Fortinet FCP FMG AD 7 6 Exam Questions
Questions for the FCP FMG AD 7 6 were updated on : Feb 22 ,2026
Page 1 out of 3. Viewing questions 1-15 out of 33
Question 1
Refer to the exhibits.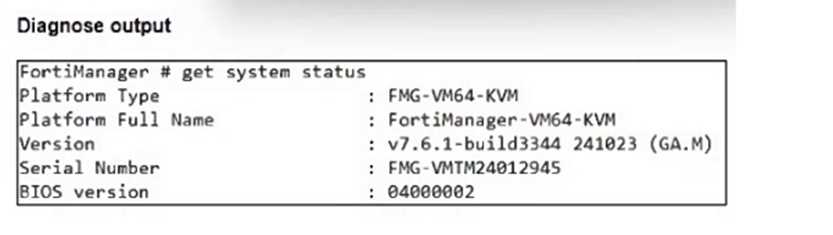

An administrator runs the reload failure command diagnose test deploymanager reloadconf 262 on
FortiManager.
Why does the administrator receive an error message?
- A. The administrator must use the FortiGate name instead of the ID number.
- B. The administrator just recently added FortiGate HQ-NGFW as a model device.
- C. FortiManager requires the FortiGate serial number instead of the ID number.
- D. FortiManager does not support FortiOS version 7.0.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The error occurs because the FortiGate HQ-NGFW device with ID 262 is a newly added model device
and has not yet been fully synchronized or installed with a configuration package, which causes the
reload configuration command to fail.
Question 2
Refer to the exhibit.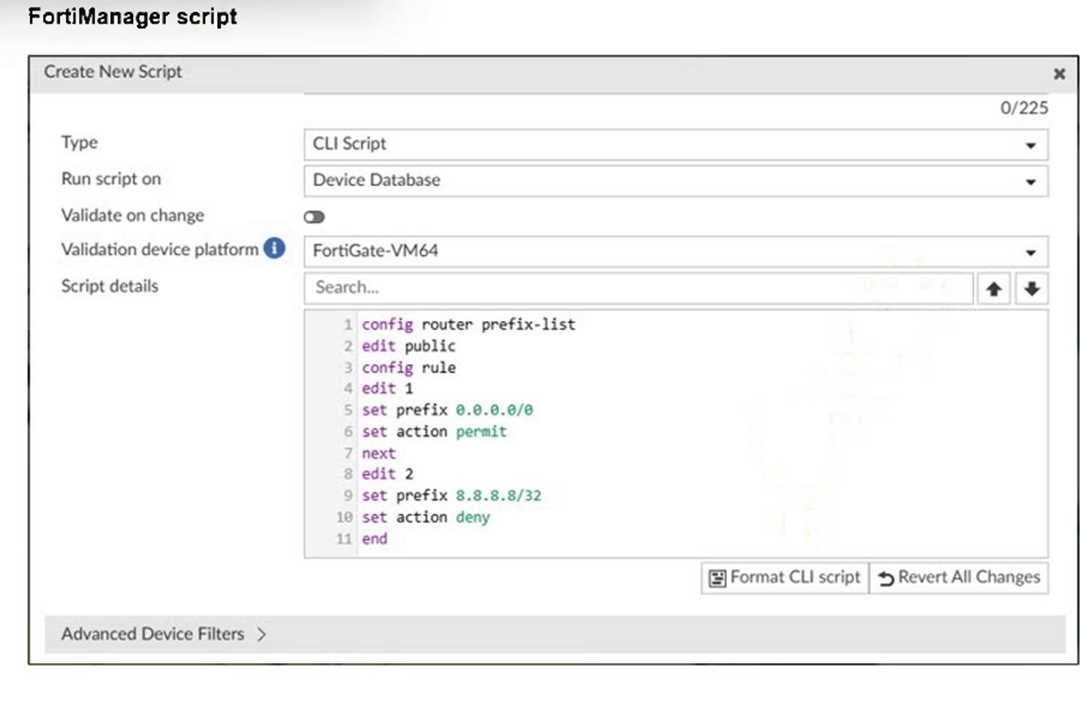
Which two results occur if you run the script using the Device Database option? (Choose two.)
