Refer to the exhibit, which shows a network diagram showing the addition of site 2 with an
overlapping network segment to the existing VPN IPsec connection between the hub and site 1.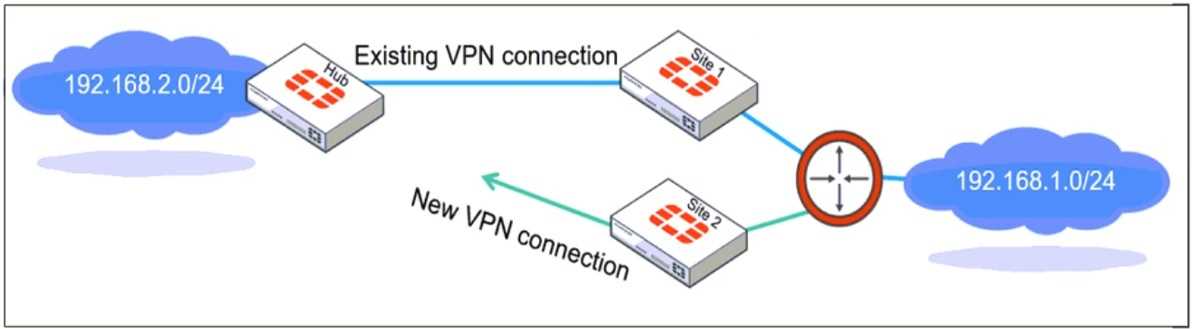
Which IPsec phase 2 configuration must an administrator make on the FortiGate hub to enable
equal-cost multi-path (ECMP) routing when multiple remote sites connect with overlapping subnets?
- A. Set route-overlap to either use-new or use-old
- B. Set net-device to ecmp
- C. Set single-source to enable
- D. Set route-overlap to allow
Answer:
A
Explanation:
When multiple remote sites connect to the same hub using overlapping subnets, FortiGate needs to
determine which route should be used for traffic forwarding. The route-overlap setting in IPsec Phase
2 allows FortiGate to handle this scenario by deciding whether to keep the existing route (use-old) or
replace it with a new route (use-new).
In an ECMP (Equal-Cost Multi-Path) routing setup, both routes should be retained and balanced, but
FortiGate does not support ECMP directly over overlapping routes in IPsec Phase 2. Instead, an
administrator must decide which connection takes precedence using route-overlap settings.
Question 6
Refer to the exhibit.
The routing tables of FortiGate_A and FortiGate_B are shown. FortiGate_A and FortiGate_B are in
the same autonomous system.
The administrator wants to dynamically add only route 172.16.1.248/30 on FortiGate_A.
What must the administrator configure?
- A. The prefix 172.16.1.248/30 in the BGP Networks section on FortiGate_B
- B. A BGP route map out for 172.16.1.248/30 on FortiGate_B
- C. Enable Redistribute Connected in the BGP section on FortiGate_B.
- D. A BGP route map in for 172.16.1.248/30 on FortiGate_A
Answer:
B
Explanation:
FortiGate_A and FortiGate_B are in the same autonomous system (AS), and FortiGate_A does not
currently have route 172.16.1.248/30 in its routing table. However, FortiGate_B has this route as a
connected route.
To dynamically advertise only 172.16.1.248/30 from FortiGate_B to FortiGate_A, the administrator
must configure a BGP route map out on FortiGate_B that specifically permits only this prefix.
A BGP route map out on FortiGate_B controls which routes FortiGate_B advertises to FortiGate_A. If
no filtering is applied, FortiGate_B might advertise all BGP-learned and connected routes, which is
not what the administrator wants. The route map should include a prefix-list that explicitly allows
only 172.16.1.248/30 and denies everything else.
Question 7
A FortiGate device with UTM profiles is reaching the resource limits, and the administrator expects
the traffic in the enterprise network to increase.
The administrator has received an additional FortiGate of the same model.
Which two protocols should the administrator use to integrate the additional FortiGate device into
this enterprise network? (Choose two.)
