amazon AWS Certified SysOps Administrator - Associate exam practice questions
Questions for the SOA-C02 were updated on : Feb 04 ,2026
Page 1 out of 38. Viewing questions 1-15 out of 557
Question 1
A company hosts an application on an Amazon EC2 instance in a single AWS Region. The application
requires support for non-HTTP TCP traffic and HTTP traffic.
The company wants to deliver content with low latency by leveraging the AWS network. The
company also wants to implement an Auto Scaling group with an
Elastic Load Balancer.
How should a SysOps administrator meet these requirements?
- A. Create an Auto Scaling group with an Application Load Balancer (ALB). Add an Amazon CloudFront distribution with the ALB as the origin.
- B. Create an Auto Scaling group with an Application Load Balancer (ALB). Add an accelerator with AWS Global Accelerator with the ALB as an endpoint.
- C. Create an Auto Scaling group with a Network Load Balancer (NLB). Add an Amazon CloudFront distribution with the NLB as the origin.
- D. Create an Auto Scaling group with a Network Load Balancer (NLB). Add an accelerator with AWS Global Accelerator with the NLB as an endpoint.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
AWS Global Accelerator and Amazon CloudFront are separate services that use the AWS global
network and its edge locations around the world. CloudFront improves performance for both
cacheable content (such as images and videos) and dynamic content (such as API acceleration and
dynamic site delivery). Global Accelerator improves performance for a wide range of applications
over TCP or UDP by proxying packets at the edge to applications running in one or more AWS
Regions. Global Accelerator is a good fit for non-HTTP use cases, such as gaming (UDP), IoT (MQTT),
or Voice over IP, as well as for HTTP use cases that specifically require static IP addresses or
deterministic, fast regional failover. Both services integrate with AWS Shield for DDoS protection.
https://medium.com/awesome-cloud/aws-difference-between-application-load-balancer-and-
network-load-balancer-cb8b6cd296a4 https://aws.amazon.com/global-accelerator/faqs/?nc1=h_ls
Question 2
SIMULATION
[Deployment, Provisioning, and Automation]
You need to update an existing AWS CloudFormation stack. If needed, a copy to the CloudFormation
template is available in an Amazon SB bucket named cloudformation-bucket
1. Use the us-east-2 Region for all resources.
2. Unless specified below, use the default configuration settings.
3. update the Amazon EQ instance named Devinstance by making the following changes to the stack
named 1700182:
a) Change the EC2 instance type to us-east-t2.nano.
b) Allow SSH to connect to the EC2 instance from the IP address range
192.168.100.0/30.
c) Replace the instance profile IAM role with IamRoleB.
4. Deploy the changes by updating the stack using the CFServiceR01e role.
5. Edit the stack options to prevent accidental deletion.
6. Using the output from the stack, enter the value of the Prodlnstanceld in the text box below:
Answer:
See the
Explanation for
solution.
Explanation:
Here are the steps to update an existing AWS CloudFormation stack:
Log in to the AWS Management Console and navigate to the CloudFormation service in the us-east-2
Region.
Find the existing stack named 1700182 and click on it.
Click on the "Update" button.
Choose "Replace current template" and upload the updated CloudFormation template from the
Amazon S3 bucket named "cloudformation-bucket"
In the "Parameter" section, update the EC2 instance type to us-east-t2.nano and add the IP address
range 192.168.100.0/30 for SSH access.
Replace the instance profile IAM role with IamRoleB.
In the "Capabilities" section, check the checkbox for "IAM Resources"
Choose the role CFServiceR01e and click on "Update Stack"
Wait for the stack to be updated.
Once the update is complete, navigate to the stack and click on the "Stack options" button, and select
"Prevent updates to prevent accidental deletion"
To get the value of the Prodlnstanceld , navigate to the "Outputs" tab in the CloudFormation stack
and find the key "Prodlnstanceld". The value corresponding to it is the value that you need to enter in
the text box below.
Note:
You can use AWS CloudFormation to update an existing stack.
You can use the AWS CloudFormation service role to deploy updates.
