Network Address Transition
Questions for the 300-101 were updated on : Jul 07 ,2025
Topic 1
Which statement about the use of tunneling to migrate to IPv6 is true?
C
Explanation:
Using the tunneling option, organizations build an overlay network that tunnels one protocol over the other by encapsulating
IPv6 packets within IPv4 packets and IPv4 packets within IPv6 packets. The advantage of this approach is that the new
protocol can work without disturbing the old protocol, thus providing connectivity between users of the new protocol.
Tunneling has two disadvantages, as discussed in RFC 6144:
Users of the new architecture cannot use the services of the underlying infrastructure.
Tunneling does not enable users of the new protocol to communicate with users of the old protocol without dual-stack
hosts, which negates interoperability.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/ios-nx-os-software/enterprise-ipv6-solution/white_paper_c11-
676278.html
Topic 1
Which method allows IPv4 and IPv6 to work together without requiring both to be used for a single connection during the
migration process?
A
Explanation:
Dual stack means that devices are able to run IPv4 and IPv6 in parallel. It allows hosts to simultaneously reach IPv4 and
IPv6 content, so it offers a very flexible coexistence strategy. For sessions that support IPv6, IPv6 is used on a dual stack
endpoint. If both endpoints support Ipv4 only, then IPv4 is used. Benefits:
Native dual stack does not require any tunneling mechanisms on internal networks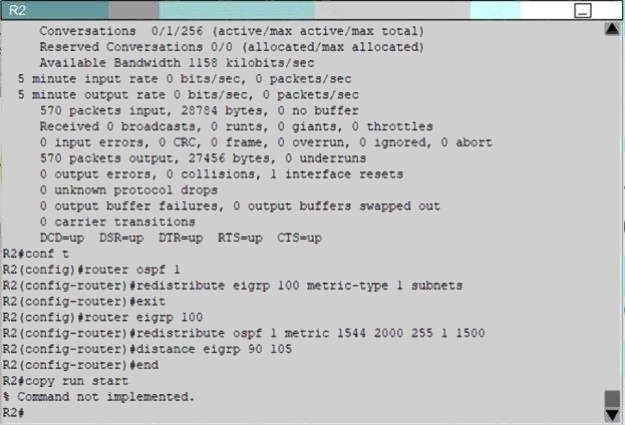
Both IPv4 and IPv6 run independent of each other
Dual stack supports gradual migration of endpoints, networks, and applications.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/web/strategy/docs/gov/IPV6at_a_glance_c45-625859.pdf
Network Address Transition
Topic 1
Refer to the exhibit.
A network administrator checks this adjacency table on a router. What is a possible cause for the incomplete marking?
A
Explanation:
To display information about the Cisco Express Forwarding adjacency table or the hardware Layer 3-switching adjacency
table, use the show adjacency command.
Reasons for Incomplete Adjacencies
There are two known reasons for an incomplete adjacency:
The router cannot use ARP successfully for the next-hop interface.
After a clear ip arp or a clear adjacency command, the router marks the adjacency as incomplete. Then it fails to clear the
entry. In an MPLS environment, IP CEF should be enameled for Label Switching. Interface level command ip route-cache
cef
No ARP Entry
When CEF cannot locate a valid adjacency for a destination prefix, it punts the packets to the CPU for ARP resolution and, in
turn, for completion of the
adjacency.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/express-forwarding-cef/17812-cef-incomp.html#t4
Dynamic routing failure
Topic 1
Which three problems result from application mixing of UDP and TCP streams within a network with no QoS? (Choose
three.)
A C E
Explanation:
It is a general best practice not to mix TCP-based traffic with UDP-based traffic (especially streaming video) within a single
service provider class due to the behaviors of these protocols during periods of congestion. Specifically, TCP transmitters
will throttle-back flows when drops have been detected. Although some UDP applications have application-level windowing,
flow control, and retransmission capabilities, most UDP transmitters are completely oblivious to drops and thus never lower
transmission rates due to dropping. When TCP flows are combined with UDP flows in a single service provider class and the
class experiences congestion, then TCP flows will continually lower their rates, potentially giving up their bandwidth to drop-
oblivious UDP flows. This effect is called TCP-starvation/UDP-dominance. This can increase latency and lower the overall
throughput.
TCP-starvation/UDP-dominance likely occurs if (TCP-based) mission-critical data is assigned to the same service provider
class as (UDP-based) streaming video and the class experiences sustained congestion. Even if WRED is enabled on the
service provider class, the same behavior would be observed, as WRED (for the most part) only affects TCP-based flows.
Granted, it is not always possible to separate TCP-based flows from UDP-based flows, but it is beneficial to be aware of this
behavior when making such application-mixing decisions.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/cc/so/neso/vpn/vpnsp/spqsd_wp.htm
Topic 1
Which two actions must you perform to enable and use window scaling on a router? (Choose two.)