- A. FGSP with external load balancers
- B. FGCP in active-active mode and with switches
- C. FGCP in active-passive mode and with VDOM disabled
- D. VRRP with switches
Answer:
A, B
Explanation:
When adding an additional FortiGate to an enterprise network that is already reaching its resource
limits, the goal is to distribute traffic efficiently and ensure high availability.
FGSP (FortiGate Session Life Support Protocol) with external load balancers
FGSP allows session-aware load balancing between multiple FortiGate units without requiring them
to be in an HA (High Availability) cluster.
With external load balancers, incoming traffic is evenly distributed across multiple FortiGate
devices.
This approach is useful for scaling out traffic handling capacity while ensuring that sessions remain
synchronized between firewalls.
FGSP is effective when stateful failover is required but without the constraints of traditional HA.
FGCP (FortiGate Clustering Protocol) in active-active mode and with switches
FGCP active-active mode enables multiple FortiGate devices to share traffic loads, increasing
throughput and efficiency.
Active-active mode is suitable for balancing UTM processing across multiple FortiGates, making it
ideal when resource limits are a concern.
Using switches ensures redundancy and avoids single points of failure in the network.
This mode is commonly used in enterprise networks where both scalability and redundancy are
required.
Question 8
Refer to the exhibit, which shows the ADVPN IPsec interface representing the VPN IPsec phase 1
from Hub A to Spoke 1 and Spoke 2, and from Hub В to Spoke 3 and Spoke 4.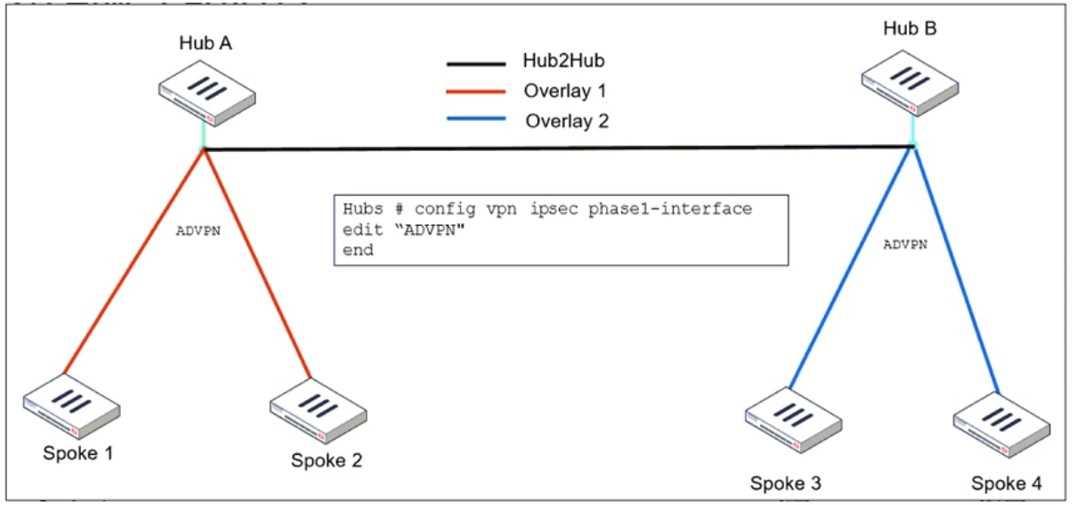
An administrator must configure an ADVPN using IBGP and EBGP to connect overlay network 1 with
2.
What must the administrator configure in the phase 1 VPN IPsec configuration of the ADVPN
tunnels?
- A. set auto-discovery-sender enable and set network-id x
- B. set auto-discovery-forwarder enable and set remote-as x
- C. set auto-discovery-crossover enable and set enforce-multihop enable
- D. set auto-discovery-receiver enable and set npu-offload enable
Answer:
C
Explanation:
When configuring ADVPN (Auto-Discovery VPN) to connect overlay networks across different hubs
using IBGP and EBGP, special configurations are required to allow spokes from different overlay
networks to dynamically establish tunnels.