- A. The device Config Status is tagged as Modified.
- B. The script history shows the successful installation of the script on the remote FortiGate.
- C. The successful execution of a script on the Device Database creates a new revision history.
- D. The administrator must install these changes on a managed device using the Install Wizard.
Answer:
A, D
Explanation:
Running a script on the Device Database marks the configuration as modified but does not
immediately apply changes to the device.
The administrator must use the Install Wizard to push and install these changes from the Device
Database onto the managed device.
Question 3
Refer to the exhibit.
What are two results from the configuration shown in the exhibit? (Choose two.)
- A. Ungraceful closed sessions will keep the ADOM in a locked state until the administrator session times out.
- B. The administrator can lock policy blocks and FortiManager global ADOM.
- C. The same administrator can lock more than one ADOM at the same time.
- D. The administrator must have access to the ADOM to approve changes.
Answer:
A, B
Explanation:
In normal workspace mode, ungraceful session closures will keep the ADOM locked until the session
times out, preventing other administrators from editing.
Normal workspace mode allows administrators to lock policy blocks and the global ADOM, providing
granular locking control.
Question 4
An administrator is copying a system template profile between ADOMs by running the following
command:
execute fmprofile export-profile ADOM 3547 /tmp/Backup_File
output dump to file: [/tmp/Backup_File]
Where does this command export the system template profile from?
- A. FortiManager /tmp/Backup_File folder
- B. FortiManager ADOM policy database
- C. ADOM device database
- D. FortiManager configuration backup file
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The command exports the system template profile from the FortiManager ADOM policy database,
which stores the configuration templates for devices within that ADOM.
Question 5
Refer to the exhibit.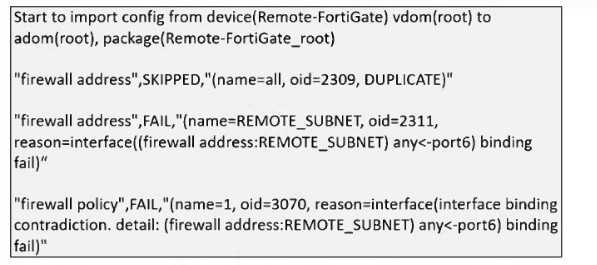
What can you conclude from the downloaded import report?
- A. FortiManager does not support per-device mapping for firewall addresses.
- B. The administrator will see a new policy package named Remote-FortiGate_root in the FortiManager ADOM database.
- C. FortiManager will change the configuration of REMOTE_SUBNET to match the interface mapping coming in from Remote-FortiGate.
- D. As a result of this policy import process, FortiManager will create a new firewall address called REMOTE_SUBNET in the ADOM database.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The import report shows that a new policy package named Remote-FortiGate_root will be created in
the FortiManager ADOM database, but some firewall addresses and policies failed to import due to
interface binding conflicts.
Question 6
A service provider administrator has assigned a global policy package to a managed customer ADOM
named My_ADOM. The customer administrator has access only to My_ADOM.
How can the customer administrator edit the global header policy of the global policy package?
- A. The customer administrator can edit the header policy by using workspace mode on the global ADOM.
- B. The customer administrator can edit the header policy by using workflow mode on the global ADOM and My_ADOM.
- C. The service provider administrator can unlock the global policy from the global ADOM to authorize changes to the customer administrator.
- D. The customer administrator cannot edit the global header policy; only the service provider administrator can make changes from the global ADOM.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The global policy package is managed only from the global ADOM by the service provider
administrator. Customer administrators with access solely to their ADOM (My_ADOM) cannot edit
the global header policy; such changes must be made by the service provider administrator in the
global ADOM.
Question 7
Which output is displayed right after moving the ISFW device from one ADOM to another?
