Adobe AD0-E722 Exam Questions
Questions for the AD0-E722 were updated on : Mar 07 ,2026
Page 1 out of 4. Viewing questions 1-15 out of 50
Question 1
An Adobe Commerce Architect is setting up a Development environment for an on-premises project
that will be used for developers to specifically test functionality, not performance, before being
passed to the Testing team.
The Magento application must run with the following requirements:
1. Errors should be logged and hidden from the user
2. Cache mode can only be changed from Command Line
3. Static files should be created dynamically and then cached
Which Application Mode is required to achieve this?
- A. Default Mode
- B. Production Mode
- C. Developer Mode
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Developer mode is the best option for setting up a development environment for testing
functionality, not performance, before being passed to the testing team. In developer mode:
Errors are logged and hidden from the user. This ensures that the user does not see any uncaught
exceptions or debugging information, but the developers can still access them from the log files.
Cache mode can only be changed from command line. This prevents any accidental or unauthorized
changes to the cache settings from the admin panel or other sources.
Static files are created dynamically and then cached. This allows the developers to see the latest
changes to the static files without having to run the static content deployment command every time.
The static files are also cached for faster loading.
Reference:
https://experienceleague.adobe.com/docs/commerce-operations/configuration-guide/setup/application-modes.html?lang=en#application-modes1
Question 2
An Adobe Commerce Architect is asked by a merchant using B2B features to help with a
configuration issue.
The Architect creates a test Company Account and wants to create Approval Rules for orders. The
Approval Rules tab does not appear in the Company section in the Customer Account Menu when
the Architect logs in using the Company Administrator account.
Which two steps must be taken to fix this issue? (Choose two.)
- A. Set 'Enable B2B Quote’ in the B2B Admin to TRUE
- B. Merchant needs to log out of frontend and then log back in to load new permissions
- C. Set 'Enable Purchase Orders' in the B2B Admin to TRUE
- D. Set 'Enable Purchase Orders' on the Company Record to TRUE
- E. Make sure that the 'Purchase Order' payment method is active
Answer:
C, E
Explanation:
The issue here is that the Approval Rules tab does not appear in the Company section in the
Customer Account Menu when the Architect logs in using the Company Administrator account. This
is because the Approval Rules feature requires two settings to be enabled: the Purchase Orders
feature and the Purchase Order payment method. The solution is to set ‘Enable Purchase Orders’ in
the B2B Admin to TRUE and make sure that the ‘Purchase Order’ payment method is active. This will
allow the Architect to create and manage Approval Rules for orders.
Reference:
https://experienceleague.adobe.com/docs/commerce-admin/b2b/purchase-orders/account-dashboard-approval-rules.html?lang=en#account-
dashboard1 https://experienceleague.adobe.com/docs/commerce-admin/b2b/purchase-orders/purchase-order-payment-method.html?lang=en#payment-method2
Question 3
An Adobe Commerce Architect notices that queue consumers close TCP connections too often on
Adobe Commerce Cloud server leading to delays in processing messages.
The Architect needs to make sure that consumers do not terminate after processing available
messages in the queue when CRON job is running these consumers.
How should the Architect meet this requirement?
- A. Set cohsumers_wait_for_max_MESSAGES variable true in deployment stage.
- B. Increase multiple_process limit to spawn more processes for each consumer
- C. Change max_messages from 10,000 to 1,000 for CRON_CONSUMERS_RUNNER variable.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Option A is correct because setting the consumers_wait_for_max_messages variable true in the
deployment stage is the best way to meet the requirement. This variable controls whether the queue
consumers should wait for a maximum number of messages to process before terminating. If this
variable is set to true, the consumers will not terminate after processing the available messages in
the queue, but will wait until they reach the max_messages limit or the cron job timeout.
This way,
the consumers can keep the TCP connections open and avoid delays in processing messages1
.
Option B is incorrect because increasing the multiple_process limit to spawn more processes for each
consumer will not solve the issue of queue consumers closing TCP connections too often. The
multiple_process limit determines how many parallel processes can be run for each consumer.
Increasing this limit may improve the throughput of message processing, but it will also consume
more server resources and may cause conflicts or errors.