● set auto-discovery-crossover enable
● This allows cross-hub tunnel discovery in an ADVPN deployment where multiple hubs are used.
● Since Hub A and Hub B belong to different overlays, enabling crossover discovery ensures that
spokes from one overlay can dynamically create direct tunnels to spokes in the other overlay when
needed.
● set enforce-multihop enable
● This setting ensures that BGP peers using loopback interfaces can establish connectivity even if
they are not directly connected.
● Multihop BGP sessions are required when using loopback addresses as BGP peer sources
because the connection might need to traverse multiple routers before reaching the BGP neighbor.
● This is especially useful in ADVPN deployments with multiple hubs, where routes might need to
cross from one hub to another.
Question 9
An administrator is designing an ADVPN network for a large enterprise with spokes that have varying
numbers of internet links. They want to avoid a high number of routes and peer connections at the
hub.
Which method should be used to simplify routing and peer management?
- A. Deploy a full-mesh VPN topology to eliminate hub dependency.
- B. Implement static routing over IPsec interfaces for each spoke.
- C. Use a dynamic routing protocol using loopback interfaces to streamline peers and routes.
- D. Establish a traditional hub-and-spoke VPN topology with policy routes.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
When designing an ADVPN (Auto-Discovery VPN) network for a large enterprise with spokes that
have varying numbers of internet links, the main challenge is to minimize the number of peer
connections and routes at the hub while maintaining scalability and efficiency.
Using a dynamic routing protocol (such as BGP or OSPF) with loopback interfaces helps in several
ways:
● Reduces the number of peer connections at the hub by using a single loopback address per spoke
instead of individual physical interfaces.
● Enables simplified route advertisement by dynamically learning and propagating routes instead of
manually configuring static routes.
● Supports multiple internet links per spoke efficiently, as dynamic routing can automatically adjust
to the best available path.
● Allows seamless failover if a spoke’s internet link fails, ensuring continuous connectivity.
Question 10
What action can be taken on a FortiGate to block traffic using IPS protocol decoders, focusing on
network transmission patterns and application signatures?
- A. Use the DNS filter to block application signatures and protocol decoders.
- B. Use application control to limit non-URL-based software handling.
- C. Enable application detection-based SD-WAN rules.
- D. Configure a web filter profile in flow mode.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
FortiGate's IPS protocol decoders analyze network transmission patterns and application signatures
to identify and block malicious traffic. Application Control is the feature that allows FortiGate to
detect, classify, and block applications based on their behavior and signatures, even when they do
not rely on traditional URLs.
● Application Control works alongside IPS protocol decoders to inspect packet payloads and enforce
security policies based on recognized application behaviors.
● It enables granular control over non-URL-based applications such as P2P traffic, VoIP, messaging
apps, and other non-web-based protocols that IPS can identify through protocol decoders.
● IPS and Application Control together can detect evasive or encrypted applications that might
bypass traditional firewall rules.