A B
Explanation:
The TCP Window Scaling feature adds support for the Window Scaling option in RFC 1323, TCP Extensions for High
Performance. A larger window size is recommended to improve TCP performance in network paths with large bandwidth-
delay product characteristics that are called Long Fat Networks (LFNs). The TCP Window Scaling enhancement provides
that support.
The window scaling extension in Cisco IOS software expands the definition of the TCP window to 32 bits and then uses a
scale factor to carry this 32bit value in the 16-bit window field of the TCP header. The window size can increase to a scale
factor of 14. Typical applications use a scale factor of 3 when deployed in LFNs.
The TCP Window Scaling feature complies with RFC 1323. The larger scalable window size will allow TCP to perform better
over LFNs. Use the ip tcp window-size command in global configuration mode to configure the TCP window size. In order for
this to work, the remote host must also support this feature and its window size must be increased.
Topic 1
Which difference in the packet fragmentation feature between IPv4 and IPv6 devices is true?
D
Topic 1
Under which condition does UDP dominance occur?
A
Explanation:
Mixing TCP with UDP
It is a general best practice to not mix TCP-based traffic with UDP-based traffic (especially Streaming-Video) within a single
service-provider class because of the behaviors of these protocols during periods of congestion. Specifically, TCP
transmitters throttle back flows when drops are detected. Although some UDP applications have application-level windowing,
flow control, and retransmission capabilities, most UDP transmitters are completely oblivious to drops and, thus, never lower
transmission rates because of dropping.
When TCP flows are combined with UDP flows within a single service-provider class and the class experiences congestion,
TCP flows continually lower their transmission rates, potentially giving up their bandwidth to UDP flows that are oblivious to
drops. This effect is called TCP starvation/UDP dominance.
TCP starvation/UDP dominance likely occurs if (TCP-based) Mission-Critical Data is assigned to the same service-provider
class as (UDPbased) Streaming-Video and the class experiences sustained congestion. Even if WRED is enabled on the
service-provider class, the same behavior would be observed because WRED (for the most part) manages congestion only
on TCP-based flows.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/solutions/Enterprise/WAN_and_MAN/QoS_SRND/QoS-SRND-
Book/VPNQoS.html
Topic 1
Refer to the exhibit.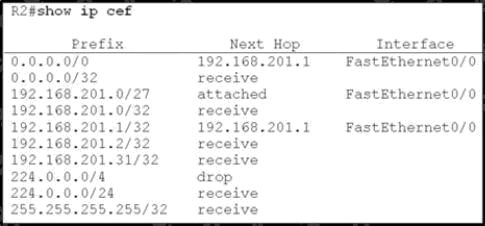
Based on this FIB table, which statement is correct?
C
Explanation:
The 0.0.0.0/0 route is the default route and is listed as the first CEF entry. Here we see the next hop for this default route
lists 192.168.201.1 as the default router (gateway of last resort).
Topic 1
Which switching method is used when entries are present in the output of the command show ip cache?
A
Explanation:
Fast switching allows higher throughput by switching a packet using a cache created by the initial packet sent to a particular
destination. Destination addresses are stored in the high-speed cache to expedite forwarding. Routers offer better packet-
transfer performance when fast switching is enabled.
Fast switching is enabled by default on all interfaces that support fast switching.
To display the routing table cache used to fast switch IP traffic, use the show ip cache EXEC command.
Topic 1
A network administrator executes the command clear ip route. Which two tables does this command clear and rebuild?
(Choose two.)
A B
Explanation:
To clear one or more entries in the IP routing table, use the following commands in any mode:
Reference:
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/datacenter/nexus5000/sw/unicast/5_0_3_N1_1/Cisco_n5k_layer3_ucast_cfg
_rel_503_N1_1/ l3_manage-routes.html
Topic 1
Which three TCP enhancements can be used with TCP selective acknowledgments? (Choose three.)
B C D
Explanation:
TCP Selective Acknowledgment
The TCP Selective Acknowledgment feature improves performance if multiple packets are lost from one TCP window of
data.
Prior to this feature, because of limited information available from cumulative acknowledgments, a TCP sender could learn
about only one lost packet per-round-trip time. An aggressive sender could choose to resend packets early, but such re-sent
segments might have already been successfully received.
The TCP selective acknowledgment mechanism helps improve performance. The receiving TCP host returns selective
acknowledgment packets to the sender, informing the sender of data that has been received. In other words, the receiver
can acknowledge packets received out of order. The sender can then resend only missing data segments (instead of
everything since the first missing packet).
Prior to selective acknowledgment, if TCP lost packets 4 and 7 out of an 8-packet window, TCP would receive
acknowledgment of only packets 1, 2, and 3. Packets 4 through 8 would need to be re-sent. With selective acknowledgment,
TCP receives acknowledgment of packets 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, and 8.
Only packets 4 and 7 must be re-sent.
TCP selective acknowledgment is used only when multiple packets are dropped within one TCP window. There is no
performance impact when the feature is enabled but not used. Use the ip tcp selective-ack command in global configuration
mode to enable TCP selective acknowledgment. Refer to RFC 2018 for more details about TCP selective acknowledgment.