Moreover, it will not prevent the consumers
from terminating after processing the available messages in the queue2
.
Option C is incorrect because changing the max_messages from 10,000 to 1,000 for
CRON_CONSUMERS_RUNNER variable will worsen the issue of queue consumers closing TCP
connections too often. The max_messages variable defines how many messages each consumer
should process before terminating. Decreasing this variable will make the consumers terminate more
frequently, which will result in more TCP connections being closed and reopened.
This will increase
the delays in processing messages3
.
Reference:
: Configure message queues | Adobe Commerce Developer Guide
: Configure message queues | Adobe Commerce Developer Guide
: Configure message queues | Adobe Commerce Developer Guide
Question 4
An Architect is investigating a merchant's Adobe Commerce production environment where all
customer session data is randomly being lost. Customer session data has been configured to be
persisted using Redis, as are all caches (except full page cache, which is handled via Varnish).
After an initial review, the Architect is able to replicate the loss of customer session data by flushing
the Magento cache storage, either via the Adobe Commerce Admin Panel or running bin/magento
cache: flush on the command line. Refreshing all the caches in the Adobe Commerce Admin Panel or
running bin/magento cache: clean on the command line does not cause session data to be lost.
What should be the next step?
- A. Check app/etc/env.php and make sure that the Redis configuration for caches and session data use different database numbers.
- B. Educate the merchant to not flush cache storage and only refresh the caches in future.
- C. Set the Stores > Configuration' option for Store Session Data Separately' to 'Yes' in the Adobe Commerce Admin Panel.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The issue here is that the customer session data is randomly being lost when flushing the Magento
cache storage. This is because the Redis configuration for caches and session data might be using the
same database number, which causes the session data to be deleted along with the caches. The
solution is to check the app/etc/env.php file and make sure that the Redis configuration for caches
and session data use different database numbers.
This will prevent the session data from being
affected by the cache operations. Reference: https://experienceleague.adobe.com/docs/commerce-cloud-service/user-guide/develop/deploy/redis.html?lang=en#configure-redis1
Question 5
An Architect is configuring the preload.keys for Redis on an Adobe Commerce on-premise instance.
The Architect discovers that the following cache keys are loaded on each frontend request:
EAV_ENTITY_TYPES, GLOBAL_PLUGIN_LIST, DB_IS_UP_TO_DATE, SYSTEM_DEFAULT.
• The id_prefix of the frontend => page_cache is set to 063_.
• The id_pref ix of frontend => default is set to 762_.
• The Architect has enabled and configured Redis L2 caching.
How should the preload.keys be configured?
A)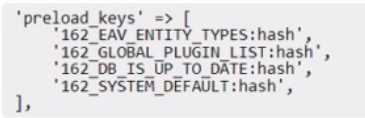
B)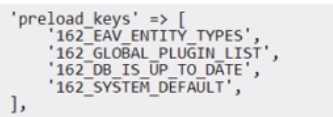
C)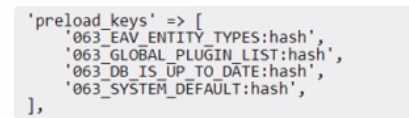
D)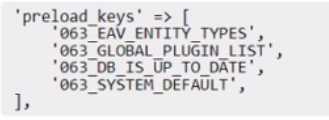
- A. Option A
- B. Option B
- C. Option C
- D. Option D
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Option C is correct because it configures the preload.keys correctly for Redis L2 caching on an Adobe
Commerce on-premise instance. Redis L2 caching is a feature that allows storing the cache data in
both Redis and the local file system. This way, the cache data can be loaded faster from the local
storage, while Redis acts as a cache invalidation service.
To use Redis L2 caching, the backend option
for both frontend => page_cache and frontend => default must be set to
Magento\Framework\Cache\Backend\RemoteSynchronizedCache1
. To enable the preload feature,
which reduces the number of requests to Redis, the preload.keys option must be specified with the
cache keys that are loaded on each frontend request.