Question 11
Refer to the exhibit, which shows an enterprise network connected to an internet service provider.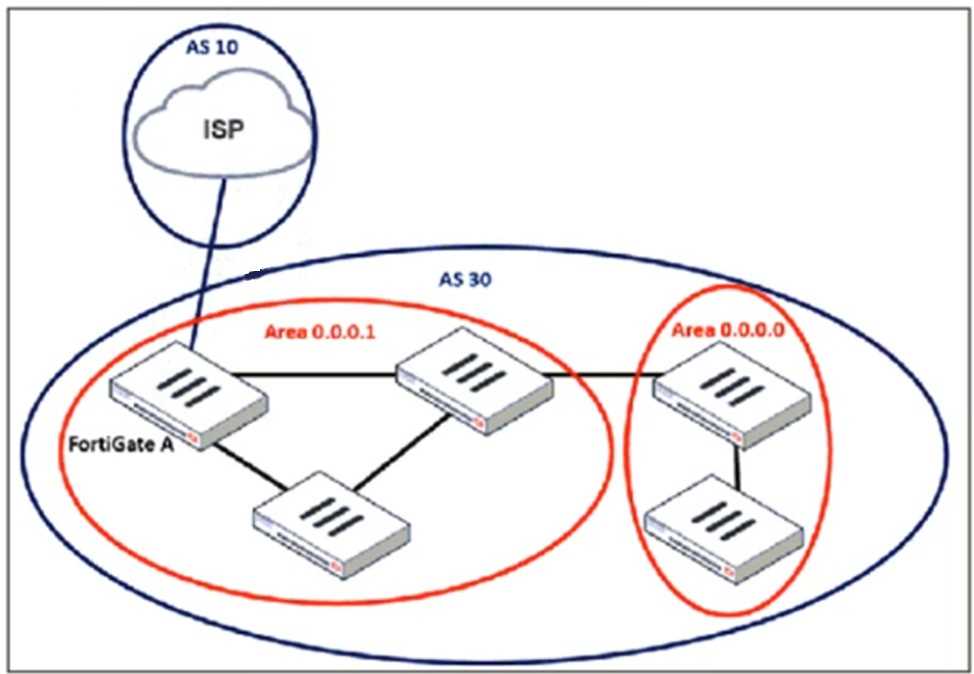
An administrator must configure a loopback as a BGP source to connect to the ISP.
Which two commands are required to establish the connection? (Choose two.)
- A. ebgp-enforce-multihop
- B. update-source
- C. ibgp-enforce-multihop
- D. recursive-next-hop
Answer:
A, B
Explanation:
When configuring a loopback interface as the BGP source for connecting to an ISP, two important
settings must be applied:
1. Enable EBGP Multihop (ebgp-enforce-multihop)
BGP normally expects directly connected neighbors, but since the ISP and FortiGate A are using
loopback interfaces, packets will not be sent directly between their physical interfaces.
The ebgp-enforce-multihop command allows BGP to form an eBGP peering over multiple hops.
2. Set the Update Source (update-source)
Since FortiGate is using a loopback interface as the source, the update-source command ensures
that BGP updates originate from the loopback interface rather than a physical interface.
This is essential because BGP peers must match the source IP with the configured neighbor address.
Question 12
An administrator must standardize the deployment of FortiGate devices across branches with
consistent interface roles and policy packages using FortiManager.
What is the recommended best practice for interface assignment in this scenario?
- A. Enable metadata variables to use dynamic configurations in the standard interfaces of FortiManager.
- B. Use the Install On feature in the policy package to automatically assign different interfaces based on the branch.
- C. Create interfaces using device database scripts to use them on the same policy package of FortiGate devices.
- D. Create normalized interface types per-platform to automatically recognize device layer interfaces based on the FortiGate model and interface name.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
When standardizing the deployment of FortiGate devices across branches using FortiManager, the
best practice is to use metadata variables. This allows for dynamic interface configuration while
maintaining a single, consistent policy package for all branches.
● Metadata variables in FortiManager enable interface roles and configurations to be dynamically
assigned based on the specific FortiGate device.
● This ensures scalability and consistent security policy enforcement across all branches without
manually adjusting interface settings for each device.
● When a new branch FortiGate is deployed, metadata variables automatically map to the correct
physical interfaces, reducing manual configuration errors.
Question 13
An administrator must minimize CPU and RAM use on a FortiGate firewall while also enabling
essential security features, such as web filtering and application control for HTTPS traffic.
Which SSL inspection setting helps reduce system load while also enabling security features, such as
web filtering and application control for encrypted HTTPS traffic?
- A. Use full SSL inspection to thoroughly inspect encrypted payloads.
- B. Disable SSL inspection entirely to conserve resources.
- C. Configure SSL inspection to handle HTTPS traffic efficiently.