TCP Time Stamp
The TCP time-stamp option provides improved TCP round-trip time measurements. Because the time stamps are always
sent and echoed in both directions and the time-stamp value in the header is always changing, TCP header compression will
not compress the outgoing packet. To allow TCP header compression over a serial link, the TCP time-stamp option is
disabled. Use the ip tcp timestamp command to enable the TCP time-stamp option.
TCP Explicit Congestion Notification
The TCP Explicit Congestion Notification (ECN) feature allows an intermediate router to notify end hosts of impending
network congestion. It also provides enhanced support for TCP sessions associated with applications, such as Telnet, web
browsing, and transfer of audio and video data that are sensitive to delay or packet loss. The benefit of this feature is the
reduction of delay and packet loss in data transmissions. Use the ip tcp ecn command in global configuration mode to enable
TCP ECN.
TCP Keepalive Timer
The TCP Keepalive Timer feature provides a mechanism to identify dead connections.
When a TCP connection on a routing device is idle for too long, the device sends a TCP keepalive packet to the peer with
only the Acknowledgment (ACK) flag turned on. If a response packet (a TCP ACK packet) is not received after the device
sends a specific number of probes, the connection is considered dead and the device initiating the probes frees resources
used by the TCP connection.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/ipapp/configuration/xe-3s/asr1000/iap-xe-3s-asr1000-book/iap-
tcp.html#GUID-22A82C5F631F-4390-9838-F2E48FFEEA01
Topic 1
A network administrator uses IP SLA to measure UDP performance and notices that packets on one router have a higher
one-way delay compared to the opposite direction. Which UDP characteristic does this scenario describe?
A
Explanation:
Cisco IOS IP SLAs provides a proactive notification feature with an SNMP trap. Each measurement operation can monitor
against a pre-set performance threshold. Cisco IOS IP SLAs generates an SNMP trap to alert management applications if
this threshold is crossed. Several SNMP traps are available: round trip time, average jitter, one-way latency, jitter, packet
loss, MOS, and connectivity tests. Here is a partial sample output from the IP SLA statistics that can be seen: router#show ip
sla statistics 1 Round Trip Time (RTT) for Index 55
Latest RTT: 1 ms
Latest operation start time: *23:43:31.845 UTC Thu Feb 3 2005 Latest operation return code: OK RTT Values:
Number Of RTT: 10 RTT Min/Avg/Max: 1/1/1 milliseconds Latency one-way time:
Number of Latency one-way Samples: 0
Source to Destination Latency one way Min/Avg/Max: 0/0/0 milliseconds
Destination to Source Latency one way Min/Avg/Max: 0/0/0 milliseconds
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/technologies/tk648/tk362/tk920/technologies_white_paper09186a00802d5efe.html
Topic 1
A network engineer notices that transmission rates of senders of TCP traffic sharply increase and decrease simultaneously
during periods of congestion. Which condition causes this?
A
Explanation:
TCP global synchronization in computer networks can happen to TCP/IP flows during periods of congestion because each
sender will reduce their transmission rate at the same time when packet loss occurs.
Routers on the Internet normally have packet queues, to allow them to hold packets when the network is busy, rather than
discarding them.
Because routers have limited resources, the size of these queues is also limited. The simplest technique to limit queue size
is known as tail drop. The queue is allowed to fill to its maximum size, and then any new packets are simply discarded, until
there is space in the queue again.
This causes problems when used on TCP/IP routers handling multiple TCP streams, especially when bursty traffic is
present. While the network is stable, the queue is constantly full, and there are no problems except that the full queue results
in high latency. However, the introduction of a sudden burst of traffic may cause large numbers of established, steady
streams to lose packets simultaneously. Reference: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/TCP_global_synchronization
Topic 2, Layer 2 Technologies
Topic 2
A network engineer has been asked to ensure that the PPPoE connection is established and authenticated using an
encrypted password. Which technology, in combination with PPPoE, can be used for authentication in this manner?
D
Explanation:
With PPPoE, the two authentication options are PAP and CHAP. When CHAP is enabled on an interface and a remote
device attempts to connect to it, the access server sends a CHAP packet to the remote device. The CHAP packet requests
or challenges the remote device to respond. The challenge packet consists of an ID, a random number, and the host name
of the local router.
When the remote device receives the challenge packet, it concatenates the ID, the remote devices password, and the
random number, and then encrypts all of it using the remote devices password. The remote device sends the results back to
the access server, along with the name associated with the password used in the encryption process.
When the access server receives the response, it uses the name it received to retrieve a password stored in its user
database. The retrieved password should be the same password the remote device used in its encryption process. The
access server then encrypts the concatenated information with the newly retrieved password if the result matches the
result sent in the response packet, authentication succeeds.
The benefit of using CHAP authentication is that the remote devices password is never transmitted in clear text (encrypted).
This prevents other devices from stealing it and gaining illegal access to the ISPs network.
Topic 2
Under which circumstance can flooding occur in a Layer 2 network?
D
Tunneling destination