ericsson ECP-206 Exam Questions
Questions for the ECP-206 were updated on : Feb 20 ,2026
Page 1 out of 4. Viewing questions 1-15 out of 60
Question 1
In an Ethernet frame carrying a VLAN tag, where does the VLAN tag appear?
- A. after the type field
- B. before the length field
- C. before the type field
- D. after the length field
Answer:
C
Explanation:
In an Ethernet frame carrying a VLAN tag, the VLAN tag appears before the type field. A VLAN tag is a
4-byte field that is inserted into an Ethernet frame to indicate the VLAN membership and priority of
the frame. The VLAN tag consists of two subfields: the tag protocol identifier (TPID) and the tag
control information (TCI). The TPID subfield is a 16-bit field that identifies the frame as an IEEE
802.1Q-tagged frame, with a value of 0x8100. The TCI subfield is a 16-bit field that contains the
priority code point (PCP), the drop eligible indicator (DEI), and the VLAN identifier (VID). The VLAN
tag appears between the source MAC address and the type fields of the original frame, shifting the
type field by four bytes. The type field indicates the type of the payload, such as IP or ARP .
Reference: [IEEE 802.1Q - Wikipedia], [VLAN Tagging Explained with DTP Protocol - GeeksforGeeks]
Question 2
A network operator wants to make sure voice data is prioritized.
In this scenario, to which Ethernet traffic class should it be assigned.
- A. 0
- B. 2
- C. 4
- D. 6
Answer:
D
Explanation:
A network operator who wants to make sure voice data is prioritized should assign it to Ethernet
traffic class 6. Ethernet traffic class is a term used to refer to the priority code point (PCP) field in the
VLAN header of an Ethernet frame. The PCP field is a 3-bit field that can encode up to eight different
priority levels, ranging from 0 (lowest) to 7 (highest). The PCP values can be mapped to different
types of traffic according to their QoS requirements. The recommended mapping is as follows :
PCP 0: Best effort (default)
PCP 1: Background
PCP 2: Spare
PCP 3: Excellent effort
PCP 4: Controlled load
PCP 5: Video
PCP 6: Voice
PCP 7: Network control
Voice data is a type of real-time traffic that requires the highest priority and lowest delay in the
network. Therefore, it should be assigned to PCP 6, which corresponds to Ethernet traffic class 6 .
Reference: [IEEE 802.1Q - Wikipedia], [What is “link aggregation” and how does it benefit your
network? | PC Gamer]
Question 3
Which statement accurately defines an Autonomous System (AS)?
- A. An AS is a set of routers under a single administration, using an interior gateway protocol and common metrics to route packets within the AS.
- B. An AS is a group of networks directly connected to each other that can distribute eBGP information using directly established links.
- C. An AS is a network that is capable of autonomously forwarding packets, regardless of direct or indirect connectivity to the Internet.
- D. An AS is a collection of IS-IS routes imported into BGP and presented in such a way that networks connected to the AS have a global overview of the network.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The statement that accurately defines an Autonomous System (AS) is that an AS is a set of routers
under a single administration, using an interior gateway protocol and common metrics to route
packets within the AS. An AS is a logical grouping of networks that share a common routing policy
and operate under a single administrative authority. An AS can be a single network or a collection of
networks that are interconnected by routers. An AS uses an interior gateway protocol (IGP), such as
OSPF or IS-IS, to exchange routing information within the AS. An IGP uses common metrics, such as
hop count or bandwidth, to determine the best path to each destination within the AS. An AS also
has a unique number assigned by IANA, called an AS number (ASN), which identifies the AS in
interdomain routing .