You can refer to the AWS CloudFormation documentation for more information on how to update
and manage stacks:
https://aws.amazon.com/cloudformation/
Question 3
SIMULATION
[High Availability, Backup, and Recovery]
A webpage is stored in an Amazon S3 bucket behind an Application Load Balancer (ALB). Configure
the SS bucket to serve a static error page in the event of a failure at the primary site.
1. Use the us-east-2 Region for all resources.
2. Unless specified below, use the default configuration settings.
3. There is an existing hosted zone named lab-
751906329398-26023898.com that contains an A record with a simple routing policy that routes
traffic to an existing ALB.
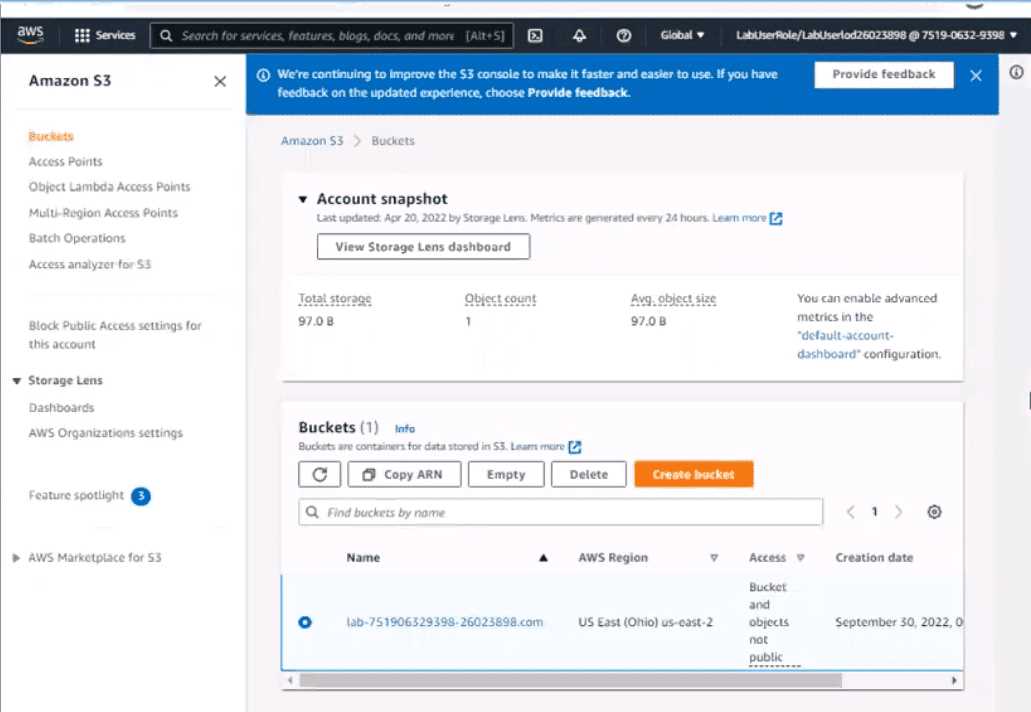
4. Configure the existing S3 bucket named lab-751906329398-26023898.com as a static hosted
website using the object named index.html as the index document
5. For the index-html object, configure the S3 ACL to allow for public read access. Ensure public
access to the S3 bucketjs allowed.
6. In Amazon Route 53, change the A record for domain lab-751906329398-26023898.com to a
primary record for a failover routing policy. Configure the record so that it evaluates the health of the
ALB to determine failover.
7. Create a new secondary failover alias record for the domain lab-751906329398-26023898.com
that routes traffic to the existing 53 bucket.
Answer:
See the
Explanation for
solution.
Explanation:
Here are the steps to configure an Amazon S3 bucket to serve a static error page in the event of a
failure at the primary site:
Log in to the AWS Management Console and navigate to the S3 service in the us-east-2 Region.
Find the existing S3 bucket named lab-751906329398-26023898.com and click on it.
In the "Properties" tab, click on "Static website hosting" and select "Use this bucket to host a
website".In"IndexDocument"field,enterthenameoftheobjectthatyouwanttouseastheindexdocument,inthiscase,"index.html"
In the "Permissions" tab, click on "Block Public Access", and make sure that "Block all public access"
is turned OFF.
