amazon AWS Certified SysOps Administrator - Associate (SOA-C02) exam practice questions
Questions for the AWS CERTIFIED SYSOPS ADMINISTRATOR ASSOCIATE SOA C02 were updated on : Jul 02 ,2025
Page 1 out of 8. Viewing questions 1-15 out of 115
Question 1
A SysOps administrator is reviewing AWS Trusted Advisor warnings and encounters a warning for an S3 bucket policy that
has open access permissions. While discussing the issue the bucket owner, the administrator realizes the S3 bucket is an
origin for an Amazon CloudFront web distribution.
Which action should the administrator take to ensure that users access objects in Amazon S3 by using only CloudFront
URLs?
- A. Encrypt the S3 bucket content with Server-Side Encryption with Amazon S3-Managed Keys (SSE-S3).
- B. Create an origin access identity and grant it permissions to read objects in the S3 bucket.
- C. Assign an IAM user to the CloudFront distribution and grant the user permissions in the S3 bucket policy.
- D. Assign an IAM role to the CloudFront distribution and grant the role permissions in the S3 bucket policy.
Answer:
B
Question 2
A company has an Amazon Route 53 private hosted zone in its AWS account. The private hosted zone is connected to the
companys on-premises data center by an AWS Direct Connect connection. Virtual machines (VMs) in the on-premises data
center need to resolve DNS queries that exist in the private hosted zone.
What is the MOST operationally efficient solution that meets this requirement?
- A. Create a Route 53 inbound resolver. Configure the on-premises VMs to use the inbound resolver.
- B. Create a Route 53 outbound resolver. Configure the on-premises VMs to use the outbound resolver.
- C. Configure the security group on the Route 53 private hosted zone by adding an inbound rule for the on-premises CIDR range.
- D. Configure a Route 53 public hosted zone. Create an NS record for the private hosted zone. Query the public hosted zone from the on-premises VMs.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Reference: https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/security/how-to-centralize-dns-management-in-a-multi-account-environment/
Question 3
A company uses AWS Organizations to host several applications across multiple AWS accounts. Several teams are
responsible for building and maintaining the infrastructure of the application across the AWS accounts.
A SysOps administrator must implement a solution to ensure that user accounts and permissions are centrally managed.
The solution must be integrated with the companys existing on-premises Active Directory environment. The SysOps
administrator already has enabled AWS Single Sign-On (AWS SSO) and has set up an AWS Direct Connect connection.
What is the MOST operationally efficient solution that meets these requirements?
- A. Create a Simple AD domain, and establish a forest trust relationship with the on-premises Active Directory domain. Set the Simple AD domain as the identity source for AWS SSO. Create the required role-based permission sets. Assign each group of users to the AWS accounts that the group will manage.
- B. Create an Active Directory domain controller on an Amazon EC2 instance that is joined to the on-premises Active Directory domain. Set the Active Directory domain controller as the identity source for AWS SSO. Create the required role- based permission sets. Assign each group of users to the AWS accounts that the group will manage.
- C. Create an AD Connector that is associated with the on-premises Active Directory domain. Set the AD Connector as the identity source for AWS SSO. Create the required role-based permission sets. Assign each group of users to the AWS accounts that the group will manage.
- D. Use the built-in SSO directory as the identity source for AWS SSO. Copy the users and groups from the on-premises Active Directory domain. Create the required role-based permission sets. Assign each group of users to the AWS accounts that the group will manage.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Reference: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/singlesignon/latest/userguide/connectonpremad.html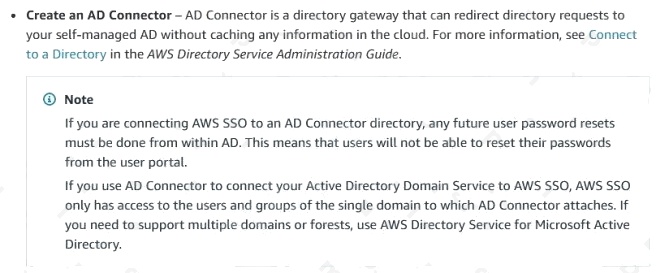
Question 4
A company is trying to connect two applications. One application runs in an on-premises data center that has a hostname of
host1.onprem.private. The other application runs on an Amazon EC2 instance that has a hostname of
host1.awscloud.private. An AWS Site-to-Site VPN connection is in place between the on-premises network and AWS.