Reference: [Autonomous system (Internet) - Wikipedia], [What Is an Autonomous System? - Cisco]
Question 4
Review the exhibit.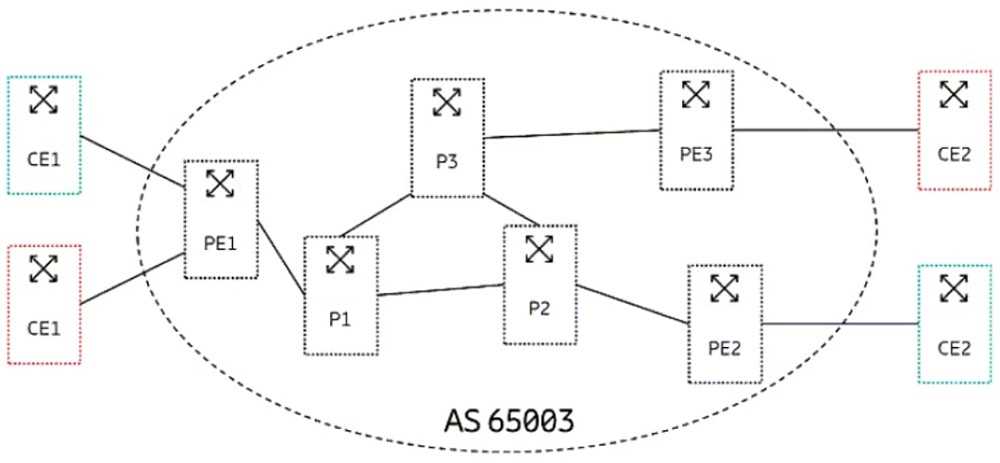
A service provider wants to connect the sites for two customers (indicated in red and green in the
exhibit). The two customers are using the same IP ranges 192.168.0.0/16.
Referring to the exhibit, what should the service provider do to accomplish this task?
- A. Implement L3VPN using the MP-BGP protocol.
- B. Connect each customer to dedicated PEs.
- C. Use a separate OSPF instance for each customer.
- D. Use a unique AS number for each customer.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Referring to the exhibit, the service provider should implement L3VPN using the MP-BGP protocol to
connect the sites for two customers (indicated in red and green in the exhibit). L3VPN is a type of
VPN that uses MPLS to provide IP connectivity between customer sites across a service provider
network. L3VPN allows customers to use overlapping or identical IP addresses without causing
conflicts or requiring NAT. L3VPN uses MP-BGP to exchange VPN routes between PE routers, which
are routers that connect customer networks to the service provider network. MP-BGP is an extension
of BGP that can carry multiple address families, such as VPNv4 or VPNv6, along with additional
attributes, such as route distinguisher (RD) and route target (RT).
RD is used to make customer routes
unique within the service provider network, while RT is used to control which routes are imported or
exported between different VPNs3
.
Reference:
L3VPN - Layer 3 Virtual Private Networks - Mpirical
, [Use of MP-BGP Extensions for IPv6
Interdomain Routing]
Question 5
Based on industry standard practice, what is the correct order of DiffServ priority (highest to lowest)
for the DiffServ classes: Default Forwarding (DF), Network Control (NC), Assured Forwarding (AF), and
Expedited Forwarding (EF)?
- A. EF, NC, AF, DF
- B. EF, AF, NC, DF
- C. NC, EF, DF, AF
- D. NC, EF, AF, DF
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The correct order of DiffServ priority (highest to lowest) for the DiffServ classes: Default Forwarding
(DF), Network Control (NC), Assured Forwarding (AF), and Expedited Forwarding (EF) is EF, NC, AF, DF.
DiffServ is a QoS model that classifies and prioritizes traffic into different service classes based on the
DSCP field in the IP header. The DSCP field is a 6-bit field that can encode up to 64 different per-hop
behaviors (PHBs). The DiffServ classes are predefined groups of PHBs that have similar characteristics
and requirements. The four main DiffServ classes are:
EF: This class provides the highest priority and lowest delay for real-time applications such as voice
and video.
The DSCP value for EF is 101110 or 46 in decimal12
.
NC: This class provides the second highest priority and low delay for network control traffic such as
routing protocols and network management.
The DSCP value for NC is 110000 or 48 in decimal12
.
AF: This class provides four levels of assured forwarding with different drop probabilities for each
level. AF is suitable for applications that require guaranteed bandwidth and delivery assurance, such
as web browsing and email.
The DSCP values for AF range from 001010 to 011110 or 10 to 46 in
decimal12
.
DF: This class provides the lowest priority and best-effort service for applications that can tolerate
packet loss and delay, such as file transfer and backup.
