comptia CS0-003 Exam Questions
Questions for the CS0-003 were updated on : Jan 28 ,2026
Page 1 out of 29. Viewing questions 1-15 out of 428
Question 1
A security analyst provides the management team with an after-action report for a security incident.
Which of the following is the management team most likely to review in order to correct validated
issues with the incident response processes?
- A. Tabletop exercise
- B. Lessons learned
- C. Root cause analysis
- D. Forensic analysis
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The lessons learned phase is a formal step in the incident response process where teams review
what went wrong, what worked, and how to improve future responses. Management uses this to
adjust policies, procedures, and controls based on real incident experiences.
Tabletop (A) is a simulated discussion, not post-incident.
Root cause analysis (C) finds technical origins but doesn’t focus on process improvement.
Forensics (D) supports investigation but not process revision.
Reference:
CS0-003 Domain 3.0 – Post-Incident Activities
Chapple & Seidl – Study Guide, Chapter 11: Containment and Recovery
Question 2
Which of the following is the best way to provide realistic training for SOC analysts?
- A. Phishing assessments
- B. OpenVAS
- C. Attack simulation
- D. SOAR
- E. Honeypot
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Attack simulations provide realistic, hands-on scenarios that mirror true incidents, allowing SOC
analysts to practice detection, analysis, and response skills under real-world pressure. These
simulations are crucial for developing and reinforcing SOC procedures and incident workflows.
Phishing assessments (A) are targeted, limited training.
OpenVAS (B) is a vulnerability scanner, not a training tool.
SOAR (D) is a response automation tool.
Honeypots (E) help observe attacker behavior, but aren't training-focused.
Reference:
CS0-003 Objectives 3.3 – Incident Response Training
Mya Heath All-in-One – Chapter 14: Post-Incident Activities and Training
Question 3
When undertaking a cloud migration of multiple SaaS applications, an organization’s systems
administrators struggled with the complexity of extending identity and access management to cloud-
based assets. Which of the following service models would have reduced the complexity of this
project?
- A. RADIUS
- B. SDN
- C. ZTNA
- D. SWG
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) simplifies secure remote access to cloud and SaaS applications by
enforcing identity-based, least-privilege access policies. It eliminates the need to extend traditional
network-based access models to the cloud. ZTNA ensures that each user is verified continuously
regardless of their network location, aligning perfectly with complex multi-cloud or SaaS
environments.
RADIUS (A) is an older authentication protocol, not ideal for SaaS cloud scale.
SDN (B) controls network flow, not identity management.
SWG (D) is a secure web proxy, not for access control and IAM extension.
Reference:
CS0-003 Exam Objectives 1.1 – Identity and Access Management
Sybex Study Guide – Chapple & Seidl, Chapter 2: Zero Trust & Cloud IAM
Question 4
A security administrator is tasked with modifying the vulnerability scan process to reduce the
network traffic but maintain thorough checks. Which of the following scanning approaches should be
implemented?
- A. Credentialed scans
- B. Individual scans
- C. Security baseline scans
- D. Agent-based scans
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Agent-based scans are run locally on hosts via installed agents, which significantly reduces network
traffic while allowing in-depth visibility and accurate scanning. They’re ideal for bandwidth-limited or
sensitive networks.
Credentialed scans (A) still transmit data over the network.
Individual scans (B) is ambiguous and not a standard term.
Baseline scans (C) focus on policy compliance, not reducing traffic.
? Reference:
Chapple & Seidl – Vulnerability Management, Chapter 6: Scanning Techniques
CS0-003 Domain 2.1 – Vulnerability Scanning Methods
Question 5
Which of the following documents should link to the recovery point objectives and recovery time
objectives on critical services?
- A. Disaster recovery plan
- B. Business impact analysis
- C. Playbook
- D. Backup plan
Answer:
B
Explanation:
A Business Impact Analysis (BIA) is the correct document that identifies critical services and defines
Recovery Point Objectives (RPOs) and Recovery Time Objectives (RTOs). It helps organizations
determine the impact of downtime and the maximum tolerable outages for business functions.
Disaster recovery plan (A) uses the information from the BIA.
Playbooks (C) are tactical and focus on specific incidents.
Backup plans (D) support BIA but don't define RPO/RTO themselves.