However, unlike Redis L1 caching, the
preload.keys must include the suffix :hash to indicate that only the hash values of the cache data are
stored in Redis2
. Therefore, the correct configuration for preload.keys is:
<preload_keys’
=>
[
‘762_EAV_ENTITY_TYPES:hash’,
‘762_GLOBAL_PLUGIN_LIST:hash’,
‘762_DB_IS_UP_TO_DATE:hash’, ‘762_SYSTEM_DEFAULT:hash’, ],
Option A is incorrect because it configures the preload.keys incorrectly for Redis L2 caching. It uses
the id_prefix of frontend => page_cache (063_) instead of frontend => default (762_) for the cache
keys. This will cause a mismatch between the cache keys and the cache data, and result in incorrect
or missing cache data.
Moreover, it does not include the suffix :hash for the preload.keys, which is
required for Redis L2 caching2
.
Option B is incorrect because it configures the preload.keys incorrectly for Redis L2 caching.
It does
not include the suffix :hash for the preload.keys, which is required for Redis L2 caching2
. It also uses
a wrong cache key (GLOBAL_PLUGIN_LIST) instead of GLOBAL_PLUGIN_LIST.
Option D is incorrect because it configures the preload.keys incorrectly for Redis L2 caching. It uses a
wrong id_prefix (162_) instead of frontend => default (762_) for the cache keys. This will cause a
mismatch between the cache keys and the cache data, and result in incorrect or missing cache data.
It also uses a wrong cache key (EAV_ENTITY_TYPES) instead of EAV_ENTITY_TYPES.
Reference:
:
Two-level caching | Adobe Commerce Developer Guide
:
Use Redis for default cache | Adobe Commerce Developer Guide
Question 6
An Adobe Commerce Architect is supporting deployment and building tools for on-premises Adobe
Commerce projects. The tool is executing build scripts on a centralized server and using an SSH
connection to deploy to project servers.
A client reports that users cannot work with Admin Panel because the site breaks every time they
change interface locale.
Considering maintainability, which solution should the Architect implement?
- A. Modify project config.php file, configure 'admin_locales_for_deploy' value, and specify all required locales
- B. Edit project env.php file, configure 'adminJocales_for_build' value, and specify all required locales
- C. Adjust the tools build script and specify required locales during *setup:static-content:deploy' command
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The issue here is that the site breaks every time the users change interface locale in the Admin Panel.
This is because the static content for the different locales is not generated during the deployment
process. The solution is to adjust the tools build script and specify required locales during
*setup:static-content:deploy’ command.
This will ensure that the static content for all the needed
locales
is
generated
and
deployed
to
the
project
servers. Reference:
https://experienceleague.adobe.com/docs/commerce-cloud-service/user-guide/develop/deploy/static-content.html?lang=en#deploy-static-view-files1
Question 7
An Adobe Commerce Architect is troubleshooting an issue on an Adobe Commerce Cloud project
that is not yet live.
The developers copied the Staging Database to Production in readiness to Go Live. However, when
the developers test their Product Import feature, the new products do not appear on the front end.
The developers suspect the Varnish Cache is not being cleared. Staging seems to work as expected.
Production was working before the database migration.
What is the likely cause?
- A. The fatly credentials in the Production Database are incorrect.
- B. A deployment should have been done on Production to initialize Fatly caching.
- C. The site URLs in the Production Database are the URLs of the Staging Instance and must be updated
Answer:
C
Question 8
An Architect needs to create an additional regional UK website with its own website currency set to
GBP in Adobe Commerce. An existing US website is using USD as a default base and website
currency.
After the first week of sales in the new UK website, an administrator notices that all sales totals in
Sales Orders report show £0.00.
How should this issue be resolved?
- A. Configure currency rates for GBP and USD, so they are not empty.
- B. Refresh Lifetime Statistics for "Total Invoiced'.
- C. Make sure that orders are shipped and not left in processing state.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The issue here is that the sales totals in Sales Orders report show £0.00 for the new UK website. This
is because the currency rates for GBP and USD are not configured, so the system cannot convert the
order amounts from GBP to USD. The solution is to configure the currency rates for GBP and USD, so
they are not empty.
This will allow the system to calculate the sales totals in USD for the
report. Reference:
https://experienceleague.adobe.com/docs/commerce-admin/stores-sales/site-store/currency/currency-update.html?lang=en1
Question 9
A client is migrating to Adobe Commerce Cloud and has approximately 800 existing redirects that
must be implemented. The number of redirects cannot be reduced because all redirects are specific,
and do not match any pattern.