The DSCP value for DF is 000000 or 0 in
decimal12
.
Reference:
Differentiated Services - Wikipedia
,
DSCP - Differentiated Services Code Point - Mpirical
Question 6
Which two statements are true about the Ericsson Router 6000 series? (Choose two.)
- A. The Router 6000 uses the same building practice and accessories as the Ericsson Radio System.
- B. The Router 6000 can host containerized applications such as firewalls.
- C. The Router 6000 is solely built as a radio cell site router.
- D. The Router 6000 products range from all-outdoor small site routers to large aggregation routers.
Answer:
A, D
Explanation:
Two statements that are true about the Ericsson Router 6000 series are:
The Router 6000 uses the same building practice and accessories as the Ericsson Radio System. The
Ericsson Radio System is a modular and scalable radio access network solution that supports multiple
standards, bands, and layers. The Router 6000 series is fully integrated into the Ericsson Radio
System, using the same building practice and accessories such as mounting kits, cables, power
supplies, etc.
This simplifies installation, operation, and maintenance of both radio and transport
equipment78
.
The Router 6000 products range from all-outdoor small site routers to large aggregation routers. The
Router 6000 series consists of three main products: the Router 6672 for access, the Router 6675 for
pre-aggregation, and the Router 6274 for metro aggregation. The Router 6672 is an all-outdoor small
cell site router with high-capacity and low-power consumption. The Router 6675 is a combined
access and E-RAN switch with hardware-accelerated IPSec and high-accuracy internal clock.
The
Router 6274 is a high-capacity metro aggregation router with SDN functionality and flexible interface
options78
.
Reference:
Router 6000 Series - Ericsson
,
New Ericsson Router 6000 series couples radio and IP
transport for 5G future - Global Brands Magazine
Question 7
Which device will fragment IPv6 packets?
- A. source host
- B. router
- C. firewall
- D. destination host
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The device that will fragment IPv6 packets is the source host. Fragmentation is a process of dividing a
large packet into smaller pieces that can fit the maximum transmission unit (MTU) of the network
link. In IPv4, fragmentation can be performed by either the source host or any intermediate router
along the path. However, in IPv6, fragmentation is only allowed at the source host, and routers are
not allowed to fragment packets. This reduces the processing overhead and complexity at routers
and avoids potential fragmentation attacks.
If a router receives an IPv6 packet that is too large for the
next-hop link, it will drop the packet and send an ICMPv6 Packet Too Big message back to the source
host56
.
Reference:
IPv6 address - Wikipedia
,
IPv6 Fragmentation - Cisco
Question 8
Which statement about IPv6 is correct?
- A. An interface can only be configured with one IPv6 address.
- B. Broadcast has been replaced with multicast.
- C. There are four billion available addresses.
- D. Addresses are not hierarchical and are assigned at random.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The statement about IPv6 that is correct is that broadcast has been replaced with multicast. IPv6 is
the most recent version of Internet Protocol (IP), which provides an identification and location
system for computers on networks and routes traffic across the Internet. IPv6 has several
improvements over IPv4, such as a larger address space, simplified header format, enhanced
security, and better support for mobility and QoS. One of the changes in IPv6 is that it does not
support broadcast, which is a method of sending a packet to all nodes on a network
segment.
Instead, IPv6 uses multicast, which is a method of sending a packet to a group of nodes
that have joined a multicast address34
.
Reference:
IPv6 - Wikipedia
,
What Is IPv6? - Cisco
Question 9
What is the function of LSR from an LDP perspective?
- A. The LSR distributes labels of LDP to its FEC peers.
- B. The LSR distributes packets of FEC to its LDP peers.
- C. The LSR distributes packets of LDP to its FEC peers.
- D. The LSR distributes labels of FEC to its LDP peers.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The function of LSR from an LDP perspective is to distribute labels of FEC to its LDP peers. LSR stands
for Label Switching Router, which is a router that forwards packets based on labels rather than IP
addresses in an MPLS network. LDP stands for Label Distribution Protocol, which is a protocol that
distributes labels for MPLS forwarding along the shortest path calculated by an IGP. FEC stands for
Forwarding Equivalence Class, which is a group of packets that are forwarded in the same manner by
an LSR.