A)
B)
C)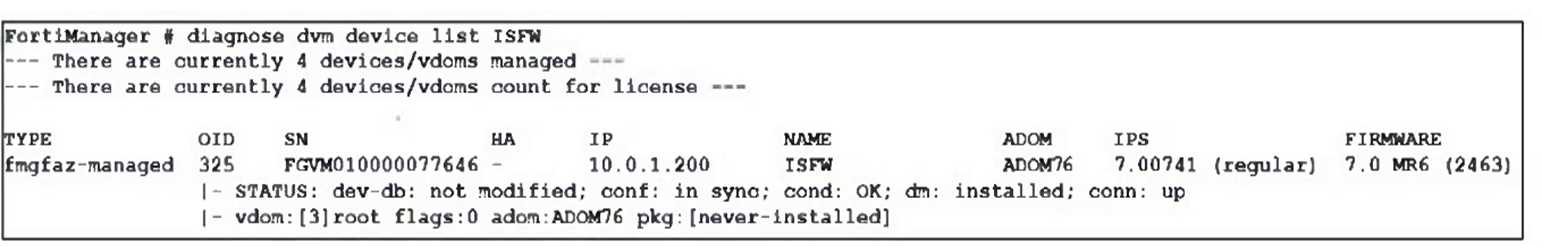
D)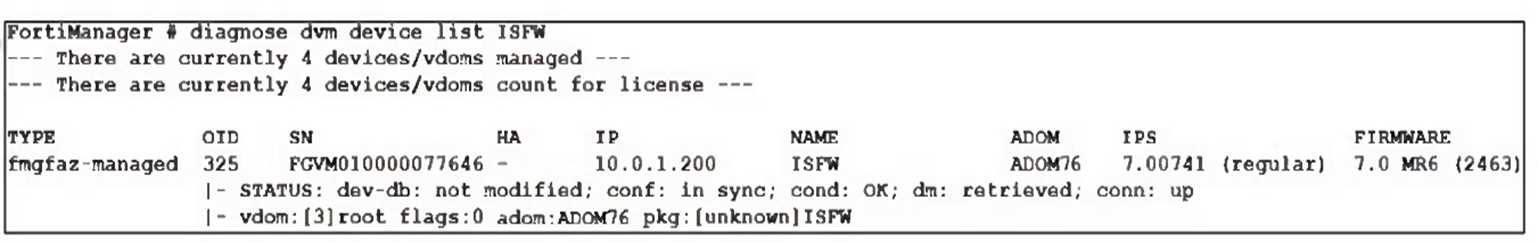
- A. Option A
- B. Option B
- C. Option C
- D. Option D
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Right after moving the ISFW device to a new ADOM, the status typically shows the policy package as
never-installed, indicating that the device has been assigned to the new ADOM but no policy package
has yet been installed in that ADOM.
Question 8
After correcting a policy package configuration issue, you want to prevent administrators from
repeating the mistake that caused the issue.
Which FortiManager approach best meets this need?
- A. Configure an TCL script to run locally on FortiManager for each FortiGate.
- B. Restrict administrators with an administration profile from viewing the revision history to limit who can make changes.
- C. Enable the change note to require administrators to add a note whenever they change object configurations.
- D. Enable a workflow requiring approval before installing policy packages on any FortiGate.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Enabling a workflow with approval ensures that any policy package changes must be reviewed and
approved before installation, preventing administrators from repeating configuration mistakes and
enforcing change control.
Question 9
Refer to the exhibits.
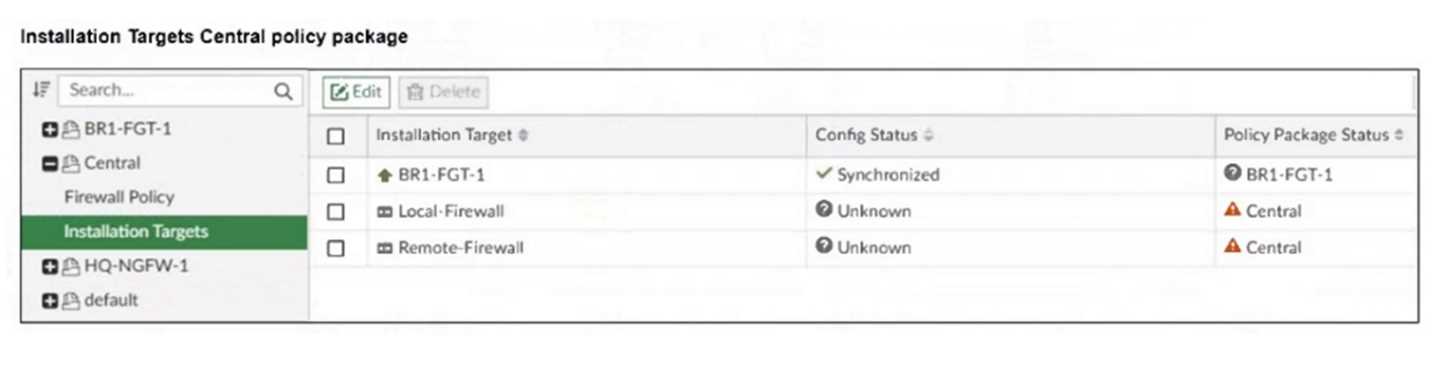
An administrator has been asked to install the same policies from a central policy package onto the
BR1-FGT-1 firewall.