How should the redirects be configured to ensure performance?
- A. Add each redirect in the magento/routes.yaml file.
- B. Use VCL snippets to offload the redirect to Fastly.
- C. Add each redirect as a URL rewrite via the admin Ul.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Option B is correct because using VCL snippets to offload the redirect to Fastly is the best way to
configure the redirects and ensure performance. VCL snippets are custom code segments that can be
added to the Fastly configuration to modify the behavior of the caching service. By using VCL
snippets, the redirects can be handled at the edge server level, without reaching the Magento
application or the database.
This reduces the server load and improves the response time for the
redirected requests1
.
Option A is incorrect because adding each redirect in the magento/routes.yaml file is not a
recommended way to configure the redirects. The magento/routes.yaml file is used to define custom
routes for Magento Cloud projects, such as mapping domains or subdomains to environments or
services.
Adding redirects in this file can cause conflicts with the existing routes and affect the routing
logic of the project2
.
Option C is incorrect because adding each redirect as a URL rewrite via the admin UI is not an
optimal way to configure the redirects. The URL rewrite feature in Magento allows creating custom
URLs for products, categories, and CMS pages, and redirecting them to their canonical URLs.
However, adding a large number of URL rewrites can increase the database size and affect the
performance of the Magento application.
Moreover, using the admin UI for this task can be tedious
and error-prone3
.
Reference:
: Custom VCL snippets | Adobe Commerce Developer Guide
: Configure routes | Adobe Commerce Developer Guide
: URL Rewrites | Adobe Commerce User Guide
Question 10
An Architect is investigating a deployment issue with a server that is configured to work under the
symlink directory /var/www/current, which lead to the latest released version of the application.
The deployment process performs the following steps: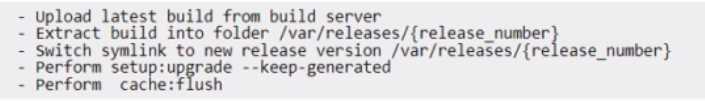
After the last deployment, the merchant reported that the Adobe Commerce Import/Export
functionality to export Customer Main File data is not working. The Architect discovered that the
export file is not shown in the list of generated files.
Which change to the deployment process should be performed to solve this issue?
- A. Restart the consumer process during deployment to use the directory with a new application version for export files.
- B. Execute Command config:set export/customr/files_directory /var/releases/{release_nunber} to Set the new export path.
- C. Doable Crontab before deployment and re-launch after deployment.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The issue is that the export file is not shown in the list of generated files. This is because the export
path is not set correctly. The solution is to execute the command config:set
export/customr/files_directory /var/releases/{release_nunber} to set the new export path.
This will
ensure that the export file is saved in the correct directory and can be accessed from the Admin
Panel. Reference:
https://experienceleague.adobe.com/docs/commerce-cloud-service/user-guide/develop/deploy/staging-production.html?lang=en#deploy-to-staging-and-production1
Question 11
An Adobe Commerce Architect is working on a scanner that will pull prices from multiple external
product feeds. The Architect has a list of vendors and decides to create new config file
marketplace.feeds.xml.
Which three steps can the Architect take to ensure validation of the configuration files with unique
validation rules for the individual and merged files? (Choose three.)
- A. Implement validation rules in the Converter class for the Config Reader
- B. Create validation rules in marketplace.schema.xsd.
- C. Provide schema to validate a merged file.
- D. Add the Uniform Resource Name to the XSD file in the config XML file.
- E. Provide schema to validate an individual file.
- F. Create a class that implements \Magento\Framework\Config\Datainterface.
Answer:
B, C, E
Explanation:
The Architect can take the following steps to ensure validation of the configuration files with unique
validation rules for the individual and merged files:
Create validation rules in marketplace.schema.xsd. This file defines the structure and constraints of
the XML elements and attributes for the marketplace.feeds.xml configuration file. The Architect can
use this file to specify the required and optional elements, data types, values, and patterns for the
configuration file.
