Adobe AD0-E207 Exam Questions
Questions for the AD0-E207 were updated on : Mar 07 ,2026
Page 1 out of 4. Viewing questions 1-15 out of 50
Question 1
A company wants to track their website's usage without visitors seeing which data points are being
collected. The following information must be tracked:
• Page names
• Form names
• A counter event for each page of the checkout flow
• s.products populated on each page of the checkout flow
Which approach should the Architect recommend?
- A. Copy tracking calls from global report suite to site report suite via VISTA Rules
- B. Import web server log data via Data Sources
- C. Send tracking calls using CNAME pointer
- D. Send tracking calls server-side via Data Insertion API
Answer:
D
Explanation:
To track website usage without visitors seeing which data points are being collected, the
recommended approach is to send tracking calls server-side via the Data Insertion API. This method
allows for the collection of page names, form names, a counter event for each page of the checkout
flow, and the s.products variable while keeping the tracking logic and data points hidden from the
client side.
Reference:
Adobe Analytics Data Insertion API
Question 2
What three are attributes of virtual report suites? (Choose three.)
- A. Some settings are inherited from the parent report suite
- B. Classification data can be uploaded
- C. They are an alternative to multi-suite tagging
- D. They can be added individually to permission groups
- E. Current and real-time data is supported
Answer:
A, E, D
Explanation:
Virtual report suites in Adobe Analytics have the following attributes:
Some settings are inherited from the parent report suite: Virtual report suites inherit certain
configurations from the parent report suite, such as variable definitions and processing rules.
They can be added individually to permission groups: Virtual report suites can be assigned to
different user groups, allowing for controlled access based on permissions.
Current and real-time data is supported: Virtual report suites support current and real-time data,
enabling up-to-date reporting and analysis.
These attributes make virtual report suites a flexible and powerful tool for segmenting and managing
data within Adobe Analytics.
Reference:
Adobe Analytics Virtual Report Suites
Question 3
A company develops a new website using a Single Page Application framework. A data layer variable
called dataLayer.url is updated with the correct URL when each state change happens.
Which variable should the Architect map to dataLayer.url?
- A. s.pageURL
- B. s.linklnternalFilters
- C. s.url
- D. s.spaURL
Answer:
A
Explanation:
For Single Page Applications (SPAs), it is important to capture the URL changes correctly. The
s.pageURL variable should be mapped to dataLayer.url to ensure that Adobe Analytics captures the
correct URL each time the state changes in the SPA. This allows accurate tracking of user navigation
within the SPA framework.
Reference:
Adobe Analytics SPA Implementation
Question 4
Which item must be embedded in your pages to asynchronously deploy Adobe Analytics with
Launch?
- A. Reports & Analytics page code
- B. Header code
- C. Header and Footer code
- D. Reference to AppMeasurement.js
Answer:
B
Explanation:
To deploy Adobe Analytics with Launch asynchronously, the necessary JavaScript library must be
referenced in the header code of the HTML page. This ensures that the Launch library is loaded early
in the page load process, allowing it to manage and fire tags efficiently.
Reference:
Adobe Launch Implementation Guide
Question 5
A company is beginning a full re-architecture of their website. They will use Adobe Launch as the tag
management system. How should an Architect recommend that the data layer object be generated
each time a page is requested?
- A. Via logic in the tag management system, executed on DOMReady
- B. Via server-side code and included in a <script> block in the page HTMLs <head> section
- C. Via server-side code and included in a <meta> tag in the page HTMLs <head> section
- D. Via DOM scraping initialized by a custom external JavaScript file
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The best practice for generating the data layer object each time a page is requested is to use server-
side code to include the data layer in a <script> block in the page HTML’s <head> section. This
ensures that the data layer is available as soon as the page starts loading and can be used by Adobe
Launch and other scripts. By having the data layer generated server-side, it reduces reliance on the
client-side code and ensures the data is consistent and accurate for each page load.
Reference:
Adobe Launch Data Layer Guide
Question 6
A company has an issue with some links on their site containing Personal Identifiable Information
(Pll). For example, to access their account, users click a link that contains their first and last name.
Currently Activity Map is collecting the Pll contained in some of their links.
How should the Architect disable Activity Map?
- A. Set s.trackExternalLinks to false
- B. Set s.tracklnlineStats to false
- C. Set s.linkName to false
- D. Set s.linkURL to false
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Business Requirement: Disable Activity Map to prevent collecting Personal Identifiable Information
(PII) in links.
Method:
s.trackInlineStats: Setting this to false disables Activity Map tracking.
Explanation:
s.trackInlineStats to false: This setting stops Activity Map from tracking link clicks and capturing PII in
links.
Verification: According to Adobe Analytics Activity Map documentation, disabling Activity Map by
setting s.trackInlineStats to false prevents the collection of potentially sensitive data (Adobe Activity
Map Documentation).