Click on "Bucket Policy" and add the following policy to allow public read access:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement":
[
{
"Sid": "PublicReadGetObject",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": "*",
"Action": "s3:GetObject",
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::lab-751906329398-26023898.com/*"
}
]
}
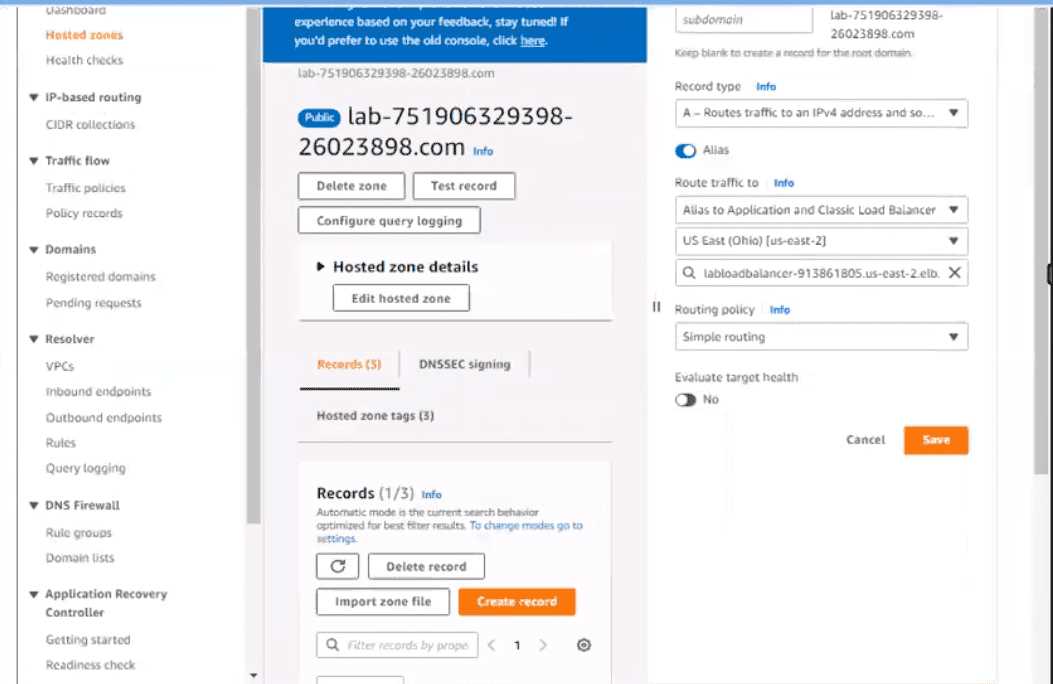
Now navigate to the Amazon Route 53 service, and find the existing hosted zone named lab-
751906329398-26023898.com.
Click on the "A record" and update the routing policy to "Primary - Failover" and add the existing ALB
as the primary record.
Click on "Create Record" button and create a new secondary failover alias record for the domain lab-
751906329398-26023898.com that routes traffic to the existing S3 bucket.
Now, when the primary site (ALB) goes down, traffic will be automatically routed to the S3 bucket
serving the static error page.
Note:
You can use CloudWatch to monitor the health of your ALB.
You can use Amazon S3 to host a static website.
You can use Amazon Route 53 for routing traffic to different resources based on health checks.
You can refer to the AWS documentation for more information on how to configure and use these
services:
https://aws.amazon.com/s3/
https://aws.amazon.com/route53/
https://aws.amazon.com/cloudwatch/
Graphical user interface, application, Teams Description automatically generated
Question 4
SIMULATION
[Monitoring, Reporting, and Automation]
If your AWS Management Console browser does not show that you are logged in to an AWS account,
close the browser and relaunch the
console by using the AWS Management Console shortcut from the VM desktop.
If the copy-paste functionality is not working in your environment, refer to the instructions file on the
VM desktop and use Ctrl+C, Ctrl+V or Command-C , Command-V.
Configure Amazon EventBridge to meet the following requirements.
1. use the us-east-2 Region for all resources,
2. Unless specified below, use the default configuration settings.
3. Use your own resource naming unless a resource
name is specified below.