The administrator added BR1-FGT-1 as a target in the central policy package installation.
What should the administrator do when reinstalling the central policy package on the BR1-FGT-1
firewall?
- A. Assign only one policy package to the firewall because FortiManager does not allow more than one policy package assigned per device at the same time.
- B. Import the policy package to change the unknown status and synchronize the policy package.
- C. Use the install wizard to install the central policy package on the BR1-FGT-1 firewall.
- D. First resolve the modified status in the configuration and provisioning templates to allow a smooth installation.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Using the Install Wizard is the recommended method to reinstall the central policy package on the
BR1-FGT-1 firewall, ensuring all settings, installation targets, and dependencies are correctly
processed during installation.
Question 10
Refer to the exhibit.
Which two statements about the output are true? (Choose two.)
- A. The latest revision history for the managed FortiGate does not match the device-level database.
- B. Configuration changes have been installed on FortiGate, updating policy and device-level database.
- C. The latest revision history for the managed FortiGate does match the FortiManager policy database.
- D. The system template default will override device-level database configurations.
Answer:
A, D
Explanation:
The status "pending" indicates the latest revision history does not match the device-level database,
meaning there are unapplied changes.
The template is marked as [modified], so the system template default will override device-level
database configurations when installed.
Question 11
Refer to the exhibits.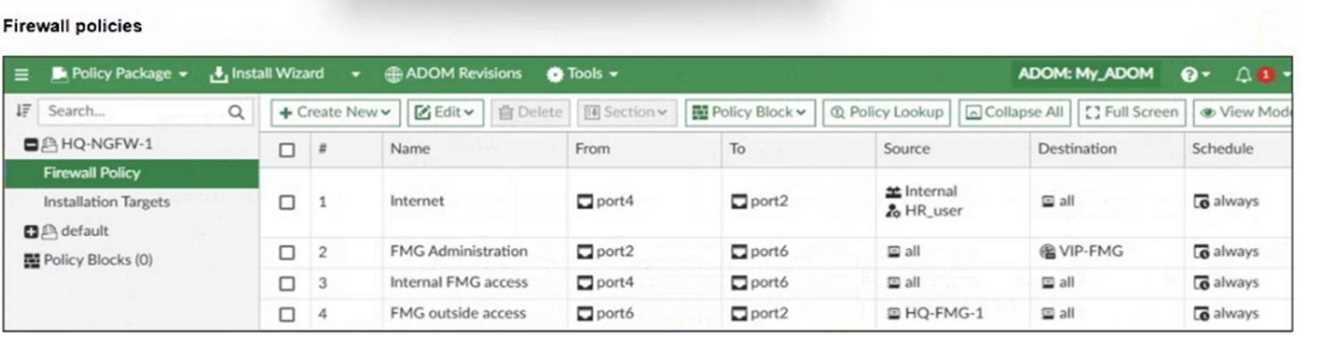

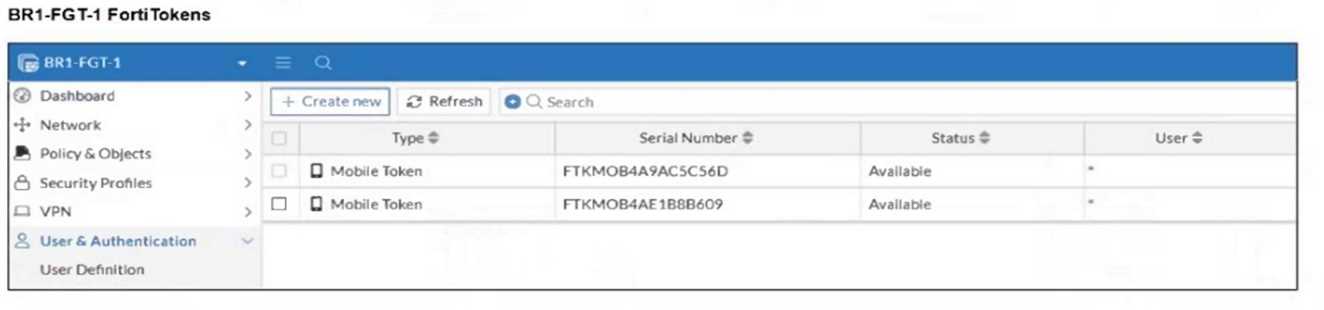
An administrator needs to push a FortiToken Mobile to assign it to HR_user in the HQ-NGFW-1.