Provide schema to validate a merged file. This schema is used to validate the final configuration file
that is generated after merging all the individual configuration files from different modules. The
Architect can use this schema to check the consistency and completeness of the merged
configuration file.
Provide schema to validate an individual file. This schema is used to validate each individual
configuration file from each module before merging them. The Architect can use this schema to
check the syntax and validity of each configuration file.
Reference:
https://experienceleague.adobe.com/docs/commerce-cloud-service/user-guide/architecture/starter-architecture.html?lang=en#configuration-
files1 https://devdocs.magento.com/guides/v2.4/extension-dev-guide/build/XSD-XML-validation.html2
Question 12
An Adobe Commerce Architect needs to ensure zero downtime during the deployment process of
Adobe Commerce on-premises. Which two steps should the Architect follow? (Choose two.)
- A. Enable Config flag Under deployement/blue_green/enabled
- B. Run bin/magento setup:upgrade --dry-run=true to upgrade database
- C. Run bin/magento setup:upgrade - -keep-generated to Upgrade database
- D. Run bin/magento setup:upgrad --convert-old-scripts-true to Upgrade database
- E. Enable Config flag Under developer/zero_down_time/enabled
Answer:
AC
Explanation:
Option A is correct because enabling the config flag under deployment/blue_green/enabled is one of
the steps to ensure zero downtime during the deployment process of Magento 2 on-premises. This
flag enables the blue-green deployment feature, which allows deploying a new version of the
Magento application to a separate environment (blue) without affecting the current live
environment (green).
Once the new version is ready, the traffic can be switched from green to blue
with minimal or no downtime1
.
Option C is correct because running bin/magento setup:upgrade --keep-generated is another step to
ensure zero downtime during the deployment process of Magento 2 on-premises. This command
updates the database schema and data without deleting the generated code and static view
files.
This way, the Magento application can still serve requests from the cache while the database is
being upgraded2
.
Option B is incorrect because running bin/magento setup:upgrade --dry-run=true does not upgrade
the database, but only checks if there are any errors or conflicts in the database schema or data.
This
command can be used for testing purposes, but it does not affect the deployment process or the
downtime3
.
Option D is incorrect because there is no such option as --convert-old-scripts-true for the
bin/magento setup:upgrade command. This option does not exist in Magento 2 and does not have
any effect on the deployment process or the downtime.
Option E is incorrect because there is no such config flag as developer/zero_down_time/enabled in
Magento 2. This flag does not exist in Magento 2 and does not have any effect on the deployment
process or the downtime.
Reference:
: Blue-green deployment | Adobe Commerce Developer Guide
: Deploy Magento to production | Adobe Commerce Developer Guide
: Command-line installation options | Adobe Commerce Developer Guide
Question 13
An Adobe Commerce Architect designs and implements functionality that introduces a new Complex
Product Type to the existing Adobe Commerce website. Besides visual demonstration of the new
product type, the changes include adjustments to the price index.
The website utilizes a multi-dimensional indexer feature to store the price index. The Architect
decides to cover it with integration tests. After creating and running one test, the Architect discovers
that database storage is not being fully cleaned.
The test method has the following annotation declaration: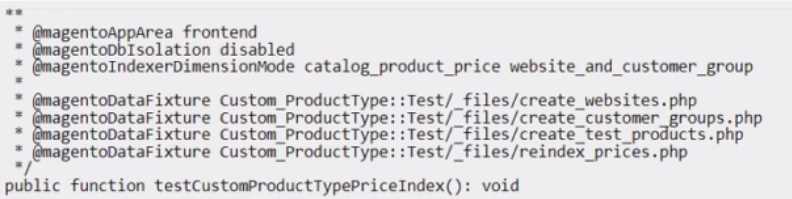
Which adjustment should the Architect make to fix this issue?
- A. Add annotation @magentoApplsolation enabled to method PHPDoc
- B. Modify method PHPDoc and change annotation @magentoDbIsolation to enabled
- C. Create Customer_ProductType: :Test/_files/{fixture_name)_rollback.php for every fixture
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The issue here is that the database storage is not being fully cleaned after the test is run. The
solution is to modify the method PHPDoc and change the annotation @magentoDbIsolation to
enabled.