An LSR uses LDP to advertise the label mappings for each FEC to its LDP peers, which are
other LSRs that have established an LDP session with it12
.
Reference:
Ldp | Microsoft Learn
,
Label Distribution Protocol - Wikipedia
Question 10
What is used for Ethernet loop avoidance?
- A. Time-to-Live (TTL)
- B. Poison-Reverse
- C. Split-Horizon
- D. Spanning-Tree
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Spanning-Tree is used for Ethernet loop avoidance. Spanning-Tree is a protocol that prevents loops in
Ethernet networks by creating a logical tree topology of the network switches. Spanning-Tree blocks
some of the redundant links between switches to ensure that there is only one active path between
any two nodes in the network.
Spanning-Tree also detects and recovers from link failures by
activating alternative paths when needed56
.
Reference:
Network loops and loop avoidance - Medium
,
Spanning Tree Protocol - Wikipedia
Question 11
What is a label-edged router (LER)?
- A. a CE router
- B. a P router
- C. a PE router
- D. a DR router
Answer:
C
Explanation:
A label-edged router (LER) is a PE router. A PE router is a provider edge router, which is a router that
connects an MPLS network to a customer network. A LER is a term used in MPLS to describe a router
that resides at the ingress and egress points of an MPLS network, handling both labelled and
unlabelled packets.
A LER performs label operations such as adding, removing, or swapping labels on
packets entering or leaving the MPLS network34
.
Reference:
What is Label Edge Router (LER)? - Definition from Techopedia
,
LER - Label Edge Router -
Mpirical
Question 12
Review the exhibit.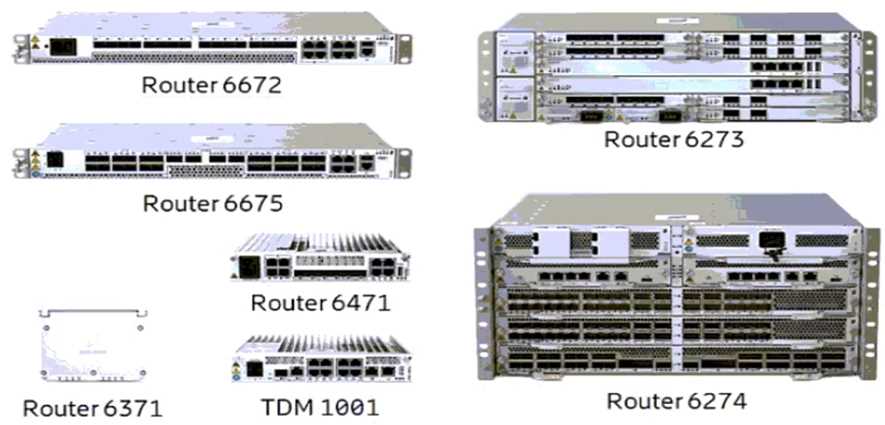
Referring to the exhibit, which two Ericsson routers support the 100GE interface? (Choose two.)
- A. Router 6471
- B. Router 6273
- C. Router 6675
- D. Router 6672
Answer:
C, D
Explanation:
Referring to the exhibit, the two Ericsson routers that support the 100GE interface are Router 6675
and Router 6672. The 100GE interface is a high-speed Ethernet interface that operates at 100
gigabits per second. The Ericsson Router 6000 series is a family of routers that provide IP transport
for mobile and fixed networks. The Router 6675 is a 5G combined access and E-RAN switch with
100GE interfaces and 320Gb forwarding capacity.
The Router 6672 is a high-capacity metro
aggregation router with 100GE interfaces and 1.6Tb forwarding capacity12
.
