comptia CAS-005 Exam Questions
Questions for the CAS-005 were updated on : Feb 22 ,2026
Page 1 out of 20. Viewing questions 1-15 out of 290
Question 1
An organization is increasing its focus on training that addresses new social engineering and phishing
attacks. Which of the following is the organization most concerned about?
- A. Meeting existing regulatory compliance
- B. Overreliance on AI support bots
- C. Generative AI tools increasing the quality of exploits
- D. Differential analysis using AI models
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The organization is most concerned about Generative AI improving phishing and social engineering
attacks. Tools like ChatGPT can generate highly convincing phishing emails, fake websites, and
human-like interactions that bypass traditional detection methods. Employees who were trained to
spot poor grammar or obvious scams may now struggle to detect AI-crafted exploits.
Option A relates to compliance but not AI-driven threats. Option B (overreliance on AI bots) is
operational risk, not phishing. Option D (differential analysis) applies to AI privacy issues, not
phishing.
CAS-005 emphasizes adapting training to emerging threats, including AI-enabled social engineering.
This ensures users remain resilient against modern attacks, making C the correct answer.
Question 2
4d 5a 90 00 03 00 00 00 04 00 00 00 ff ff 00 00 b8 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 40 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 80 00 00 00 0e 1f ba 0e 00 b4 09 cd 21 b8 01 4c cd 21 54 68 69 73 20 70 72 6f 67 72 61 6d
20 63 61 6e 6e 6f 74 20 62 65 20 72 75 6e 20 69 6e 20 44 4f 53 20
6d 6f 64 65 2e 0d 0d 0a 24 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
50 45 00 00 4c 01 03 00 34 6d be 66 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 e0 00 0f 03 0b 01 05 00 00 70 00 00 00
10 00 00 00 d0 00 00 70 4c 01 00 00 e0 00 00 00 50 01 00 00 00 40 00
00 10 00 00 00 02 00 00 04 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 04 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 60 01 00 00 02 00 00 00
00 00 00 03 00 00 00 00 00 10 00 00 10 00 00 00 00 10 00 00 10 00 00
00 00 00 00 10 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
Attempts to run the code in a sandbox produce no results. Which of the following should the
malware analyst do next to further analyze the malware and discover useful IoCs?
- A. Convert the hex-encoded sample to binary and attempt to decompile it.
- B. Run the encoded sample through an online vulnerability tool and check for any matches.
- C. Pad the beginning and end of the sample with binary executables and attempt to execute it.
- D. Use a disassembler on the unencoded snippet to convert from binary to ASCII text.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The provided hex sequence begins with "4d 5a," which corresponds to the ASCII characters "MZ,"
indicating the presence of a DOS MZ executable file header. This suggests that the sample is a
Windows executable file. To analyze this malware effectively, the analyst should convert the hex-
encoded data back into its binary form to reconstruct the executable file. Once converted, the analyst
can use decompilation tools to translate the binary code into a higher-level programming language,
facilitating a deeper understanding of the malware's functionality and the extraction of Indicators of
Compromise (IoCs).
Other options, such as running the sample through an online vulnerability tool (Option B) or padding
it with executables (Option C), are less effective without first converting the hex data back to its
original binary form. Using a disassembler on the unencoded snippet (Option D) would not be
feasible until the hex data is properly reconstructed into its executable binary format.
Reference:CompTIA SecurityX CAS-005 Official Study Guide, Chapter 5: "Malware Analysis," Section
5.3: "Static and Dynamic Analysis Techniques."
Question 3
A company needs to define a new roadmap for improving secure coding practices in the software
development life cycle and implementing better security standards. Which of the following is the
best way for the company to achieve this goal?
- A. Performing a Software Assurance Maturity Model (SAMM) assessment and generating a roadmap as a final result
- B. Conducting a threat-modeling exercise for the main applications and developing a roadmap based on the necessary security implementations
- C. Developing a new roadmap including secure coding best practices based on the security area roadmap and annual goals defined by the CISO
- D. Using the best practices in the OWASP secure coding manual to define a new roadmap
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The best way is to perform a Software Assurance Maturity Model (SAMM) assessment. SAMM
provides a structured framework to evaluate current software security maturity across people,
process, and technology. The assessment highlights gaps and generates a roadmap tailored to the
organization’s development environment.