Reference:
CompTIA CySA+ Study Guide – Chapple & Seidl, Chapter 9
CySA+ Exam Objectives: Domain 3.0 – Incident Response and Management
Question 6
A user reports a message as suspicious to the IT security team. An analyst reviews the message and
notices that the following text string becomes a hyperlink in an email:
%77%77%77%2e%69%63%65%2d%70%74%69%63%2e%63%6f%6d
Which of the following would most likely explain this behavior?
- A. The string contains obfuscated JavaScript shellcode
- B. The text is encoded and designed to bypass spam filters.
- C. The email client has a parsing error elsewhere in the message.
- D. The sandboxed PC used for testing has non-default configurations.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The string provided is percent-encoded text, commonly used to obfuscate URLs. When decoded, it
translates to www.ice-ptic.com. Such encoding is used to bypass email security filters and spam
detectors, making the malicious link appear as benign or unreadable to the automated scanners.
Option A is incorrect: The string does not match JavaScript shellcode formats.
Option C and D are unlikely and unrelated to the actual behavior.
? Reference:
CySA+ All-in-One Exam Guide by Mya Heath – Chapter 4, Obfuscated Links
CompTIA Exam Objectives: 1.2 – Indicators of Malicious Activity
Question 7
A security analyst has just received an incident ticket regarding a ransomware attack. Which of the
following would most likely help an analyst properly triage the ticket?
- A. Incident response plan
- B. Lessons learned
- C. Playbook
- D. Tabletop exercise
Answer:
C
Explanation:
A playbook provides a step-by-step guide for handling specific types of incidents like ransomware,
making it invaluable during triage. It outlines predefined procedures, aiding consistent and fast
decision-making.
The incident response plan (A) provides high-level structure.
Lessons learned (B) apply after the incident.
Tabletop exercises (D) are training tools, not live guides.
Reference: Chapple & Seidl, CySA+ Practice Tests, Incident Response, Chapter 3 – Playbooks and
Procedures.
Objective: 3.1 - Apply incident response procedures based on an incident classification.
Question 8
To minimize the impact of a security incident in a heavily regulated company, a cybersecurity analyst
has configured audit settings in the organization's cloud services. Which of the following security
controls has the analyst configured?
- A. Preventive
- B. Corrective
- C. Directive
- D. Detective
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Audit settings provide visibility into user actions and system events. These are classified as detective
controls because they enable the detection of anomalies, policy violations, or unauthorized access by
generating logs or alerts. They do not prevent actions (Preventive) or reverse harm (Corrective), nor
do they provide policy guidance (Directive).
Reference: CompTIA CySA+ All-in-One by Mya Heath, Chapter 13, “Vulnerability Handling and
Response” – Control Types and Functions.
Objective: 2.5 - Explain the importance of prioritization, remediation, and mitigation of
vulnerabilities.
Question 9
An incident response team is assessing attack vectors of malware that is encrypting data with
ransomware. There are no indications of a network-based intrusion.
Which of the following is the most likely root cause of the incident?
- A. USB drop
- B. LFI
- C. Cross-site forgery
- D. SQL injection
Answer:
A
Explanation:
A USB drop attack is a common method for delivering ransomware, where an attacker leaves
infected USB drives in strategic locations, tricking employees into plugging them into corporate
devices.
Option B (LFI - Local File Inclusion) exploits web applications, but the scenario lacks network
intrusion indicators.
Option C (Cross-site request forgery - CSRF) is used for exploiting authenticated web sessions, not
ransomware delivery.
Option D (SQL injection) is used for database exploitation, not file encryption malware.
Thus, A (USB drop) is the correct answer, as physical malware introduction is a known ransomware
attack vector.
Question 10
A Chief Information Security Officer has requested a dashboard to share critical vulnerability
management goals with company leadership.
Which of the following would be the best to include in the dashboard?
- A. KPI
- B. MOU
- C. SLO
- D. SLA
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) track the effectiveness of a security program, providing
measurable insights into vulnerability detection, patching efficiency, and risk reduction. This makes
KPIs ideal for executive dashboards.
Option B (MOU - Memorandum of Understanding) refers to agreements between parties, not
performance tracking.
Option C (SLO - Service Level Objective) defines operational targets but is not a tracking metric.