Question 7
An Architect is using dynamic variables in an Adobe Analytics implementation. eVar32 is used to
collect the current page URL.
Which syntax should be used?
- A. s.eVar32="D=g'
- B. s.eVar32='D=cp"
- C. s.eVar32=*D=host'
- D. s eVar32="D=url"
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Business Requirement: Use dynamic variables to collect the current page URL in eVar32.
Method:
Dynamic Variable Syntax: D=cp references the current page URL.
Explanation:
s.eVar32="D=cp": This syntax tells Adobe Analytics to dynamically populate eVar32 with the current
page URL.
Verification: According to Adobe Analytics dynamic variables documentation, using D=cp correctly
references and captures the current page URL in eVars (Adobe Analytics Dynamic Variables Guide).
Question 8
An Architect is implementing Adobe Analytics across 3 different websites using one Adobe Launch
property. Each website is on its own domain and has its own report suite in Adobe Analytics.
What should the Architect do to determine the report suite IDs when pages load?
- A. Use processing rules to populate the report suite IDs
- B. Use a dynamic variable to populate the report suite IDs
- C. Add all 3 report suite IDs to the Adobe Analytics extension configuration
- D. Use a data element to populate the report suite IDs
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Business Requirement: Determine the appropriate report suite IDs for different websites using one
Adobe Launch property.
Method:
Data Element: Utilizes a data element to dynamically determine and populate the report suite ID
based on the domain or other contextual information.
Explanation:
Data Element: Provides flexibility to dynamically assign the correct report suite ID for each website
based on defined conditions or context.
Verification: According to Adobe Launch best practices, using data elements to populate report suite
IDs ensures accurate and context-specific tracking across multiple domains (Adobe Launch
Documentation).
====
Question 9
A company wants to report on the internal search keywords and their contribution to the revenue.
The Architect instructs the developer to create the digitalData.search.keyword'' data object in the
data layer so it can be
mapped to eVarl.
Which syntax should the Architect recommend?
A)
B)
C)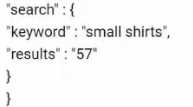
D)
- A. Option A
- B. Option B
- C. Option C
- D. Option D
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Business Requirement: The company needs to report on internal search keywords and their
contribution to revenue by creating the digitalData.search.keyword data object in the data layer.
Recommended Syntax: The syntax must be correctly structured to allow Adobe Analytics to map the
data object to eVar1 efficiently.
Explanation:
Question 10
A customer launches a new checkout flow that includes all checkout steps in a Single Page
Application.
The development team must be instructed on how to indicate when a user moves to the next step of
the checkout flow so this information can be tracked in Adobe Analytics using Adobe Launch.
The customer wants to be able to report on each step of the checkout as different page views.
Which configuration of an Adobe Launch rule must the tagging engineer configure in Adobe Launch
to meet these requirements?
- A. Direct Call Event with an s.t() beacon
- B. Click Event with an s.t()
- C. Direct Call Event with an s.tl() beacon
- D. DOM Ready Event with an s.t()
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Business Requirement: Track each step of the checkout process as separate page views in a Single
Page Application (SPA).
Configuration:
Direct Call Event: Triggered explicitly by the application code when a user moves to the next step.
s.t() beacon: Sends a page view beacon, suitable for capturing page views in SPAs.
Explanation:
Direct Call Event: Allows developers to indicate specific points in the SPA where analytics tracking
should occur.
s.t() beacon: Suitable for recording page views, capturing each step in the checkout flow as a
separate page view.
Verification: According to Adobe Launch documentation, using Direct Call Events with s.t() beacons
is the recommended approach for tracking page views in SPAs (Adobe Launch Implementation
Guide).
Question 11
The Architect needs to collect a value in a prop to use it within pathing reports and an eVar so that
the value can persist. The Architect also needs to reduce the size of the server call as much as
possible.
Which method should the Architect use?
- A. A VISTA rule to copy the prop value to the eVar
- B. s.eVarl = s.propl
- C. s.eVarl = "D=c1"
- D. A processing rule to copy the prop value to the eVar
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Introduction: The requirement is to use a value in both a prop (for pathing reports) and an eVar (for
persistence) while minimizing the size of the server call.
Explanation of Methods:
A . A VISTA rule to copy the prop value to the eVar:
VISTA (Visitor Identification, Segmentation & Transformation Architecture) rules are server-side rules
that can copy values between variables. However, they are complex, incur additional costs, and do
not reduce server call size.
Reference: Adobe Analytics VISTA Rule Guide.
B . s.eVar1 = s.prop1:
Directly setting the eVar value to the prop value in the code is straightforward but does not minimize
the server call size as both values are separately included in the request.
Reference: Adobe Analytics Implementation Documentation on setting variable values.
C . s.eVar1 = "D=c1":
This method uses dynamic variable substitution, which reduces the server call size by referencing the
prop value (c1) directly in the eVar without duplicating the data in the request.