Option B (threat modeling) only applies to specific applications, not the entire SDLC process. Option
C risks misalignment with technical practices by relying only on CISO goals. Option D (OWASP secure
coding manual) is useful but provides guidelines, not a maturity-based roadmap.
CAS-005 stresses leveraging maturity models for structured, measurable improvements. SAMM
directly addresses this by producing a customized, actionable roadmap for secure coding practices.
Question 4
A security engineer receives the following findings from a recent security audit:
• Data should be protected based on user permissions and roles.
• User action tracking should be implemented across the network.
• Digital identities should be validated across the data access workflow.
Which of the following is the first action the engineer should take to address the findings?
- A. Implement continuous and context-based authentication and authorization
- B. Use an enhanced user credential provisioning workflow and data monitoring tools
- C. Improve federation services for digital identities and data access
- D. Deploy OpenID Connect for API authentication
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The first action is to implement continuous and context-based authentication and authorization (A).
Traditional authentication validates users only at login, which creates gaps during active sessions.
Continuous authentication ensures validation throughout the data access workflow, incorporating
contextual factors like device state, geolocation, and behavioral analysis. This directly aligns with
audit findings requiring protection by role, identity validation, and action tracking.
Option B improves onboarding and monitoring but does not enforce continuous access control.
Option C improves identity federation but does not provide session-by-session validation. Option D
secures APIs but is too narrow for organization-wide identity workflows.
CAS-005 stresses Zero Trust and context-aware IAM, making continuous authentication and
authorization the top priority.
Question 5
A security analyst is developing a threat model that focuses on attacks associated with the
organization's storage products. The products:
• Are used in commercial and government user environments
• Are required to comply with crypto-export requirements
• Include both hardware and software components that are developed by external vendors in Europe
and Asia
Which of the following are the most important for the analyst to consider when developing the
model? (Select two).
- A. Contractual obligations
- B. Legal hold obligations
- C. Trust boundaries
- D. Cloud services enumeration
- E. Supply chain access
- F. Homomorphic encryption usage
Answer:
C, E
Explanation:
The most critical considerations are trust boundaries (C) and supply chain access (E). Trust
boundaries define where sensitive data crosses between systems or organizations, requiring strict
cryptographic protections—especially important in government and commercial environments
subject to crypto-export controls.
Supply chain access is also critical because hardware and software are sourced from external
vendors. If suppliers are compromised, attackers could introduce malicious code, backdoors, or
tampered firmware, endangering customers worldwide.
Option A (contractual obligations) and B (legal hold) are compliance-related but not direct security
threats. Option D (cloud services enumeration) is irrelevant unless the storage is cloud-based. Option
F (homomorphic encryption) is an advanced technology but not required for base threat modeling.
CAS-005 highlights modeling adversary capabilities at trust boundaries and accounting for supply
chain risks, making C and E the most important.
Question 6
A security engineer receives an alert from the SIEM platform indicating a possible malicious action
on the internal network. The engineer generates a report that outputs the logs associated with the
incident:
Which of the following actions best enables the engineer to investigate further?
- A. Consulting logs from the enterprise password manager
- B. Searching dark web monitoring resources for exposure
- C. Reviewing audit logs from privileged actions
- D. Querying user behavior analytics data
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The best step is to query user behavior analytics (UBA) data. SIEM alerts provide potential security
events, but without additional context, they may lead to false positives. UBA solutions detect
anomalies by comparing user activity against baselines of normal behavior, highlighting unusual
login patterns, lateral movement, or privilege escalation.
Option A (password manager logs) focuses only on credential use and lacks behavioral insight.
Option B (dark web monitoring) helps identify compromised accounts but does not investigate the
internal incident. Option C (audit logs for privileged actions) is useful but narrow in scope—it only
covers administrator accounts.