Option D (SLA - Service Level Agreement) defines expectations between service providers and
clients, not security metrics.
Thus, A (KPI) is the correct answer, as KPIs provide actionable insights into security effectiveness.
Question 11
A security analyst must assist the IT department with creating a phased plan for vulnerability
patching that meets established SLAs.
Which of the following vulnerability management elements will best assist with prioritizing a
successful plan?
- A. Affected hosts
- B. Risk score
- C. Mitigation strategy
- D. Annual recurrence
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Risk scoring is the best method for prioritizing patching, as it considers factors like CVSS severity,
exploitability, asset criticality, and business impact.
Option A (Affected hosts) is relevant but does not determine priority without a risk assessment.
Option C (Mitigation strategy) is useful but focuses on alternative protections rather than
prioritization.
Option D (Annual recurrence) is not a standard method for vulnerability prioritization.
Thus, B is the correct answer, as risk scores allow organizations to prioritize patching efforts
effectively.
Question 12
A SOC manager reviews metrics from the last four weeks to investigate a recurring availability issue.
The manager finds similar events correlating to the times of the reported issues.
Which of the following methods would the manager most likely use to resolve the issue?
- A. Vulnerability assessment
- B. Root cause analysis
- C. Recurrence reports
- D. Lessons learned
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is the best approach to identify and resolve the underlying cause of
recurring incidents. It involves a systematic investigation of logs, configurations, and operational data
to pinpoint the reason behind persistent security issues.
Option A (Vulnerability assessment) helps identify security weaknesses but does not focus on
recurring operational issues.
Option C (Recurrence reports) track patterns but do not resolve the root cause.
Option D (Lessons learned) is valuable but is typically a post-mortem discussion rather than an
investigative method.
Thus, B is the correct answer, as root cause analysis is the best approach for diagnosing recurring
availability issues.
Question 13
Which of the following best describes the importance of KPIs in an incident response exercise?
- A. To identify the personal performance of each analyst
- B. To describe how incidents were resolved
- C. To reveal what the team needs to prioritize
- D. To expose which tools should be used
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) in incident response exercises help organizations prioritize
improvements by measuring response effectiveness, containment success, and recovery speed. This
ensures that resources are focused on the most critical areas for enhancement.
Option A (Personal performance tracking) is more relevant to HR evaluations rather than
cybersecurity operations.
Option B (Describing incident resolution) is important but does not define future priorities.
Option D (Identifying tools to use) is useful but not the primary function of KPIs.
Thus, C is the correct answer, as KPIs help teams identify the most urgent areas for improvement.
Question 14
A security analyst is reviewing a recent vulnerability scan report for a new server infrastructure. The
analyst would like to make the best use of time by resolving the most critical vulnerability first. The
following information is provided: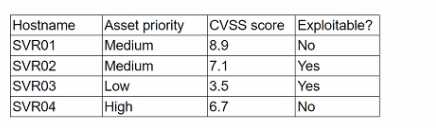
Which of the following should the analyst concentrate remediation efforts on first?
- A. SVR01
- B. SVR02
- C. SVR03
- D. SVR04
Answer:
B
Explanation:
SVR02 has a CVSS score of 7.1 and is exploitable, making it the highest priority for remediation .
SVR01 (CVSS 8.9) is not exploitable, so it is a lower risk.
SVR03 (CVSS 3.5) is exploitable but has a lower severity than SVR02.
SVR04 (CVSS 6.7) is not exploitable, reducing its urgency.
Thus, B (SVR02) is the correct answer, as it presents the highest immediate risk .
Question 15
Several incidents have occurred with a legacy web application that has had little development work
completed. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the incidents?
- A. Misconfigured web application firewall
- B. Data integrity failure
- C. Outdated libraries
- D. Insufficient logging
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Outdated libraries in a legacy web application introduce security vulnerabilities, as they lack modern
patches and contain known exploits .
Option A (Misconfigured WAF) can contribute to security issues but is not inherent to legacy
applications.
Option B (Data integrity failure) is a potential impact but not a direct cause of recurring incidents.
Option D (Insufficient logging) affects detection, but the root cause is insecure, outdated
components.
Thus, C (Outdated libraries) is the correct answer, as legacy applications frequently suffer from
unpatched vulnerabilities .