4. Ensure all Amazon EC2 events in the default event
bus are replayable for the past 90 days.
5. Create a rule named RunFunction to send the exact message every 1 5 minutes to an existing AWS
Lambda function named LogEventFunction.
6. Create a rule named SpotWarning to send a notification to a new standard Amazon SNS topic
named TopicEvents whenever an Amazon EC2
Spot Instance is interrupted. Do NOT create any topic subscriptions. The notification must match the
following structure:
Input Path:
{“instance” : “$.detail.instance-id”}
Input template:
“ The EC2 Spot Instance <instance> has been on account.
Answer:
See the
Explanation for
solution.
Explanation:
Here are the steps to configure Amazon EventBridge to meet the above requirements:
Log in to the AWS Management Console by using the AWS Management Console shortcut from the
VM desktop. Make sure that you are logged in to the desired AWS account.
Go to the EventBridge service in the us-east-2 Region.
In the EventBridge service, navigate to the "Event buses" page.
Click on the "Create event bus" button.
Give a name to your event bus, and select "default" as the event source type.
Navigate to "Rules" page and create a new rule named "RunFunction"
In the "Event pattern" section, select "Schedule" as the event source and set the schedule to run
every 15 minutes.
In the "Actions" section, select "Send to Lambda" and choose the existing AWS Lambda function
named "LogEventFunction"
Create another rule named "SpotWarning"
In the "Event pattern" section, select "EC2" as the event source, and filter the events on "EC2 Spot
Instance interruption"
In the "Actions" section, select "Send to SNS topic" and create a new standard Amazon SNS topic
named "TopicEvents"
In the "Input Transformer" section, set the Input Path to {“instance” : “$.detail.instance-id”} and
Input template to “The EC2 Spot Instance <instance> has been interrupted on account.
Now all Amazon EC2 events in the default event bus will be replayable for past 90 days.
Note:
You can use the AWS Management Console, AWS CLI, or SDKs to create and manage EventBridge
resources.
You can use CloudTrail event history to replay events from the past 90 days.
You can refer to the AWS EventBridge documentation for more information on how to configure and
use the service: https://aws.amazon.com/eventbridge/
Question 5
[Cost and Performance Optimization]
A company runs a workload on a high performance computing (HPC) cluster on AWS. The workload is
Linux-based and uses three Amazon EC2 instances. Each EC2 instance has a 10 TiB Throughput
Optimized HDD (st1) Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS) volume.
A SysOps administrator determines that the current storage is not meeting the workload's
performance needs. The workload needs a durable file store that has throughput of 100,000 IOPS.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
- A. Create an Amazon ElastiCache (Redis OSS) instance. Keep the append-only file (AOF) feature disabled.
- B. Create an Amazon S3 bucket in the same AWS Region where the HPC cluster is deployed. Use the same S3 bucket prefix on all objects.
- C. Create an Amazon FSx for Lustre file system. Configure an appropriate number of IOPS.
- D. Create an Amazon S3 bucket in the same AWS Region where the HPC cluster is deployed. Enable S3 Transfer Acceleration.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Amazon FSx for Lustre is purpose-built for compute-intensive workloads that require high IOPS, low
latency, and fast throughput—ideal for HPC use cases.
Key benefits include:
High IOPS: Lustre file systems can scale to hundreds of thousands of IOPS.
Low Latency: Sub-millisecond latency suitable for large-scale parallel processing.
Durability: Fully managed by AWS and integrated with Amazon S3 for persistent storage.
POSIX Compliance: Supports Linux-based applications.
This makes FSx for Lustre the optimal solution for HPC workloads where existing Throughput
Optimized HDDs (st1) fall short in performance.
Exact Reference from AWS Documentation:
FSx for Lustre is designed for high-performance workloads and can deliver 100,000+ IOPS, addressing
demanding storage needs.
[Source: Amazon FSx for Lustre Performance Guide]
Topic 2, Simulation
Question 6
[Networking and Content Delivery]
An application is running on an Amazon EC2 instance in a VPC with the default DHCP option set. The
application connects to an on-premises Microsoft SQL Server database with the DNS name
mssql.example.com. The application is unable to resolve the database DNS name.
Which solution will fix this problem?