The application that runs in the data center tries to connect to the application that runs on the EC2 instance, but DNS
resolution fails. A SysOps administrator must implement DNS resolution between onpremises and AWS resources.
Which solution allows the on-premises application to resolve the EC2 instance hostname?
- A. Set up an Amazon Route 53 inbound resolver endpoint with a forwarding rule for the onprem.private hosted zone. Associate the resolver with the VPC of the EC2 instance. Configure the on-premises DNS resolver to forward onprem.private DNS queries to the inbound resolver endpoint.
- B. Set up an Amazon Route 53 inbound resolver endpoint. Associate the resolver with the VPC of the EC2 instance. Configure the on-premises DNS resolver to forward awscloud.private DNS queries to the inbound resolver endpoint.
- C. Set up an Amazon Route 53 outbound resolver endpoint with a forwarding rule for the onprem.private hosted zone. Associate the resolver with the AWS Region of the EC2 instance. Configure the onpremises DNS resolver to forward onprem.private DNS queries to the outbound resolver endpoint.
- D. Set up an Amazon Route 53 outbound resolver endpoint. Associate the resolver with the AWS Region of the EC2 instance. Configure the on-premises DNS resolver to forward awscloud.private DNS queries to the outbound resolver endpoint.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Reference: https://aws.amazon.com/premiumsupport/knowledge-center/route53-resolve-with-inbound-endpoint/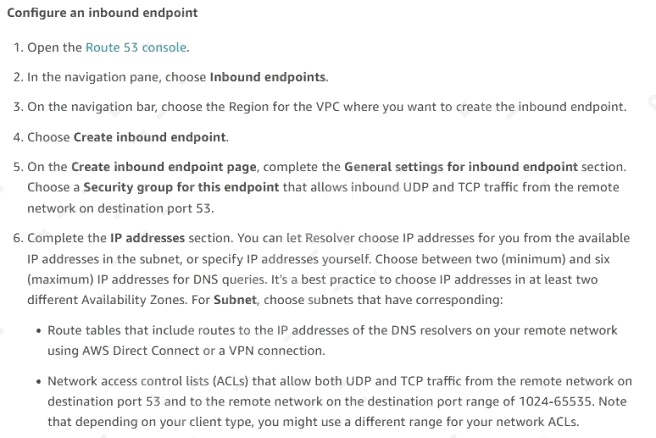
Question 5
A company manages an application that uses Amazon ElastiCache for Redis with two extra-large nodes spread across two
different Availability Zones. The company's IT team discovers that the ElastiCache for Redis cluster has 75% freeable
memory. The application must maintain high availability.
What is the MOST cost-effective way to resize the cluster?
- A. Decrease the number of nodes in the ElastiCache for Redis cluster from 2 to 1.
- B. Deploy a new ElastiCache for Redis cluster that uses large node types. Migrate the data from the original cluster to the new cluster. After the process is complete, shut down the original cluster.
- C. Deploy a new ElastiCache for Redis cluster that uses large node types. Take a backup from the original cluster, and restore the backup in the new cluster. After the process is complete, shut down the original cluster.
- D. Perform an online resizing for the ElastiCache for Redis cluster. Change the node types from extra-large nodes to large nodes.
Answer:
B
Question 6
With the threat of ransomware viruses encrypting and holding company data hostage, which action should be taken to
protect an Amazon S3 bucket?
- A. Deny Post, Put, and Delete on the bucket.
- B. Enable server-side encryption on the bucket.
- C. Enable Amazon S3 versioning on the bucket.
- D. Enable snapshots on the bucket.
Answer:
C
Question 7
A SysOps administrator noticed that a large number of Elastic IP addresses are being created on the companys AWS
account, but they are not being associated with Amazon EC2 instance, and are incurring Elastic IP address charges in the
monthly bill.