By correlating SIEM data with UBA, the engineer can validate whether the flagged activity indicates
real malicious behavior or benign anomalies. CAS-005 emphasizes advanced analytics integration
(UEBA/UBA) to strengthen investigation and reduce false positives, making Option D the most
effective choice.
Question 7
A company is migrating from a Windows Server to Linux-based servers. A security engineer must
deploy a configuration management solution that maintains security software across all the Linux
servers. Which of the following configuration file snippets is the most appropriate to use?
A.
---
- name: deployment
hosts: linux_servers
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: Install security software
ansible.builtin.apt:
B.
<hosts>linux_servers</hosts>
<os_type>Linux 3.1</os_type>
<SElinux>true</SElinux>
<source>com.canonical.io</source>
C.
{"name":"deployment",
"hosts":"linux_servers",
"remote_user":"Administrator",
"tasks":{"name":"Install security software",
"com.microsoft.store.latest"}
}
D.
{"task":"install",
"hosts":"linux_servers",
"remote_user":"root",
"se_linux":"false",
"application":"AppX"}
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The correct snippet is Option A, which shows an Ansible YAML playbook designed to deploy and
maintain security software on Linux servers. Ansible is a configuration management tool widely used
in enterprise environments, and the ansible.builtin.apt module specifically manages package
installation on Debian/Ubuntu-based Linux distributions. This ensures consistent security software
deployment across multiple servers.
Option B is XML-based and does not represent a valid configuration management script. Option C
incorrectly uses JSON format and references Microsoft’s store (com.microsoft.store.latest), which is
irrelevant for Linux. Option D also uses JSON syntax with “AppX,” which applies to Windows
applications, not Linux.
CAS-005 emphasizes infrastructure as code (IaC) and automation as best practices for secure system
configuration. YAML-based playbooks in Ansible provide repeatability, auditability, and scalability,
making Option A the most secure and appropriate solution.
Question 8
A game developer wants to reach new markets and is advised by legal counsel to include specific
age-related sign-up requirements. Which of the following best describes the legal counsel's
concerns?
- A. GDPR
- B. LGPD
- C. PCI DSS
- D. COPPA
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The correct regulation is COPPA (Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act). COPPA is a U.S. law that
requires organizations to obtain parental consent and implement specific protections before
collecting personal data from children under the age of 13. Since the legal counsel is advising about
age-related sign-up requirements, the concern clearly points to COPPA compliance.
GDPR (A) is a European regulation governing privacy and data protection but is broader and not
specifically tied to children’s age verification, though it has related provisions. LGPD (B) is Brazil’s
data protection law, similar in scope to GDPR. PCI DSS (C) is focused on protecting cardholder data in
payment environments, unrelated to age-related concerns.
CAS-005 covers the importance of aligning software platforms with legal and regulatory frameworks.
For gaming and online services, COPPA compliance is crucial to avoid fines and reputational harm,
ensuring the platform properly handles children’s data.
Question 9
A security administrator needs to review the efficacy of the detection rules configured on the SIEM
by employing real-world attacker TTPs. Which of the following actions should the security
administrator take to accomplish this objective?
- A. Perform an internal penetration test.
- B. Use adversary emulation.
- C. Execute an internal vulnerability assessment.
- D. Perform a threat hunt exercise.
- E. Ingest new threat intelligence feeds.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The best option is adversary emulation. Adversary emulation involves simulating real-world attacker
Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs) based on frameworks like MITRE ATT&CK. Unlike
penetration tests, which primarily focus on identifying exploitable vulnerabilities, adversary
emulation specifically tests the effectiveness of detection and response capabilities against known
adversarial behaviors.
Option A (penetration testing) provides value but may not align test cases with SIEM detection rules.
Option C (vulnerability assessment) identifies weaknesses but does not test detection rules. Option D
(threat hunting) is proactive analysis but does not validate existing SIEM rule coverage in a structured
manner. Option E (threat feeds) enrich SIEM data but do not test its efficacy.