Reference:
Router 6000 Series - Ericsson
,
New Ericsson Router 6000 series couples radio and IP
transport for 5G future - Global Brands Magazine
Question 13
Review the exhibit.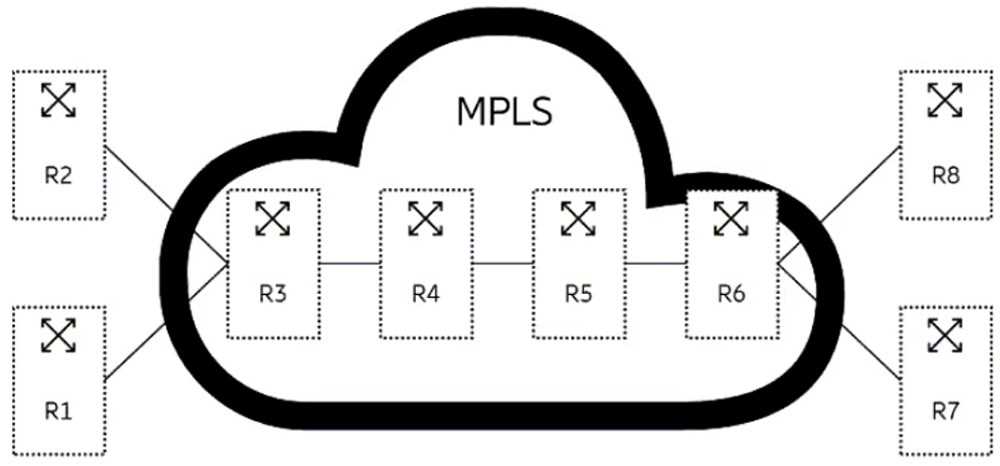
In the exhibit, which action is performed by router R3 for traffic arriving from router R2 towards
router R4?
- A. push
- B. pop
- C. swap
- D. PHP
Answer:
D
Explanation:
In the exhibit, the action performed by router R3 for traffic arriving from router R2 towards router R4
is PHP, which stands for penultimate hop popping. PHP is a process in which the penultimate hop
router (the router before the egress router) removes the top label from an MPLS packet before
forwarding it to the egress router. This reduces the label stack depth of the packet and relieves the
egress router from performing a label lookup operation. In the exhibit, router R3 is the penultimate
hop for traffic arriving from router R2 towards router R4.
Router R3 will perform a PHP operation,
removing the top label from the incoming packet before forwarding it to router R478
.
Reference:
PHP Tutorial - W3Schools
,
PHP: Downloads
Question 14
What is the purpose of the RT attribute?
- A. to identify the destination VPN on the efress PE
- B. to prevent OSPF routing loops in an L3VPN environment
- C. to indicate an MPLS LSP as the next hop routing target
- D. to request BGP neighbors to avoid routing through a private AS
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The purpose of the RT attribute is to identify the destination VPN on the egress PE. RT stands for
route target, which is a BGP extended community attribute that is used in MPLS VPNs. RT is attached
to VPN routes by the ingress PE router and is used to control the import and export of routes
between different VPNs.
The egress PE router uses the RT value to determine which VPN routes
belong to which VPN customers and installs them in the appropriate VRF table56
.
Reference:
IP Routing: BGP Configuration Guide - BGP-RT and VPN … - Cisco
,
<rt>: The Ruby Text
element - MDN Web Docs
Question 15
Which two statements are correct for LDP? (Choose two.)
- A. LSRs send UDP hello messages for neighbor discovery.
- B. LSRs send ICMP hello messages for neighbor discovery
- C. LSRs use TCP to negotiate LDP session parameters.
- D. LSRs use UDP for session establishment.
Answer:
A, C
Explanation:
Two statements that are correct for LDP are:
LSRs send UDP hello messages for neighbor discovery. LDP is a protocol that distributes labels for
MPLS forwarding along the shortest path calculated by an IGP. LDP uses two types of messages:
discovery messages and session messages. Discovery messages are used to discover and maintain
adjacency with other LSRs that support LDP.
Discovery messages are sent as UDP datagrams to the
well-known multicast address 224.0.0.2 (all routers on this subnet) on port 64634
.
LSRs use TCP to negotiate LDP session parameters. Session messages are used to establish, maintain,
and terminate LDP sessions between LSRs. Session messages are also used to exchange label
mappings, notification messages, and keepalive messages.
Session messages are sent as TCP
segments to port 64634
.
Reference:
Ldp | Microsoft Learn
,
Label Distribution Protocol - Wikipedia