- A. Create an Amazon Route 53 Resolver inbound endpoint. Add a forwarding rule for the domain example.com. Associate the forwarding rule with the VPC.
- B. Create an Amazon Route 53 Resolver inbound endpoint. Add a system rule for the domain example.com. Associate the system rule with the VPC.
- C. Create an Amazon Route 53 Resolver outbound endpoint. Add a forwarding rule for the domain example.com. Associate the forwarding rule with the VPC.
- D. Create an Amazon Route 53 Resolver outbound endpoint. Add a system rule for the domain example.com. Associate the system rule with the VPC.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
When EC2 instances in a VPC cannot resolve on-premises DNS names like mssql.example.com, it is
usually because the default DHCP options set provided by AWS does not allow forwarding DNS
queries outside of the VPC.
To resolve this, you must:
Create a Route 53 Resolver outbound endpoint in your VPC.
Define a forwarding rule for the example.com domain, specifying the on-premises DNS server as the
target.
Associate the forwarding rule with the VPC where the EC2 instance resides.
This setup enables DNS queries for example.com to be forwarded from AWS to the on-premises DNS
servers, thereby enabling name resolution for hybrid environments.
Exact Reference from AWS Documentation:
AWS Route 53 Resolver enables hybrid cloud DNS resolution. An outbound endpoint forwards DNS
queries from the VPC to on-premises DNS servers via defined rules.
[Source: Amazon Route 53 Resolver Documentation – Forwarding outbound queries]
Question 7
[Monitoring, Reporting, and Automation]
A company's application runs on Amazon EC2 instances behind an Application Load Balancer (ALB).
The company has configured an Amazon CloudWatch alarm to monitor the
HTTPCode_Target_5XX_Count metric. The application crashes every few days during business hours.
The crashes trigger the CloudWatch alarm and result in service disruption.
The cause of the crashes is a memory leak in the application. While developers work to fix the
problem, a SysOps administrator needs to implement a temporary solution. The solution must
automatically reboot the EC2 instances every day and must minimize application disruption during
business hours.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
- A. Create an Amazon EventBridge rule that is scheduled to run outside of business hours. Configure the rule to invoke the StartInstances operation on the EC2 instances.
- B. Use AWS Systems Manager to create a daily maintenance window that is outside of business hours. Register the EC2 instances as a target. Assign the AWS-RestartEC2Instance runbook to the maintenance window.
- C. Configure an additional CloudWatch alarm to monitor the StatusCheckFailed_System metric for the EC2 instances. Configure an EC2 action on the additional alarm to reboot the instances.
- D. Configure an additional CloudWatch alarm that is triggered every time the application crashes. Configure an EC2 action on the additional alarm to restart the application on the EC2 instances.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
AWS Systems Manager Maintenance Windows allow you to define a schedule for performing
administrative tasks on your instances. By setting up a maintenance window:
Schedule Reboots:
Define a maintenance window outside business hours.
Register the EC2 instances as targets.
Assign the AWS-RestartEC2Instance Automation document to the task.
This setup ensures that instances are rebooted regularly, mitigating the effects of the memory leak
until a permanent fix is implemented.
Reference:
AWS Systems Manager Maintenance Windows
Question 8
[Deployment, Provisioning, and Automation]
A SysOps administrator creates a new VPC that includes a public subnet and a private subnet. The
SysOps administrator successfully launches 11 Amazon EC2 instances in the private subnet. The
SysOps administrator attempts to launch one more EC2 instance in the same subnet. However, the
SysOps administrator receives an error message that states that not enough free IP addresses are
available.
What must the SysOps administrator do to deploy more EC2 instances?
- A. Edit the private subnet to change the CIDR block to /27.
- B. Edit the private subnet to extend across a second Availability Zone.
- C. Assign additional Elastic IP addresses to the private subnet.
- D. Create a new private subnet to hold the required EC2 instances.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
In AWS, each subnet has a fixed CIDR block, and the number of available IP addresses is determined
by this block. For example, a /28 subnet provides 16 IP addresses, but 5 are reserved by AWS, leaving
11 usable IPs.
Since the subnet is already at capacity:
Create a New Subnet:
Choose a CIDR block that doesn't overlap with existing subnets.