Verification: Check the Adobe Analytics server call in the Network tab to confirm the reduced size.
Reference: Adobe Analytics Documentation on Dynamic Variable Substitution.
D . A processing rule to copy the prop value to the eVar:
Processing rules can be used to copy values server-side, similar to VISTA rules but without the
additional cost. However, this approach does not minimize the server call size.
Reference: Adobe Analytics Processing Rules Guide.
Detailed Steps:
Dynamic Variable Substitution:
Set the eVar value to reference the prop value using the syntax s.eVar1 = "D=c1".
This tells Adobe Analytics to dynamically substitute the value of c1 (prop1) into eVar1 without
sending redundant data.
Example:
s.prop1 = "exampleValue";
s.eVar1 = "D=c1";
Benefits:
Reduced Server Call Size: By using dynamic variable substitution, the server call payload is smaller,
optimizing data transmission.
Efficient Data Handling: The value is captured once in the prop and referenced in the eVar,
maintaining efficiency and persistence.
References:
Adobe Analytics Implementation Documentation:
Dynamic Variable Substitution
Adobe Analytics Network Call Analysis Guide:
Understanding Server Calls
By using s.eVar1 = "D=c1", the Architect achieves the goal of collecting the value in both a prop and
an eVar efficiently while minimizing the server call size.
Question 12
An Architect advises a site developer to embed the Adobe Launch script in the <head> and to place
the data layer before the closing </body> tag of a web page.
During testing, an Adobe Analytics page view call fires successfully. Several Adobe variables are not
defined in the call. The embedded Launch script and the data layer are implemented correctly per
the Architect's specifications.
What should the Architect do to resolve the issue?
- A. Move the data layer to before the Adobe Launch script in the <head>.
- B. Move the data layer just before the </body> tag.
- C. Move the data layer to after the Adobe Launch script in the <head>.
- D. Move the data layer just before the <body> tag
Answer:
A
Explanation:
To ensure that Adobe Launch and its variables are correctly defined and available when the page
view call is fired, the data layer should be placed before the Adobe Launch script in the <head>
section of the webpage. This ensures that all data layer variables are available to the Launch script
during its execution.
Reference:
Adobe Launch Implementation Guide
Question 13
A product was viewed on two different pages and was added to the cart from one of the pages.
Below are the product syntax used for each page.
Page 1:
s.products = ";prod123;1;100;;evar2=merch_category1";
Page 2:
s.products = ";prod123;1;100;;evar2=merch_category2";
If the product was checked out and purchased for $100, how might revenue be attributed to eVar2 if
merchandising is enabled? (Choose two.)
- A. $100 against merch.category1 and $100 against merch_category2 for linear allocation
- B. $100 against merch.category1 for original allocation
- C. $200 against merch_category2 for most recent allocation
- D. $200 against merch.category1 for original allocation
- E. $100 against merch_category2 for most recent allocation
Answer:
A E
Explanation:
When merchandising is enabled in Adobe Analytics, revenue attribution can vary based on the
allocation method:
Linear Allocation: Distributes revenue equally across all instances of the product view and add-to-cart
events. Thus, $100 would be attributed to both merch_category1 and merch_category2.
Most Recent Allocation: Attributes the revenue to the most recent instance of the variable. Thus,
$100 would be attributed to merch_category2.
This approach ensures that revenue attribution accurately reflects user interactions with products.
Reference:
Adobe Analytics Merchandising eVars
Question 14
What are three uses of Processing Rules? (Choose three.)
- A. Clean up misspelled site sections
- B. Populate campaign with a query string parameter
- C. Copy an eVar into a prop to see pathing
- D. Add classification rules for props and eVars
- E. Read eVar values from the product string
Answer:
A, B, C
Explanation:
Processing Rules in Adobe Analytics are versatile and can be used for various purposes:
Clean up misspelled site sections: Corrects misspelled values in data collection to ensure accurate
reporting.
Populate campaign with a query string parameter: Extracts query string parameters and uses them to
populate campaign variables.
Copy an eVar into a prop to see pathing: Allows copying values from an eVar to a prop to enable
pathing analysis on that variable.
These rules help maintain data quality and flexibility in reporting.
Reference:
Adobe Analytics Processing Rules
Question 15
One of the records in the data sources files does not have the same number of columns as the
header record. What will be the outcome of this file upload?
- A. The file is not processed due to column mismatch.
- B. The file is partially processed only for the existing records.
- C. The file is partially processed only for the existing columns.
- D. The file is not processed due to row mismatch.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
When uploading data source files to Adobe Analytics, it is crucial that each record has the same
number of columns as the header record. If one of the records does not match the number of
columns, the entire file will not be processed due to the column mismatch. This ensures data
integrity and consistency in the uploaded data.
Reference:
Adobe Analytics Data Sources Guide