- D. Enable SSL certificate inspection mode to perform basic checks without decrypting traffic.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
To minimize CPU and RAM usage while still enforcing security features like web filtering and
application control, SSL certificate inspection mode is the best choice.
● SSL certificate inspection allows FortiGate to inspect only the SSL/TLS handshake, including the
Server Name Indication (SNI) and certificate details, without decrypting the full encrypted payload.
● This enables features like web filtering and application control because FortiGate can determine
the destination website or application based on SNI and certificate information.
● It significantly reduces system load compared to full SSL inspection, which requires full decryption
and re-encryption of traffic.
Question 14
Refer to the exhibits. The exhibits show a network topology, a firewall policy, and an SSL/SSH
inspection profile configuration.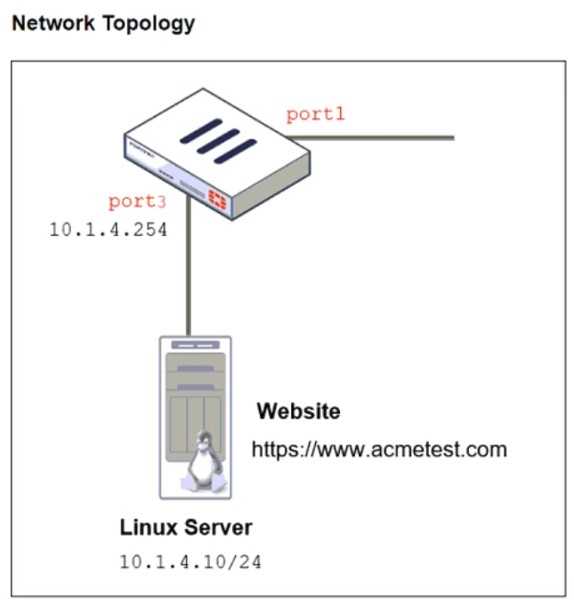
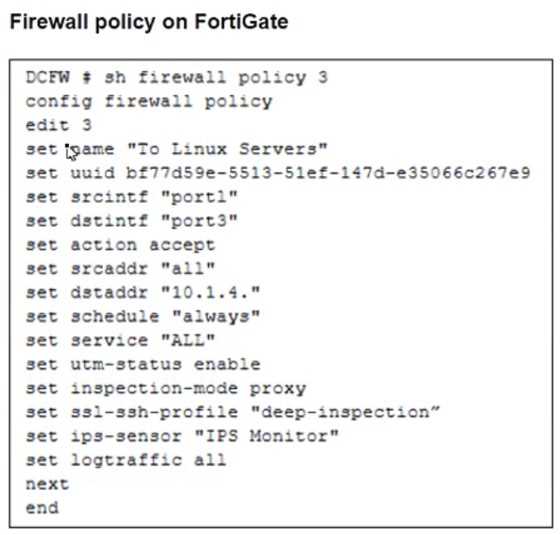
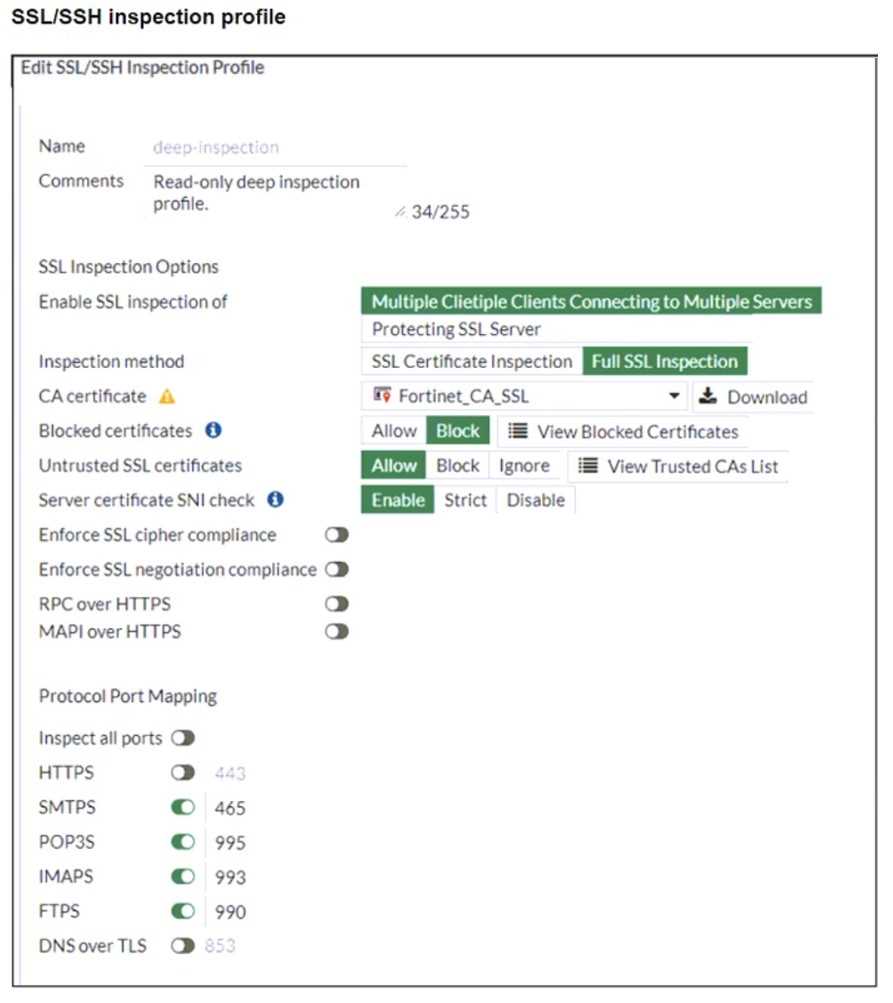
Why is FortiGate unable to detect HTTPS attacks on firewall policy ID 3 targeting the Linux server?
- A. The administrator must set the policy to inspection mode to analyze the HTTPS packets as expected.
- B. The administrator must enable HTTPS in the protocol port mapping of the deep- inspection SSL/SSH inspection profile.
- C. The administrator must enable SSL inspection of the SSL server and upload the certificate of the Linux server website to the SSL/SSH inspection profile.
- D. The administrator must enable cipher suites in the SSL/SSH inspection profile to decrypt the message.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The FortiGate SSL/SSH inspection profile is configured for Full SSL Inspection, which is necessary to