Ensure it's within the VPC's CIDR range.
Launch additional EC2 instances in this new subnet.
This approach allows for the deployment of more instances without modifying existing subnets.
Reference:
Subnet CIDR blocks - Amazon Virtual Private Cloud
Question 9
[Networking and Content Delivery]
A SysOps administrator is creating a simple, public-facing website running on Amazon EC2. The
SysOps administrator created the EC2 instance in an existing public subnet and assigned an Elastic IP
address to the instance. Next, the SysOps administrator created and applied a new security group to
the instance to allow incoming HTTP traffic from 0.0.0.0/0. Finally, the SysOps administrator created
a new network ACL and applied it to the subnet to allow incoming HTTP traffic from 0.0.0.0/0.
However, the website cannot be reached from the internet.
What is the cause of this issue?
- A. The SysOps administrator did not create an outbound rule that allows ephemeral port return traffic in the new network ACL.
- B. The SysOps administrator did not create an outbound rule in the security group that allows HTTP traffic from port 80.
- C. The Elastic IP address assigned to the EC2 instance has changed.
- D. There is an additional network ACL associated with the subnet that includes a rule that denies inbound HTTP traffic from port 80.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Network ACLs (Access Control Lists) are stateless, meaning that return traffic must be explicitly
allowed. While the inbound rule allows HTTP traffic on port 80, the absence of an outbound rule
permitting return traffic on ephemeral ports (typically 1024-65535) prevents the response from
reaching the client.
To resolve this:
Add an Outbound Rule:
Protocol: TCP
Port Range: 1024-65535
Destination: 0.0.0.0/0
Action: Allow
This configuration ensures that the server can send responses back to clients initiating HTTP
requests.
Reference:
Control subnet traffic with network access control lists
Question 10
[High Availability, Backup, and Recovery]
A company has an Amazon EC2 instance that supports a production system. The EC2 instance is
backed by an Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS) volume. The EBS volume's drive has filled to
100% capacity, which is causing the application on the EC2 instance to experience errors.
Which solution will remediate these errors in the LEAST amount of time?
- A. Modify the EBS volume by adding additional drive space. Log on to the EC2 instance. Use the file system-specific commands to extend the file system.
- B. Create a snapshot of the existing EBS volume. When the snapshot is complete, create an EBS volume of a larger size from the snapshot in the same Availability Zone as the EC2 instance. Attach the new EBS volume to the EC2 instance. Mount the file system.
- C. Create a new EBS volume of a larger size in the same Availability Zone as the EC2 instance. Attach the EBS volume to the EC2 instance. Copy the data from the existing EBS volume to the new EBS volume.
- D. Stop the EC2 instance. Change the EC2 instance to a larger instance size that includes additional drive space. Start the EC2 instance.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
To address the issue of a fully utilized EBS volume causing application errors, the most efficient
solution is to dynamically resize the existing EBS volume and extend the file system. AWS EBS
supports Elastic Volumes, allowing you to increase volume size without detaching or stopping the
instance.
Steps:
Modify the EBS Volume:
Navigate to the Amazon EC2 console.
Select the EBS volume attached to the instance.
Choose "Modify Volume" and increase the size as needed.
Confirm the modification.
Extend the File System:
Connect to the EC2 instance.
Use the lsblk command to identify the volume and partition.
If necessary, use the growpart command to extend the partition.
Depending on the file system:
For XFS: sudo xfs_growfs -d /mount-point
For ext4: sudo resize2fs /dev/xvda1
This approach minimizes downtime and avoids the need for creating new volumes or stopping the
instance.
Reference:
Extend the file system after resizing an Amazon EBS volume
Question 11
[High Availability, Backup, and Recovery]
A company has an NFS server running on a single Amazon EC2 instance. A SysOps administrator
needs to replace the NFS server with a highly available file system. A total of 30 EC2 instances, spread
across multiple Availability Zones, must connect to the file system to store and retrieve shared
images and dat
a. The administrator plans to use Amazon Elastic File System (Amazon EFS) for the file system.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
- A. Create a new EFS file system in each Availability Zone. Configure the file systems to use the EFS One Zone storage class. Create an Amazon Route 53 alias record. Turn on health checks. Configure the record to resolve to the EFS file systems. Configure each EC2 instance to connect to the alias record.