How can the administrator identify who is creating the Elastic IP addresses?
- A. Attach a cost-allocation tag to each requested Elastic IP address with the IAM user name of the developer who creates it.
- B. Query AWS CloudTrail logs by using Amazon Athena to search for Elastic IP address events.
- C. Create a CloudWatch alarm on the EIPCreated metric and send an Amazon SNS notification when the alarm triggers.
- D. Use Amazon Inspector to get a report of all Elastic IP addresses created in the last 30 days.
Answer:
A
Question 8
A SysOps administrator needs to design a high-traffic static website. The website must be highly available and must provide
the lowest possible latency to users across the globe.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
- A. Create an Amazon S3 bucket, and upload the website content to the S3 bucket. Create an Amazon CloudFront distribution in each AWS Region, and set the S3 bucket as the origin. Use Amazon Route 53 to create a DNS record that uses a geolocation routing policy to route traffic to the correct CloudFront distribution based on where the request originates.
- B. Create an Amazon S3 bucket, and upload the website content to the S3 bucket. Create an Amazon CloudFront distribution, and set the S3 bucket as the origin. Use Amazon Route 53 to create an alias record that points to the CloudFront distribution.
- C. Create an Application Load Balancer (ALB) and a target group. Create an Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling group with at least two EC2 instances in the associated target group. Store the website content on the EC2 instances. Use Amazon Route 53 to create an alias record that points to the ALB.
- D. Create an Application Load Balancer (ALB) and a target group in two Regions. Create an Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling group in each Region with at least two EC2 instances in each target group. Store the website content on the EC2 instances. Use Amazon Route 53 to create a DNS record that uses a geolocation routing policy to route traffic to the correct ALB based on where the request originates.
Answer:
A
Question 9
A SysOps administrator has successfully deployed a VPC with an AWS CloudFormation template. The SysOps administrator
wants to deploy the same template across multiple accounts that are managed through AWS Organizations.
Which solution will meet this requirement with the LEAST operational overhead?
- A. Assume the OrganizationAccountAccessRole IAM role from the management account. Deploy the template in each of the accounts.
- B. Create an AWS Lambda function to assume a role in each account. Deploy the template by using the AWS CloudFormation CreateStack API call.
- C. Create an AWS Lambda function to query for a list of accounts. Deploy the template by using the AWS CloudFormation CreateStack API call.
- D. Use AWS CloudFormation StackSets from the management account to deploy the template in each of the accounts.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Reference: https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/aws/new-use-aws-cloudformation-stacksets-for-multiple-accounts-in-an-aws-
organization/
Question 10
A company has a stateless application that is hosted on a fleet of 10 Amazon EC2 On-Demand Instances in an Auto Scaling
group. A minimum of 6 instances are needed to meet service requirements.
Which action will maintain uptime for the application MOST cost-effectively?
- A. Use a Spot Fleet with an On-Demand capacity of 6 instances.
- B. Update the Auto Scaling group with a minimum of 6 On-Demand Instances and a maximum of 10 On-Demand Instances.
- C. Update the Auto Scaling group with a minimum of 1 On-Demand Instance and a maximum of 6 On-Demand Instances.
- D. Use a Spot Fleet with a target capacity of 6 instances.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling allocates your Spot Instances from the N number of pools per Availability Zone that you specify
and from the Spot Instance pools with the lowest price in each Availability Zone.
Reference: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/autoscaling/ec2/userguide/ec2-auto-scaling-mixed-instances-groups.html
Question 11
A SysOps administrator has launched a large general purpose Amazon EC2 instance to regularly process large data files.
The instance has an attached 1 TB General Purpose SSD (gp2) Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS) volume. The
instance also is EBS-optimized. To save costs, the SysOps administrator stops the instance each evening and restarts the
instance ach morning.
When data processing is active, Amazon CloudWatch metrics on the instance show a consistent 3,000 VolumeReadOps.
The SysOps administrator must improve the I/O performance while ensuring data integrity.
Which action will meet these requirements?