analyze encrypted HTTPS traffic. However, the firewall policy is protecting an SSL server (the Linux
server hosting the website), and currently, the SSL/SSH profile only applies to client-side SSL
inspection.
To detect HTTPS-based attacks targeting the Linux server:
● FortiGate must act as an SSL intermediary to inspect encrypted traffic destined for the web server.
● The administrator must upload the SSL certificate of the Linux web server to FortiGate so that the
server-side SSL inspection can decrypt incoming HTTPS traffic before analyzing it.
Question 15
An administrator is setting up an ADVPN configuration and wants to ensure that peer IDs are not
exposed during VPN establishment.
Which protocol can the administrator use to enhance security?
- A. Use IKEv2, which encrypts peer IDs and prevents exposure.
- B. Opt for SSL VPN web mode because it does not use peer IDs at all.
- C. Choose IKEv1 aggressive mode because it simplifies peer identification.
- D. Stick with IKEv1 main mode because it offers better performance.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
In ADVPN (Auto-Discovery VPN) configurations, security concerns include protecting peer IDs during
VPN establishment. Peer IDs are exchanged in the IKE (Internet Key Exchange) negotiation phase,
and their exposure could lead to privacy risks or targeted attacks.
● IKEv2 encrypts peer IDs, making it more secure compared to IKEv1, where peer IDs can be exposed
in plaintext in aggressive mode.
● IKEv2 also provides better performance and flexibility while supporting dynamic tunnel
establishment in ADVPN.