- B. Create a new EFS file system that uses the EFS Standard storage class. Configure each EC2 instance to connect to the mount target in its own AWS Region.
- C. Create a new EFS file system in each Availability Zone. Configure the file systems to use the EFS One Zone storage class. Configure each EC2 instance to connect to the mount target in its own Availability Zone.
- D. Create a new EFS file system that uses the EFS Standard storage class. Configure each EC2 instance to connect to the mount target in its own Availability Zone.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Amazon Elastic File System (EFS) provides a scalable and highly available file storage solution for use
with Amazon EC2 instances. To achieve high availability and durability:
EFS Standard Storage Class: Stores data redundantly across multiple Availability Zones, ensuring data
durability and availability.
Mount Targets: For optimal performance and availability, create a mount target in each Availability
Zone. EC2 instances should connect to the mount target in their respective Availability Zone.
By configuring EFS in this manner, the company ensures that all EC2 instances, regardless of their
Availability Zone, have reliable and efficient access to shared data.
Reference:
Amazon Elastic File System Documentation:
Amazon EFS Documentation
Question 12
[Deployment, Provisioning, and Automation]
A SysOps administrator manages the security of accounts in an organization in AWS Organizations.
The administrator must implement a solution that applies a base configuration to all accounts when
they join the organization.
Which solution will meet this requirement with the LEAST operational overhead?
- A. Create the configuration in an AWS CloudFormation template. Deploy the template to all accounts in the organization by using StackSets automatic deployments.
- B. Turn on AWS Config in the organization's management account. Use multi-account, multi-Region data aggregation. Review results on the Aggregated Resources page.
- C. Create an AWS Lambda function in the organization's management account to configure resources. Configure the Lambda function with cross-account access. Run the function when a new account is detected.
- D. Create the configuration in an AWS CloudFormation template. Deploy the template to all accounts in the organization by using an AWS Lambda function that runs when a new account is detected.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
AWS CloudFormation StackSets allows you to deploy a single CloudFormation template across
multiple AWS accounts and Regions. By using automatic deployments with StackSets:
New Accounts: When a new account is added to the organization or a specific organizational unit
(OU), the StackSet automatically deploys the specified resources.
Consistency: Ensures that all accounts have a consistent base configuration.
Operational Efficiency: Reduces manual intervention, as deployments are handled automatically.
This method provides a scalable and efficient way to enforce baseline configurations across an
organization.
Reference:
Working with AWS CloudFormation StackSets:
AWS CloudFormation StackSets Documentation
Question 13
[High Availability, Backup, and Recovery]
A company has a large on-premises tape backup solution and has started using AWS Storage
Gateway. The company created a Tape Gateway to replace the existing on-premises hardware. The
backup engineer noticed that some backup jobs intended to write to AWS failed due to a "Not
Enough Space" error. The company wants to prevent these failures and consistently have enough
tape available on AWS.
What is the MOST operationally efficient way for a SysOps administrator to meet these
requirements?
- A. Create an AWS Lambda function that runs hourly to check the number of tapes with available space. If the available tapes are below a certain threshold, provision more.
- B. Install the Amazon CloudWatch agent on the on-premises system. Push the log files to a CloudWatch log group. Create an AWS Lambda function that creates more tapes when the "Not Enough Space" error appears. Create a metric filter and a metric alarm that launches the Lambda function.
- C. Create an additional Tape Gateway with its own set of tapes. Configure Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS) to send a notification to the backup engineer if the tapes associated with the primary Tape Gateway do not have available space.
- D. Configure tape auto-create on the Tape Gateway. In the auto-create settings, configure a minimum number of tapes, an appropriate barcode prefix, and a tape pool.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
AWS Storage Gateway's Tape Gateway offers an automatic tape creation feature that ensures a
predefined minimum number of virtual tapes are always available. By configuring this feature:
Minimum Number of Tapes: Specify the least number of tapes that should be available at all times.
Barcode Prefix: Define a prefix to help identify the virtual tapes.
