comptia DY0-001 Exam Questions
Questions for the DY0-001 were updated on : Feb 22 ,2026
Page 1 out of 6. Viewing questions 1-15 out of 85
Question 1
A data scientist is performing a linear regression and wants to construct a model that explains the
most variation in the dat
a. Which of the following should the data scientist maximize when evaluating the regression
performance metrics?
- A. Accuracy
- B. R2
- C. p value
- D. AUC
Answer:
B
Question 2
Which of the following issues should a data scientist be most concerned about when generating a
synthetic data set?
- A. The data set consuming too many resources
- B. The data set having insufficient features
- C. The data set having insufficient row observations
- D. The data set not being representative of the population
Answer:
D
Explanation:
If synthetic data don’t accurately mirror the real-world distributions and relationships, any models
trained on them will perform poorly in deployment. Representativeness is the critical concern when
generating synthetic data.
Question 3
Which of the following measures would a data scientist most likely use to calculate the similarity of
two text strings?
- A. Word cloud
- B. Edit distance
- C. String indexing
- D. k-nearest neighbors
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Edit distance quantifies how many single-character insertions, deletions, or substitutions are needed
to transform one string into another, making it a direct measure of their similarity.
Question 4
A data scientist is analyzing a data set with categorical features and would like to make those
features more useful when building a model. Which of the following data transformation techniques
should the data scientist use? (Choose two.)
- A. Normalization
- B. One-hot encoding
- C. Linearization
- D. Label encoding
- E. Scaling
- F. Pivoting
Answer:
B
Explanation:
One-hot encoding creates binary indicator columns for each category, allowing models to treat
nominal categories without implying any order.
Label encoding maps categories to integer labels, which can be useful for tree-based models or when
you need a single numeric column (though you must ensure the algorithm can handle treated
ordinality appropriately).
Question 5
Given these business requirements:
Needs to most efficiently move 3,000 boxes across a river
Has one boat that holds eight boxes, travels at ten nautical miles per hour, and has a fuel economy
of six nautical miles per gallon
Has another boat that holds two boxes, travels at 50 nautical miles per hour, and has a fuel
economy of 18 nautical miles per gallon
The river is one nautical mile wide
The data scientist only has access to 125 gallons of fuel
Which of the following is the most likely optimization technique a data scientist would apply?
- A. Constrained
- B. Unconstrained
- C. Non-iterative
- D. Iterative
Answer:
A
Explanation:
You must optimize boat trips subject to strict resource limits (fuel, boat capacity, travel distance),
making this a constrained optimization problem (e.g., solvable via linear programming).
Question 6
Which of the following is best solved with graph theory?
- A. Optical character recognition
- B. Traveling salesman
- C. Fraud detection
- D. One-armed bandit
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The traveling-salesman problem is a prototypical graph theory challenge, finding the shortest tour
through a graph’s nodes, whereas the other tasks rely on different domains (OCR on image
processing, fraud detection often on statistical/anomaly methods, bandit problems on sequential
decision theory).
Question 7
A data scientist would like to model a complex phenomenon using a large data set composed of
categorical, discrete, and continuous variables. After completing exploratory data analysis, the data
scientist is reasonably certain that no linear relationship exists between the predictors and the
target. Although the phenomenon is complex, the data scientist still wants to maintain the highest
possible degree of interpretability in the final model. Which of the following algorithms best meets
this objective?
- A. Artificial neural network
- B. Decision tree
- C. Multiple linear regression
- D. Random forest
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Decision trees capture complex, nonlinear relationships with a transparent, rule-based structure.
They remain highly interpretable (each split can be visualized and explained) unlike ensembles
(random forests) or neural networks, and they don’t rely on linear assumptions.