CAS-005 identifies adversary emulation as a key strategy for validating detection and response
coverage. It provides measurable results about what alerts are triggered and where detection gaps
exist, enabling organizations to tune SIEM rules for improved efficacy.
Question 10
A security engineer receives an alert from the threat intelligence platform with the following
information: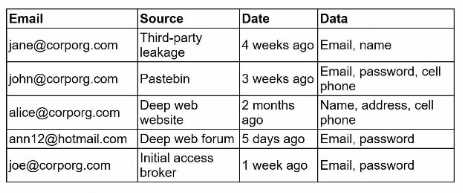
Which of the following actions should the security engineer do first?
- A. Reset John's and Joe's access.
- B. Contact John. Ann. and Joe to inform them about the incident and schedule a password reset.
- C. Reset John's, Ann's, and Joe's passwords and disconnect all users* active sessions
- D. Reset John's and Joe's passwords and inform authorities about the leakage.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The first action should be to reset access for John and Joe, who are corporate accounts belonging to
the organization. Their credentials were exposed in recent leaks, including one from an initial access
broker (Joe), which indicates an active exploitation risk. Immediate password resets and session
invalidations prevent adversaries from using the compromised credentials to gain access.
Ann’s account (@hotmail.com) is personal and not under corporate management, so while her
exposure is concerning, it does not pose a direct risk to organizational systems. Contacting her can
follow later steps but should not delay urgent remediation for John and Joe.
Option B delays remediation. Option C overreaches by including Ann in corporate resets. Option D
includes contacting authorities prematurely, which is important but secondary to immediate
containment.
CAS-005 emphasizes rapid containment of credential leaks affecting corporate identities, making
access resets for John and Joe the first step.
Question 11
A security manager at a local hospital wants to secure patient medical records. The manager needs
to:
• Choose an access control model that clearly defines who has access to sensitive information.
• Prevent those who enter new patient information from specifying who has access to this data.
Which of the following access control models is the best way to ensure the lowest risk of granting
unintentional access?
- A. Rule-based
- B. Attribute-based
- C. Mandatory
- D. Discretionary
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The best option is Mandatory Access Control (MAC). In MAC, access decisions are centrally controlled
by the system or administrators, not by individual users. This ensures that healthcare staff who enter
patient information cannot grant access to others, thereby preventing accidental or malicious
disclosure. MAC enforces strict policies based on data sensitivity and user clearance, which aligns
with compliance requirements like HIPAA.
Option A (rule-based) defines access through specific rules but is not as rigidly enforced as MAC.
Option B (attribute-based) is flexible but could still allow dynamic grants of access. Option D
(discretionary) explicitly allows users to assign access rights, which is exactly what must be avoided in
this scenario.
CAS-005 stresses using centralized, non-discretionary controls when protecting sensitive medical
data, making MAC the correct choice for hospitals.
Question 12
Consultants for a company learn that customs agents at foreign border crossings are demanding
device inspections. The company wants to:
• Minimize the risk to its data by storing its most sensitive data inside of a security container.
• Obfuscate containerized data on command.
Which of the following technologies is the best way to accomplish this goal?
- A. SED
- B. eFuse
- C. UEFI
- D. vTPM
- E. MicroSD HSM
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The best solution is to use Self-Encrypting Drives (SEDs). SEDs automatically encrypt all data stored
on the disk and can be rapidly sanitized or obfuscated by deleting or altering the encryption keys.
This provides immediate and secure protection if customs agents demand device access, as the
sensitive data inside containers becomes unreadable without the decryption key.
Option B (eFuse) and C (UEFI) are hardware mechanisms unrelated to dynamic data protection.
Option D (vTPM) provides virtualized key storage but does not obfuscate data quickly under
inspection conditions. Option E (MicroSD HSM) is useful for key storage but does not protect all data
at scale.
CAS-005 highlights hardware-based encryption solutions like SEDs for protecting sensitive data
during travel, ensuring both regulatory compliance and rapid response capabilities under hostile
conditions.