- A. Change the instance type to a large, burstable, general purpose instance.
- B. Change the instance type to an extra large general purpose instance.
- C. Increase the EBS volume to a 2 TB General Purpose SSD (gp2) volume.
- D. Move the data that resides on the EBS volume to the instance store.
Answer:
C
Question 12
A SysOps administrator is provisioning an Amazon Elastic File System (Amazon EFS) file system to provide shared storage
across multiple Amazon EC2 instances. The instances all exist in the same VPC across multiple Availability Zones. There
are two instances in each Availability Zone. The SysOps administrator must make the file system accessible to each
instance with the lowest possible latency.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
- A. Create a mount target for the EFS file system in the VPC. Use the mount target to mount the file system on each of the instances.
- B. Create a mount target for the EFS file system in one Availability Zone of the VPC. Use the mount target to mount the file system on the instances in that Availability Zone. Share the directory with the other instances.
- C. Create a mount target for each instance. Use each mount target to mount the EFS file system on each respective instance.
- D. Create a mount target in each Availability Zone of the VPC. Use the mount target to mount the EFS file system on the instances in the respective Availability Zone.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Reference: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/efs/latest/ug/accessing-fs.html
Question 13
A SysOps administrator is attempting to download patches from the internet into an instance in a private subnet. An internet
gateway exists for the VPC, and a NAT gateway has been deployed on the public subnet; however, the instance has no
internet connectivity. The resources deployed into the private subnet must be inaccessible directly from the public internet.
What should be added to the private subnets route table in order to address this issue, given the information provided?
- A. 0.0.0.0/0 IGW
- B. 0.0.0.0/0 NAT
- C. 10.0.1.0/24 IGW
- D. 10.0.1.0/24 NAT
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Reference: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/vpc/latest/userguide/VPC_Scenario2.html
Question 14
A company is running an application on a fleet of Amazon EC2 instances behind an Application Load Balancer (ALB). The
EC2 instances are launched by an Auto Scaling group and are automatically registered in a target group. A SysOps
administrator must set up a notification to alert application owners when targets fail health checks.
What should the SysOps administrator do to meet these requirements?
- A. Create an Amazon CloudWatch alarm on the UnHealthyHostCount metric. Configure an action to send an Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS) notification when the metric is greater than 0.
- B. Configure an Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling custom lifecycle action to send an Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS) notification when an instance is in the Pending: Wait state.
- C. Update the Auto Scaling group. Configure an activity notification to send an Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS) notification for the Unhealthy event type.
- D. Update the ALB health check to send an Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS) notification when an instance is unhealthy.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Reference: https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/networking-and-content-delivery/identifying-unhealthy-targets-of-elastic-load-
balancer/
Question 15
A company website contains a web tier and a database tier on AWS. The web tier consists of Amazon EC2 instances that
run in an Auto Scaling group across two Availability Zones. The database tier runs on an Amazon RDS for MySQL Multi-AZ
DB instance. The database subnet network ACLs are restricted to only the web subnets that need access to the database.
The web subnets use the default network ACL with the default rules.
The companys operations team has added a third subnet to the Auto Scaling group configuration. After an Auto Scaling
event occurs, some users report that they intermittently receive an error message. The error messages states that the server
cannot connect to the database. The operations team has confirmed that the route tables are correct and that the required
ports are open on all security groups. Which combination of actions should a SysOps administrator take so that the web
servers can communicate with the DB instance? (Choose two.)
- A. On the default ACL, create inbound Allow rules of type TCP with the ephemeral port range and the source as the database subnets.
- B. On the default ACL. Create outbound Allow rules of type MySQL/Aurora (3306). Specify the destinations as the database subnets.
- C. On the network ACLs for the database subnets, create an inbound Allow rule of type MySQL/Aurora (3306). Specify the source as the third web subnet.
- D. On the network ACLs for the database subnets, create an outbound Allow rule of type TCP with the ephemeral port range and the destination as the third web subnet.
- E. On the network ACLs for the database subnets, create an outbound Allow rule of type MySQL/Aurora (3306). Specify the destination as the third web subnet.
Answer:
B D