Tape Pool: Choose the storage class (e.g., S3 Glacier or S3 Glacier Deep Archive) for archiving ejected
tapes.
When the number of available tapes falls below the specified minimum, the Tape Gateway
automatically creates new tapes, eliminating the need for manual intervention or custom scripts.
This automated approach ensures that backup jobs have the necessary resources, preventing failures
due to insufficient tape availability.
Reference:
Managing Automatic Tape Creation:
AWS Documentation
Allowing Automatic Tape Creation:
AWS Documentation
Question 14
[Monitoring, Reporting, and Automation]
A company needs to monitor its website's availability to end users. The company requires a solution
that provides an Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS) notification if the website's
uptime decreases to less than 99%. The monitoring must accurately reflect the user experience on
the website.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
- A. Create an Amazon CloudWatch alarm based on the website's logs published to a CloudWatch Logs log group. Configure the alarm to publish an SNS notification if the number of HTTP 4xx and 5xx errors exceeds a specified threshold.
- B. Create an Amazon CloudWatch alarm based on the website's published metrics in CloudWatch. Configure the alarm to publish an SNS notification based on anomaly detection.
- C. Create an Amazon CloudWatch Synthetics heartbeat monitoring canary. Associate the canary with the website's URL for end users. Create a CloudWatch alarm for the canary. Configure the alarm to publish an SNS notification if the value of the SuccessPercent metric is less than 99%.
- D. Create an Amazon CloudWatch Synthetics broken link checker monitoring canary. Associate the canary with the website's URL for end users. Create a CloudWatch alarm for the canary. Configure the alarm to publish an SNS notification if the value of the SuccessPercent metric is less than 99%.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
To effectively monitor website availability from an end-user perspective and receive notifications
when uptime falls below a specified threshold, Amazon CloudWatch Synthetics provides a robust
solution. Specifically, the heartbeat monitoring canary is designed to:
Simulate user interactions by regularly accessing the website's URL.
Measure availability and latency, providing insights into the user experience.
Publish metrics, such as SuccessPercent, which indicates the percentage of successful canary runs.
By creating a CloudWatch alarm that monitors the SuccessPercent metric and configuring it to trigger
an SNS notification when the value drops below 99%, the company can proactively address
availability issues.
This approach ensures continuous monitoring that closely mirrors the end-user experience, allowing
for timely interventions when problems arise.
Reference:
CloudWatch metrics published by canaries:
AWS Documentation
Synthetic monitoring (canaries):
AWS Documentation
Question 15
[Monitoring, Reporting, and Automation]
A SysOps administrator needs to collect the content of log files from a custom application that is
deployed across hundreds of Amazon EC2 instances running Ubuntu. The log files need to be stored
in Amazon CloudWatch Logs.
How should the SysOps administrator collect the application log files with the LEAST operational
overhead?
- A. Configure the syslogd service on each EC2 instance to collect and send the application log files to CloudWatch Logs.
- B. Install the CloudWatch agent by using the Amazon Linux package manager on each EC2 instance. Configure each agent to collect the application log files.
- C. Install the CloudWatch agent on each EC2 instance by using AWS Systems Manager. Create an agent configuration on each instance by using the CloudWatch configuration wizard. Configure each agent to collect the application log files.
- D. Store a CloudWatch agent configuration in AWS Systems Manager Parameter Store. Install the CloudWatch agent on each EC2 instance by using Systems Manager. Configure each agent to collect the application log files.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The unified Amazon CloudWatch agent can collect both logs and metrics from Amazon EC2 instances.
To efficiently deploy and manage the CloudWatch agent across multiple EC2 instances, AWS Systems
Manager can be utilized.
By storing the CloudWatch agent configuration in AWS Systems Manager Parameter Store, you can
centrally manage the configuration and ensure consistency across all instances. Using Systems
Manager, you can automate the installation and configuration of the CloudWatch agent on each EC2
instance, reducing manual effort and operational overhead.
This approach allows for scalable and consistent log collection from a large fleet of EC2 instances,
aligning with best practices for operational efficiency.
Reference:
Amazon CloudWatch Documentation: Collect metrics, logs, and traces with the CloudWatch agent