This will ensure that the database storage is fully cleaned after the test is run. Reference:
https://developer.adobe.com/commerce/testing/guide/integration/#database-isolation1
Question 14
The development of an Adobe Commerce website is complete. The website is ready to be rolled out
on the production environment.
An Architect designed the system to run in a distributed architecture made up of multiple backend
webservers that process requests behind a Load Balancer.
After deploying the system and accessing the website for the first time, users cannot access the
Customer Dashboard after logging in. The website keeps redirecting users to the sign-in page even
though the users have successfully logged in The Architect determines that the session is not being
saved properly.
In the "app/etc/env.php", the session is configured as follows:
What should the Architect do to correct this issue?
- A. Update the session host value to a shared Redis instance
- B. increase the session size with the command config:set system/security/max_session_size_admin
- C. Utilize the Remote Storage module to synchronize sessions between the servers
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Option A is correct because updating the session host value to a shared Redis instance in the
“app/etc/env.php” file will allow the session to be saved properly and prevent users from being
redirected to the sign-in page after logging in. Redis is a fast and reliable in-memory data store that
can be used for session storage in Magento 2. By using a shared Redis instance, the session data can
be accessed by any of the backend web servers behind the load balancer, regardless of which server
handled the initial request.
This ensures that the user’s session is maintained and consistent across
different servers1
.
Option B is incorrect because increasing the session size with the command config:set
system/security/max_session_size_admin will not solve the issue of session not being saved
properly. This command only affects the admin session size limit, not the customer session size
limit.
Moreover, this command does not address the root cause of the issue, which is that the session
data is not shared among the backend web servers2
.
Option C is incorrect because utilizing the Remote Storage module to synchronize sessions between
the servers is not a viable solution for this issue. The Remote Storage module is a feature of Magento
Commerce Cloud that allows storing media files and other static content on a remote storage service
such as AWS S3 or Azure Blob Storage.
This module does not support synchronizing sessions between
servers, as sessions are dynamic and transient data that need to be stored in a fast and accessible
data store such as Redis3
.
Reference:
: Use Redis for session storage | Adobe Commerce Developer Guide
: Security | Adobe Commerce User Guide
: Remote storage | Adobe Commerce Developer Guide
Question 15
A merchant notices that product price changes do not update on the storefront.
The index management page in the Adobe Commerce Admin Panel shows the following:
• All indexes are set to 'update by schedule'
• Their status is 'ready'
• There are no items in the backlog
• The indexes were last updated 1 minute ago
A developer verifies that updating and saving product prices adds the relevant product IDs into the
catalog_product_price_cl changelog table. Which two steps should the Architect recommend to the
developer to resolve this issue? (Choose two.)
- A. Reduce the frequency of the cron job to 5 minutes so the items have more time to process.
- B. Make sure that no custom or third-party modules modify the changelog and indexing process.
- C. Make sure that the version_id for the price indexer in the mview_state table is not higher than the last entry for the same column in the changelog table and re-synchronize.
- D. Invalidate the catalog_Product_price indexer in the Adobe Commerce Admin Panel so that it is fully reindexed next time the cron runs.
- E. Manually reindex the catalog_product_price index from the command line: bin/magento indexer:reindex catalog_product_price.
Answer:
BC
Explanation:
The issue here is that the product price changes are not reflected on the storefront, even though the
indexes are set to update by schedule and there are no items in the backlog. This indicates that there
might be some problem with the changelog and indexing process, which are responsible for tracking
and applying the data changes to the index tables. Therefore, the Architect should recommend the
developer to check if any custom or third-party modules interfere with the changelog and indexing
process, and disable or fix them if needed. Additionally, the Architect should recommend the
developer to verify that the version_id for the price indexer in the mview_state table is consistent
with the last entry for the same column in the changelog table, and re-synchronize them if they are
out of sync.
This will ensure that the indexer can process all the data changes correctly and update
the index tables accordingly. Reference: https://experienceleague.adobe.com/docs/commerce-admin/systems/tools/index-management.html?lang=en#cron-groups-and-
processes1 https://devdocs.magento.com/guides/v2.4/extension-dev-guide/indexing.html#m2devgde-mview2