However, when installing the policy package, they receive the following error message: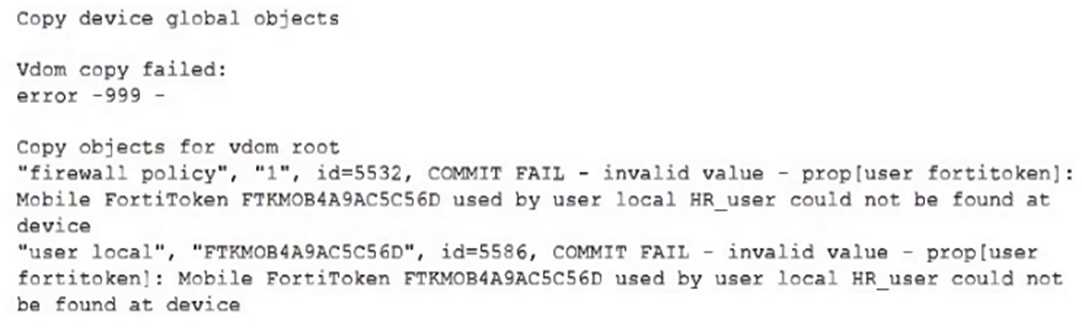
Why is the administrator not able to install the FortiToken on the HQ-NGFW-1 firewall?
- A. The administrator must use a user local meta field to assign FortiToken.
- B. The administrator must use a valid FortiToken that exists on HQ-NGFW-1.
- C. The administrator must use a metadata variable to assign the same FortiToken to multiple users in FortiManager.
- D. The administrator must use per-device mapping to assign the FortiToken to HQ-NGFW-1.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The error occurs because the FortiToken used (FTKM0B4A9AC5C56D) must already exist and be
registered on the FortiGate device HQ-NGFW-1. FortiManager cannot push or create new FortiTokens
on the device; the token must be valid and present on the FortiGate before it can be assigned to a
user.
Question 12
An administrator must create a policy and install it on a FortiGate device within an ADOM in backup
mode.
How can the administrator perform this task?
- A. Use the Install Wizard located on the device manager.
- B. Enable workflow mode to allow policy creation and approval.
- C. Make sure the ADOM and FortiGate firmware versions match and use the ADOM policy package.
- D. Use a FortiManager script to apply the configuration changes.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
In backup mode, FortiManager does not directly manage policy installation via the usual ADOM
policy packages; instead, administrators use FortiManager scripts to push configuration changes,
including policies, to FortiGate devices.