Question 8
A company created a very popular collectible card set. Collectors attempt to collect the entire set,
but the availability of each card varies, with because some cards have higher production volumes
than others. The set contains a total of 12 cards. The attributes of the cards are below: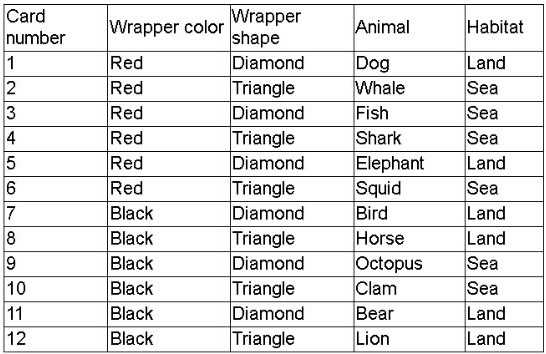
A data scientist is provided a historical record of cards purchased, which was acquired by a local
collectors' association. The data scientist needs to design an initial model iteration to predict
whether or not the animal on the card lives in the sea or on land given the provided attributes.
Which of the following is the best way to accomplish this task?
- A. ARIMA
- B. Linear regression
- C. Association rules
- D. Decision trees
Answer:
D
Explanation:
You have categorical inputs (wrapper color, shape, animal) and a binary target (sea vs. land). A
decision tree natively handles categorical features and yields clear, rule-based splits that predict
habitat, making it the most appropriate choice.
Question 9
A data scientist receives an update on a business case about a machine that has thousands of error
codes. The data scientist creates the following summary statistics profile while reviewing the logs for
each machine: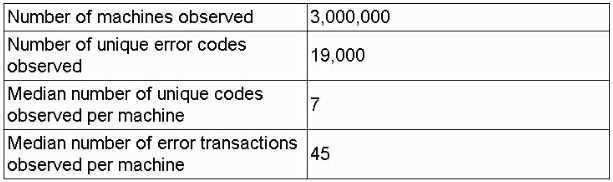
Which of the following is the most likely concern with respect to data design for model ingestion?
- A. Sparse matrix
- B. Granularity misalignment
- C. Insufficient features
- D. Multivariate outliers
Answer:
A
Explanation:
With 19,000 possible error-code features and each machine reporting only a handful (median of 7),
your feature matrix will be extremely sparse (most entries zero) which can negatively impact both
storage and model performance unless you address it (e.g., via sparse data structures or
dimensionality reduction).
Question 10
Which of the following image data augmentation techniques allows a data scientist to increase the
size of a data set?
- A. Clipping
- B. Cropping
- C. Masking
- D. Scaling
Answer:
B
Explanation:
By taking multiple crops from each original image (e.g., random or sliding-window crops), you
generate distinct new training examples, directly increasing the dataset size.
Question 11
Which of the following types of layers is used to downsample feature detection when using a
convolutional neural network?
- A. Pooling
- B. Input
- C. Output
- D. Hidden
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Pooling layers (such as max pooling or average pooling) reduce the spatial dimensions of the feature
maps by summarizing local neighborhoods, effectively downsampling the detected features and
controlling overfitting.
Question 12
Which of the following distributions would be best to use for hypothesis testing on a data set with 20
observations?
- A. Power law
- B. Normal
- C. Uniform
- D. Student's t-
Answer:
D
Explanation:
With only 20 observations and an unknown population variance, the t-distribution (with
– 1
degrees of freedom) properly accounts for the extra uncertainty in the standard error when
performing hypothesis tests.
Question 13
A data scientist is attempting to identify sentences that are conceptually similar to each other within
a set of text files. Which of the following is the best way to prepare the data set to accomplish this
task after data ingestion?
- A. Embeddings
- B. Extrapolation
- C. Sampling
- D. One-hot encoding
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Generating embeddings transforms each sentence into a dense numerical vector in a semantic
space, where conceptually similar sentences lie close together, enabling straightforward similarity
calculations (e.g., cosine similarity) to group or identify related sentences.
Question 14
Which of the following types of machine learning is a GPU most commonly used for?
- A. Deep learning/neural networks
- B. Clustering
- C. Natural language processing
- D. Tree-based
Answer:
A
Explanation:
GPUs excel at the massive parallelism required for the matrix and tensor operations at the heart of
deep neural network training and inference, making them the go-to hardware for deep learning
workloads.
Question 15
Which of the following is the naive assumption in Bayes' rule?
- A. Normal distribution
- B. Independence
- C. Uniform distribution
- D. Homoskedasticity
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Naive Bayes assumes that all predictor variables are conditionally independent of each other given
the class label, dramatically simplifying the joint probability calculation in Bayes’ rule.