Question 13
An organization is developing an in-house software platform to support capital planning and
reporting functions. In addition to role-based access controls and auditing/logging capabilities, the
product manager must include requirements associated with archiving data and immutable backups.
Which of the following organizational considerations are most likely associated with this
requirement? (Select two)
- A. Crypto-export management controls
- B. Supply chain weaknesses
- C. Device attestation
- D. Quality assurance
- E. Legal hold compliance
- F. Ransomware resilience
Answer:
E, F
Explanation:
The requirements for archiving data and immutable backups directly align with legal hold compliance
(E) and ransomware resilience (F).
Legal hold compliance ensures that organizations can retain data in a tamper-proof manner when
required for litigation, regulatory mandates, or audits. Immutable backups satisfy this by preventing
unauthorized changes or deletion, ensuring evidence and records are preserved.
Ransomware resilience is also a key factor. Immutable backups allow recovery from ransomware
attacks, as attackers cannot encrypt or delete data stored in read-only or write-once media. This
reduces downtime and supports business continuity.
Options A (crypto-export), B (supply chain), C (device attestation), and D (quality assurance) do not
relate directly to data archiving or immutable storage.
CAS-005 stresses aligning security controls with business continuity and compliance requirements.
By focusing on legal and ransomware-related considerations, the organization ensures both
regulatory and operational resilience.
Question 14
A company's Chief Information Security Officer learns that the senior leadership team is traveling to
a country accused of attempting to steal intellectual property saved on laptops. Which of the
following is the best method to protect against this attack?
- A. Configure Measured Boot to report any firmware changes.
- B. Use sanitized devices with remote connections to VDI.
- C. Deploy self-encrypting drives to protect company data.
- D. Install tamper-evident stickers over any laptop screws.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The best option is to provide sanitized devices with remote connections to a Virtual Desktop
Infrastructure (VDI). This ensures that no sensitive intellectual property is stored locally on the
laptops carried across borders. Even if the devices are inspected, seized, or tampered with, attackers
cannot access corporate data since all sensitive files remain within secure, centralized infrastructure.
Option A (Measured Boot) reports firmware tampering but does not prevent data theft if the device
is compromised. Option C (self-encrypting drives) protect data at rest but can be bypassed if customs
agents demand login credentials. Option D (tamper-evident stickers) provide only physical inspection
indicators and are ineffective against sophisticated data theft attempts.
CAS-005 emphasizes secure remote access strategies and temporary “clean laptops” for high-risk
travel scenarios. Sanitized laptops with VDI access minimize exposure while maintaining productivity,
making this the strongest mitigation.
Question 15
A security administrator is reviewing the following code snippet from a website component:
A review of the inc.tmp file shows the following: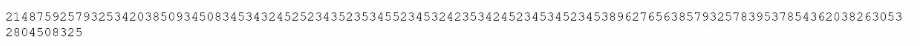
Which of the following is most likely the reason for inaccuracies?
- A. A content management solution plug-in has been exploited.
- B. A search engine's bots are being blocked at the firewall.
- C. The relevant stylesheet has become corrupted.
- D. The WAF is configured to be in transparent mode.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The code indicates that a WordPress (CMS) plug-in has likely been exploited. The function
get_hex_cache() combines obfuscated PHP code (hex2bin) with external file retrieval (inc.tmp). This
is characteristic of malicious plug-in injections in content management systems such as WordPress,
where attackers inject backdoors or malicious scripts through vulnerable plug-ins.
Option B (search engine bots blocked) and C (corrupted stylesheet) would not explain injected PHP
logic. Option D (WAF in transparent mode) reduces security controls but does not create malicious
functions inside the CMS code.
The presence of obfuscated data in inc.tmp strongly suggests tampering. Exploited CMS plug-ins are
a common initial access vector, often used to hide persistent malware or web shells.
This aligns with CAS-005 objectives on secure coding, monitoring for tampering, and conducting
regular code reviews of third-party dependencies.