Question 13
Refer to the exhibit.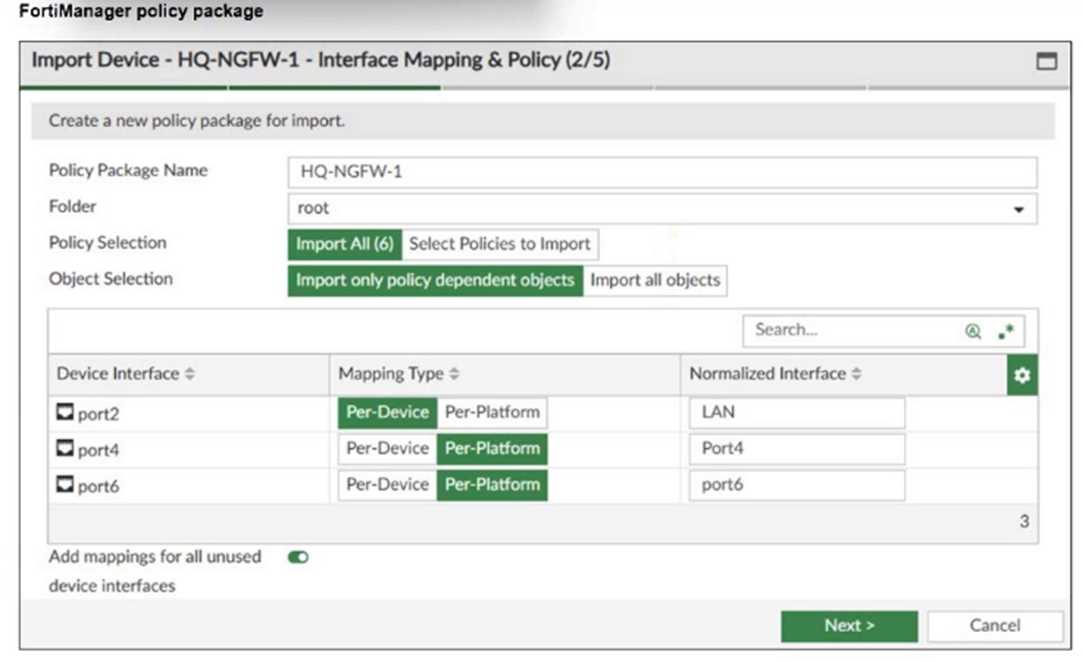
An administrator added a FortiGate device to FortiManager with the default object settings at the
ADOM layer.
What can you conclude from the import policy package process of the HQ-NGFW- 1 device?
- A. The administrator must select Per Platform for all interfaces to correctly detect all interfaces from HQ-NGFW-1.
- B. The administrator must manually create the port4 interface on the ADOM layer to avoid import policy errors.
- C. FortiManager will create LAN, port4, and port6 as normalized interfaces at the ADOM layer.
- D. FortiGate may not work as expected when the administrator does not import all objects.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The import process shows that FortiManager will create normalized interfaces named LAN, port4,
and port6 at the ADOM layer, mapping them to the corresponding device interfaces based on the
import settings.
Question 14
Company policy dictates that any time a change is made to a policy package on FortiManager an
ADOM revision is created before the change installed, and that revision is held for a minimum of
90 days.
Over the past three months, each installed change has resulted in several unused policies and
duplicate objects.
The FortiManager administrator plans to upgrade the FortiGate devices and then upgrade the
FortiManager ADOM from version 7.4 to 7.6.
Which action can the administrator take to avoid slow ADOM upgrades?
- A. Check and repair the global configuration database before upgrading.
- B. Export firewall policies to Excel, delete them on the ADOM. then reimport them after upgrading the ADOM.
- C. Find unused firmware templates, then delete them before upgrading.
- D. Limit ADOM revisions before upgrading.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Limiting ADOM revisions reduces the number of stored historical configurations, which helps avoid
performance degradation and slow ADOM upgrades caused by a large volume of revisions.
Question 15
An administrator configures a new BGP peer in the FortiManager device-level database of FortiGate.
They reinstall the policy package to the managed FortiGate device without any errors. However,
when the administrator logs in to FortiGate, they do not see the BGP configuration changes.
What is the most likely reason why FortiManager did not push the BGP peer changes to FortiGate?
- A. The administrator must run a sanity check on FortiManager to make sure the database is not corrupted.
- B. Fortigate has a BGP template assigned on the FortiManager database.
- C. The administrator must use the Install Wizard and select Install device settings only to push BGP settings
- D. The FortiGate firmware version is different from the FortiManager ADOM version.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
If a BGP template is assigned to the FortiGate device on FortiManager, device-level BGP
configurations made directly in the device-level database are overridden by the template settings, so
the changes do not get pushed to the device.